Abstract
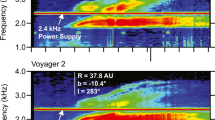
We show, using the HST — GHRS data on velocity and temperature in the nearby interstellar medium, that the observed 3 – 4 km s−1 relative velocity between the Local Interstellar Cloud (LIC) and the so-called G-cloud located in the Galactic Center hemisphere can be quite naturally explained assuming that the two clouds do interact with each other. In the proposed interpretation the two media are separated by a (quasiperpendicular) MHD shock front propagating from the LIC into the G-cloud. The LIC plasma is then nothing else but the shocked (compression 1.3 – 1.4) gas of the G-cloud. A 1-D single-fluid solution of the Rankine — Hugoniot equations can fit the most probable observed values of the relative velocity (3.75 km/s), LIC (6700 K) and G-cloud (5400 K) kinetic temperatures, if the plasma-beta of the LIC plasma is in the range 1.3 – 1.5 (Table 1). This corresponds to a super — fast magnetosonic motion of the heliosphere through the LIC, independently of LIC density. The LIC magnetic field strength is 1.9 (3.1) μG for the LIC electron density ne = 0.04 (0.10) cm−3. In this case the shock is less than 30 000 AU away and moves at about 10 km s−1 relative to the LIC plasma. The Sun is chasing the shock and should catch up with it in about 104 years. If the heliospheric VLP emissions cutoff at 1.8 kHz is indicative of ne (LIC) = 0.04 cm−3 (Gurnett et al., 1993), the (pure plasma) bowshock ahead of the heliopause could be the source of quasi-continuous heliospheric 2-kHz emission band. We believe that with the expected increase in the performance of modern spectroscopic instrumentation the proposed method of magnetic field evaluation may in the future find wider application in the studies of the interstellar medium.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
V.B. Baranov, Y.G. Malama J.Geophys.Res., 100, 14755, 1995
P. Bertin, R. Lallement, R. Ferlet, A. Vidal-Madjar, J. Geophys. Res., 98, 15193, 1993
K.-P. Cheng, F.C. Bruhweiler, Astrophys. J., 364, 573, 1990
P.C. Frisch, Space Sci. Revs., 72, 499, 1995
D.A. Gurnett, W.S. Kurth, R.L. Poynter, L.J. Granroth, I.H. Cairns, W.M. Macek, S.L. Moses, F.V. Coroniti, C.F. Kennel, D.D. Barbosa, Science, 246, 1494, 1989
D.A. Gurnett, W.S. Kurth, S.C. Allendorf, R.L. Poynter Science, 262, 199, 1993
M. Jura, Advances in Ultraviolet Astronomy, p.54, NASA-CP 2238, 1982
R. Lallement, P. Bertin Astron. Astrophys., 266, 479, 1992
R. Lallement, P. Bertin, R. Ferlet, A., Vidal-Madjar, J.L. Bertaux, Astron.Astrophys., 286, 898, 1994
R. Lallement, R. Ferlet, A. Vidal-Madjar, and C. Gry Physics of the Outer Heliosphere, Grzedzielski S., Page, D.E., (Eds.), Pergamon Press, Oxford 1990, pg 37–42
R. Lallement, R. Ferlet, A.M. Lagrange, M. Lemoine and A. Vidal-Madjar, Astron.Astrophys., 304, 461, 1995
R. Lallement, S. Grzedzielski, R. Ferlet, A. Vidal-Madjar, Science with the Hubble Telescope — II, Space Telescope Science Institute, 1996, P.Benvenuti, F.D. Macchetto, E.J. Schreier, eds.
D. Lengyel-Frey J. Geophys. Res., 97, 1609, 1992
J.F. Linsky, 1996 (this volume)
J.F. Linsky, B.E. Wood Astrophys. J. 463, 254, 1996
J.F. Linsky, A. Brown, K. Gayley, A. Diplas, B.D. Savage, T.R. Ayres, W. Landsman, S.T. Shore, S. Heap, Astrophys. J., 402, 694, 1993
L.J. Maher, B.A. Tinsley, J.Geophys.Res. 82, 689, 1977
H.L. Pauls, G.P. Zank, L.L. Williams J. Geophys. Res., 100, 21595, 1995
E.R. Priest D. Reidel Publishing Co., Dordrecht, Holland, 1982
L. Spitzer Diffuse Matter in Space, Chapter 4, John Wiley and Sons, New York, 1968
J.V. Vallerga, B.Y. Welsh, Astrophys. J., 444, 702, 1995
M. Witte, H. Rosenbauer, M. Banaszkiewicz, H.-J. Fahr Adv. Space Res. 13, (6), (6)121-(6)130, 1992
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Grzedzielski, S., Lallement, R. Possible shock wave in the local interstellar plasma, very close to the heliosphere. Space Sci Rev 78, 247–258 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00170811
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00170811