Abstract
The calcium dependency of AT1-receptor mediated contractions was studied in isolated rat portal vein preparations.
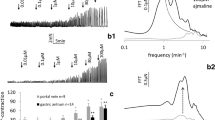
The spontaneous phasic contractile force of the rat portal vein was increased (ED50 = 1.76 mmol/l) and the frequency of contractions decreased by raising the extracellular calcium concentration. The Ang 11-induced rise in phasic contractile force (mediated by AT1-receptors, Zhang et al. 1993) proved most pronounced at 0.9 mmol/l of calcium chloride, but it was weaker at either lower or higher calcium concentrations. The maximal increases in the phasic contractile force induced by Ang II were 2.4±0.4, 14.8±0.9 and 5±0.5 mN at calcium concentrations of 0.5, 0.9 and 2.5 mmol/l, respectively. Calcium antagonists reduced at the lower and abolished at the higher concentrations (nifedipine 2×10−8 or 10−7 mol/l; verapamil 10−7 or 5 × 10−7 mol/l; diltiazem 3 × 10−7 or 10–6 mol/l) the spontaneous contractile force. All of these calcium antagonists caused a strong inhibition or suppression of the phasic contractions induced by Ang II.The rank order of potency was nifedipine >verapamil > diltiazem. Ang II (10−6 mol/l) elicited a tonic contraction which was abolished by the AT1-receptor antagonist losartan 10-6 mol/l but not by the AT2-receptor antagonist PD 123177 (10–5 mol/l). Very high concentrations of nifedipine (10–6 mol/l), verapamil (5 × 10-6 mol/l) and diltiazem (5 × 10−6 mol/l) almost suppressed the tonic effect evoked by the activation of AT1-receptors.
In a nominally Ca2+ “free”, EGTA-containing solution, a single supra-maximal concentration of Ang II (10−6 mol/l) caused a transient contraction, also mediated by AT1-receptors. This finding suggests the existence of Ang II-sensitive intracellular calcium stores in this preparation. The depletion of such stores proved complete after 4–6 min of perfusion in a Ca2+ “free”, EGTA-containing solution.
In conclusion, various types of contractions (a transient contraction in a Ca2+-“free” medium, phasic and tonic contractions) induced by Ang II in the rat portal vein proved to be mediated by AT1-receptors. These contractions were clearly modified by changes in the availability of extra- and possibly intracellular calcium ions. The calcium movements elicited by stimulation of AT1-receptors in a calcium containing solution were inhibited by the three calcium antagonists investigated.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Axelsson J, Wahlstrom B, Johansson B, Jonsson O (1967) Influence of the ionic environment on spontaneous electrical and mechanical activity of the rat portal vein. Circ Res 21:609–618
Biamino G, Johansson B (1970) Effects of calcium and sodium on contracture tension in the smooth muscle of the rat portal vein. Pfluger Arch 321:143–158
Casteels R, Droogmans G (1981) Exchange characteristics of the noradrenaline sensitive calcium store in vascular smooth muscle cells of rabbit ear artery. J Physiol 317:263–279
Cavero I, Lefevre-Borg F (1981) Effects of diltiazem and verapamil on pressor responses mediated by stimulation of α1-, α2-adrenoceptors, angiotensin II and 5-hydroxytryptamine receptors in pithed rats. Br J Pharmacol 74:839P-840P
Dacquet C, Mironneau C, Mironneau J (1987) Effects of calcium entry blockers on calcium-dependent contractions of rat portal vein. Br J Pharmacol 92:203–211
Hamon G, Worcel M (1982) Mechanism of action of angiotensin II on excitation-contraction coupling in the rat portal vein. Br J Pharmacol 75:425–432
Hof RP (1985) Modification of vasopressin- and angiotensin II-induced changes by calcium antagonists in the peripheral circulation of anaesthetized rabbits. Br J Pharmacol 85:75–87
Lananne C, Mironneau C, Mironneau J, Savineau JP (1984) Contractions of rat uterine smooth muscle induced by acetylcholine and angiotensin II in Ca2+-free medium. Br J Pharmacol 81:317–326
Lippton HL, Armstead WM, Hyman AL, Kadowitz PJ (1987) Influence of calcium-entry blockade on renin-angiotensin systems: Focus on the heart. J Hypertens 5(suppl2):570–580
Loirand G, Pacaud P, Mironneau C, Mironneau J (1986) Evidence for two distinct calcium channels in rat vascular smooth muscle cells in short-term primary culture. Pflugers Arch 407:566–568
Mantel R, Taquini AC Jr, Savino EA (1975) Effects of adrenaline, angiotensin and calcium on spontaneous active and potassium-depolarized rat portal veins. Arch Int Physiol Biochem 83:211–219
Mironneau J, Gargouil Y (1979) Action of indapamide on excitation-contraction coupling in vascular smooth muscle. Eur J Pharmacol 57:57–67
Tateishi S (1991) Regulatory mechanisms for the spontaneous contractile force and frequency of the rat portal vein. J Smooth Muscle Res 27(3):115–130
Timmermans PBMWM, Wong PC, Chin AT, Herblin WF (1991) Nonpeptide angiotensin II receptor antagonists. TIPS 12:55–62
Van Heiningen PNM, Batink HD, Van Zwieten PA (1991) Angiotensin II-induced increase in slowly exchanging 45Ca2+ in relation to contractile responses of rat and guinea-pig aorta. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 344:107–113
Zhang JS, Van Meel JCA, Pfaffendorf M, Van Zwieten PA (1993) Characterization of the angiotensin II-receptor subtype in the longitudinal smooth muscle of the rat portal vein. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 347:220–224
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Correspondence to: J. S. Zhang at the above address
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, J.S., Van Meel, J.C.A., Pfaffendorf, M. et al. Calcium dependency of the AT1-receptor mediated effects in the rat portal vein: influence of calcium antagonists. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch Pharmacol 349, 437–442 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00170892
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00170892