Abstract
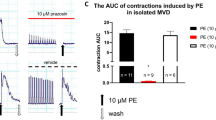
The adenosine analogue N6-cyclopentyladenosine (CPA), acting via postjunctional A1 receptors, has been shown to enhance contractions of the rat vas deferens induced by adenosine 5′-triphosphate (ATP), the sympathetic cotransmitter in this tissue. The aim of the present study was to examine the ability of CPA to enhance contractions induced by other contractile agents. CPA (0.01–0.3 μM) enhanced contractions induced by exogenous ATP (10 μM), 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT) (3 μM), tyramine (10 μM), 2-methyl-5-hydroxytryptamine (2-Me-5-HT) (10 μM) and KCl (35 mM) and this enhancement was blocked by an A1-selective concentration (3 nM) of 1,3-dipropyl-8-cyclopentylxanthine (DPCPX). CPA failed to enhance contractions induced by exogenous noradrenaline (NA) (1 μM or 10 μM), bradykinin (0.1 μM), phenylephrine (3 μM) or carbachol (10 μM).
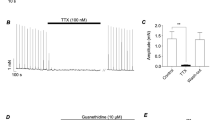
The contractions induced by ATP (10 μM), 5-HT (3 μM), 2-Me-5-HT (10 μM) and KCl (35 mM) were unaffected by tetrodotoxin (1 μM) as well as by desensitisation of the P2x-purinoceptors with the ATP analogue adenosine 5′-(α, β-methylene) triphosphonate. The contractions induced by tyramine (10 μM) and 2-Me-5-HT (10 μM) were blocked by prazosin (100 nM) or by imipramine (1 μM). Ketanserin (10 nM) antagonised the response to 5-HT giving a dose-ratio of 12.9 corresponding to an apparent pA2 of 9.1.
In conclusion, the A1-mediated effect was clearly selective for certain contractile agents and not due to a non-specific increase in contractility of the tissue. CPA enhanced contractions induced by both ATP and indirect sympathomimetics which release endogenous NA, and this enhancement of the two sympathetic cotransmitters may have a functional significance, and demonstrates the complexity of the neuromodulatory effects of adenosine in the rat vas deferens.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bean BP, Friel DD (1990) ATP-activated channels in excitable cells. In: Narahashi T (eds) Ion channels, vol. 2. Plenum Press, London/New York, p. 169–203
Brownhill VR, Hourani SMO, Kitchen I(1996) Differential distribution of adenosine receptors in the epididymal and prostatic portions of the rat vas deferens. Eur J Pharmacol (in press)
Bültmann R, Kurz AK, Starke K (1994) α1-Adrenoceptors and calcium sources in adrenergic neurogenic contractions of rat vas deferens. Br J Pharmacol 111:151–158
Bültmann R, Starke K (1993) Chloroethylclonidine: an irreversible agonist at the prejunetional α2-adrenoceptors in the rat vas deferens. Br J Pharmacol 108:336–341
Burnstock G (1990) Noradrenaline and ATP as cotransmitters in sympathetic nerves. Neurochem Int 17:357–368
Burnstock G, Kennedy C (1985) Is there a basis for distinguishing two types of P2-purinoceptors? Gen Pharmacol 16:433–440
Collis MG, Hourani SMO (1993) Adenosine receptor subtypes. Trends Pharmacol Sci 14:360–366
Dickenson JM, Hill SJ (1993) Intracellular cross-talk between receptors coupled to phospholipase C via pertussis toxin-sensitive and insensitive G-proteins in DDT1MF-2 cells. Br J Pharmacol 109:719–724
Dubyak GR, El-Moatassim C (1993) Signal transduction via P2-purinergic receptors for extracellular ATP and other nucleotides. Am J Physiol C577–C606
Fredholm BB, Abbracchio MP, Burnstock G, Daly JW, Harden TK, Jacobson KA, Leff P, Williams M (1994) Nomenclature and classification of purinoceptors. Pharmacol Rev 46:143–156
Hall JM (1992) Bradykinin receptors: pharmacological properties and biological roles. Pharmacol Ther 56:131–190
Holck MI, Marks BH (1978) Purine nucleoside and nucleotide interactions on normal and subsensitive alpha adrenoceptor responsiveness in guinea-pig vas deferens. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 205:104–117
Hourani SMO, Jones DAD (1994) Post junctional excitatory adenosine A1 receptors in the rat vas deferens. Gen Pharmacol 25:417–420
Hourani SMO, Nicholls J, Lee SBS, Halfhide EJ, Kitchen I (1993). Characterisation and ontogeny of P1-purinoceptors in rat vas deferens. Br J Pharmacol 108:754–758
Hoyer D, Clarke DE, Fozard JR, Hartig PR, Martin GR, Mylecharane EJ, Saxena PR, Humphrey PA (1994) International Union of Pharmacology classification of receptors for 5-hydroxytryptamine (serotonin). Pharmacol Rev 46:157–203
Kennedy C (1990) P1- and P2-purinoceptor subtypes—an update. Arch Int Pharmacodyn 303:30–50
Levesque L, Drapeau G, Grose JH, Rioux F, Marceau F (1993). Vascular mode of action of kinin B1 receptors and development of a cellular model for the investigation of these receptors. Br J Pharmacol109:1254–1262
Long CJ, Stone TW (1986) The effects of adenosine on receptor sensitivity in the rat vas deferens. Br J Pharmacol 132:11–19
Mallard NJ, Marshall RW, Sithers AJ, Spriggs TLB (1992) Separation of putative α1A- and α1B adrenoceptor mediated components in the tension response of the rat vas deferens to electrical field stimulation. Br J Pharmacol 105:727–731
Martin GR, Humphrey PPA (1994) Receptors for 5-hydroxytryptamine: current perspectives on classification and nomenclature. Neuropharmacology 33:261–273
Morishita H, Sakamoto Y, Furukawa T (1987) Involvement of calcium and cyclic AMP in the K+-induced rhythmic contractions of isolated rat vas deferens. Arch Int Pharmacodyn 289:118–128
Paton DM (1981) Presynaptic neuromodulation mediated by purinergic receptors. In: Burnstock G (eds) Purinergic receptors. Receptors and recognition series B, vol. 12. Chapman and Hall, London, pp. 199–219
Sneddon P, Machaly M (1992) Regional variation in purinergic and adrenergic responses in the isolated vas deferens of rat, rabbit and guinea-pig. J Auton Pharmacol 12:421–428
Vizi ES, Burnstock G (1988) Origin of ATP release in the rat vas deferens: concomitant measurement of [3H]-noradrenaline and [14C]-ATP. Eur J Pharamacol 158:69–77
von Kügelgen I, Starke K (1991) Noradrenaline-ATP co-transmission in the sympathetic nervous system. Trends Pharmacol Sci 12:319–324
White TD (1988) Role of adenine compounds in autonomic neurotransmission. Pharmacol Ther 38:129–168
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Brownhill, V., Hourani, S. & Kitchen, I. Selective enhancement by an adenosine A1 receptor agonist of agents inducing contraction of the rat vas deferens. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 353, 499–504 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00169168
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00169168