Summary
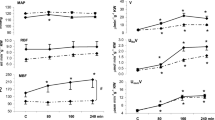
In an attempt to define the effects of a calcium antagonist, nitrendipine, on renal function, intrarenal hemodynamics, and renin release, we infused the drug into the renal artery of anesthetized dogs. Infusion of nitrendipine at a rate of 5 ltg/min in both hydropenic and hydrated dogs resulted in a significant increase in renal blood flow (RBF), glomerular filtration rate (GFR), urine flow and renin release, with no change in systemic blood pressure, indicating a significant renal vasodilation. The urinary excretion rate of sodium increased by the same proportion as that of calcium. The intrarenal blood flow as measured by hydrogen washout rate showed that the outer cortical flow increased by the same proportion as the inner cortical flow. During nitrendipine infusion, free water reabsorption rate (\(T_{H_2 O}^c\)) in hydropenic dogs or free water clearance (\(C_{H_2 O}\)) in hydrated dogs increased in proportion to the urine flow. Neither the ratio of \(T_{H_2 O}^c\) nor that of \(C_{H_2 O}\) to osmoral clearance changed throughout the experiment. These data suggest that nitrendipine may not inhibit sodium transport in the medullary portion of the ascending limb of Henle and may induce an enhancement of the delivery of sodium to the Henle loop. Thus, nitrendipine exerts its diuretic and natriuretic actions via the alteration of renal hemodynamic and the inhibitory effect on proximal sodium reabsorption.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abe Y, Okahara T, Kishimoto T, Yamamoto K, Ueda J (1973) Relationship between intrarenal distribution of blood flow and renin secretion. Am J Physiol 225:319–323
Abe Y, Komori T, Miura K, Takada T, Imanishi M, Okahara T, Yamamoto K (1983a) Effects of the calcium antagonist nicardipine on renal function and renin release in dogs. J Cardiovascular Pharmacol 5:254–259
Abe Y, Yukimura T, Iwao H, Mori N, Okahara T, Yamamoto K (1983b) Effects of EDTA and verapamil on renin release in dogs. Jap J Pharmaco133:627–633
Aoki K, Kondo S, Mochizuki A, Yoshida T, Kato S, Kato K, Takikawa K (1978) Antihypertensive effect of cardiovascular Ca2+-antagonist in hypertensive patients in the absence and presence of beta-adrenergic blockade. Am Heart J 96:218–226
Aukland K, Bower BF, Berliner RW (1964) Measurement of local blood flow with hydrogen gas. Circulation Res 14:164–187
Bonsnes RW, Taussky HH (1945) On the colorimetric determination of creatitine by the Jaffe reaction. J Biol Chem 158:581–591
Ene MD, Williamson PJ, Roberts CJC, Waddell G (1984) Natriuretic effects of nifedipine and nitrendipine. Br J Clin Pharmacol 17:193
Garthoff B, Konrr A, Thomas G, Kazda S (1982) Nitrendipine increases sodium excretion in acutely saline-loaded rats. Biochem Pharmacol 31:3015–3016
Garthoff B, Kazda S, Knorr A, Thomas G (1983) Factors involved in the antihypertensive action of calcium antagonists. Hypertension 5(Suppl 11):II-34–38
Goldberg M, Beck LH, Puschett JB, Schubert JJ (1973) In: Lant AJ, Wilson GM (eds) Modern diuretic therapy. Excerpta Medica, Amsterdam, pp 135–147
Guazzi MD, Fiorentini C, Olivari M, Bartorelli A, Necchi G, Polese A (1980) Short- and long-term efficacy of a calcium-antagonistic agent (nifedipine) combined with methyldopa in the treatment of severe hypertension. Circulation 61:913–919
Haber E, Koerner T, Page LB, Kliman B, Purnode A (1969) Application of a radioimmunoassay for angiotensin I to the physiologic measurements of plasma renin activity in normal human subjects. J Clin Endocrino 129:1349–1355
Hall CE, Hungerford S (1982) Inhibition of DOC-salt and adrenal-regeneration hypertension with the calcium blocker nifedipine. Clin Exp Hyper A4:1217–1230
Higashio T, Abe Y, Yamamoto K (1978) Renal effects of bumetanide. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 207:212–220
Johnson BF, Romero L, Marwaha R (1984) In: Scriabine A, Vanov S, Deck K (eds) Nitrendipine. Urban and Schwarzenberg, Baltimore Munich, pp 535–541
Kazda S, Garthoff B, Knorr A (1983) Nitrendipine and other calcium entry blockers (calcium antagonists) in hypertension. Fed Proc 42:196–200
Leonetti G, Sala C, Bianchini C, Terzoli L, Zanchetti A (1980) Antihypertensive and renal effects of orally administered verapamil. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 18:375–382
McNay JL, Abe Y (1970) Redistribution of cortical blood flow during renal vasodilation in dogs. Circulation Res 27:1023–1032
Olivari MT, Bartorelli C, Polese A, Fiorentini C, Moruzzi P, Guazzi MD (1979) Treatment of hypertension with nifedipine, a calcium antagonist agent. Circulation 59:1056–1062
Park CS, Sigmon DH, Ham DS, Hoeyman TW, Fray JCS (1986) Control of renin secretion by Ca2+ and cyclic AMP through two parallel mechanisms. Am J Physio1 251:R531-R536
Scriabine A, Johnson CE, Anderson CL, Steinsland OS, Janis RA (1984) Ca2+ channel inhibitory effects of nitrendipine on isolated rabbit arteries. In: Scriabine A, Vanov S, Deck K (eds) Nitrendipine. Urban and Schwarzenberg, Baltimore Munich, pp 281–292
Seldin DW, Eknoyan G, Suki W, Rector FC Jr (1965) Localization of diuretic action from the pattern of water and electrolyte excretion. Ann NY Acad Sci 139:328–348
Sokal RS, Rohlf FJ (1969) In: Biometry. New York, WH Freeman and Company
Stein JH, Ferris TF, Huprich JE, Smith TC, Osgood RW (1971) Effect of renal vasodilation on the distribution of cortical blood flow in the kidney of the dog. J Clin Invest 50:1429–1438
Stoepel K, Heise A, Kazda S (1981) Pharmacological studies of the antihypertensive effect of nitrendipine. Arzneimittelforschung 31:2056–2061
Sutton RAL, Dirks JH (1986) Calcium and magnesium: Renal handing and disorders of metabolism. In: Brenner BM, Rector FC Jr (eds) The kidney. Saunders, Philadelphia, pp 551–618
Tarazi R, Aboul-Khair M, Kobayashi K (1984) Cardiac and hemodynamic effects of nitrendipine in normotensive and hypertensive rats. In: Scriabine A, Vanov S, Deck K (eds) Nitrendipine. Urban and Schwarzenberg, Baltimore Munich, pp 251–270
Thompson RB, Kaufman CE, DiScala VA (1971) Effect of renal vasodilation on divalent ion excretion and TmPAH in anaesthetized dogs. Am J Physiol 221:1097–1103
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Send offprint requests to Y. Abe
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fukui, K., Tamaki, T., Yamamoto, A. et al. Salidiuretic action of the calcium antagonist nitrendipine in dogs. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 336, 572–577 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00169316
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00169316