Summary
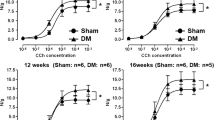
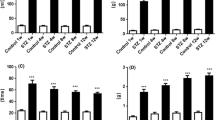
1. The effect of streptozotocin (STZ) induced diabetes on rat urinary bladder function was investigated by means of ‘in vivo’ cystometry and ‘in vitro’ recording of bladder strips contractility. A group of sucrose-fed animals was included to determine to what extent the STZ-induced changes were ascribable to the increased diuresis. 2. After 7–9 weeks from STZ injection there was a marked increase in weight of bladder and ureters. Cystometry revealed a marked increase in bladder capacity (volume threshold) although pressure threshold and amplitude of micturition contraction were unaffected. Sucrose-fed animals, having normal blood glucose levels but a similar increase in urine production exhibited cystometric changes identical to those of STZ animals. 3. ‘In vitro’ experiments indicated that the response to field stimulation (0.1–20 Hz) is reduced in STZ-pretreated but increased in sucrose-fed animals, as compared to controls. 4. The content of urinary bladder and ureters in sensory neuropeptides (substance-P, neurokinin-A and calcitonin-gene related peptide-like immunoreactivity) was increased by STZ diabetes when values were corrected for the increased weight of these organs. 5. The capsaicin-induced contraction of the rat isolated bladder strips, presumably caused by neuropeptides released from intramural sensory nerves, is unaffected by STZ diabetes. 6. These findings indicate that STZ diabetes produces, at an early stage, changes similar to those reported to occur in the human disease, e. g. a greater bladder capacity with unimpaired voiding function. The increased bladder capacity of STZ-rats seems largely, if not solely, ascribable to changes in physical properties of the detrusor muscle, thereby allowing accomodation of greater than normal volumes with similar increase of intraluminal pressure. No sign of diabetic neuropathy of the capsaicin-sensitive sensory nerves can be observed at this stage (7–9 weeks) of STZ diabetes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ballman M, Conlon JM (1985) Changes in somatostatin, Substance P and vasoactive intestinal polypeptide content of the gastrointestinal tract following streptozotocin-induced diabetes in the rat. Diabetologia 28:355–358
Belai A, Lincoln J, Miller P, Crowe R, Loesch A, Burnstock G (1985) Enteric nerves in diabetic rats: increase in vasoactive intestinal polypeptide but not substance P. Gastroenterology 89:967–976
Borsini F (1985) Randomization program for Apple Ile computer. Brain Res Bull 15:279–281
Buck AC, McRae CU, Reer PI, Chisholm GD (1974) The diabetic bladder. Proc R Soc Med 67:81–83
Carpenter FG (1981) Atropine and micturition responses by rats with intact and partially innervated bladder. Br J Pharmacol 73:837–842
Carpenter FG (1983) Impairment and restoration of rat urinary bladder responsiveness following distension. Am J Physiol 244 (Regulatory Integrative Comp Physiol 13):RI06-Rl13
Diani AR, Peterson T, Sawada GA, Wyse BM, Blanks MC, Gerristen GC, Terenghi G, Varndell IM, Polak JM, Blank MA, Bloom SR (1985) Elevated levels of vasoactive intestinal peptide in the eye and urinary bladder of diabetic and prediabetic Chinese hamsters. Diabetologica 28:302–307
Ellenberg M (1980) Development of urinary bladder dysfunction in diabetes mellitus. Ann Intern Med 92:321–323
Faerman I, Maler M, Jadzinsky M, Fox D, Alvarez E, Zilverbarg J, Cibeira JB, Colinas R (1971) A symptomatic neurogenic bladder in juvenile diabetics. Diabetologia 7:168
Faerman I, Glocer L, Celener D, Jadzinsky M, Fox D, Maler M, Alvarez E (1973) Autonomic nervous system and diabetes: Histological and histochemical study of the autonomic nerve fibers of the urinary bladder in diabetic patients. Diabetes 22:225–237
Gamse R, Jancsó G (1985) Reduced neurogenic inflammation in streptozotocin-diabetic rats due to microvascular changes but not to substance P depletion. Eur J Pharmacol 118:175–180
Gamse R, Lembeck F, Cuello AC (1979) Substance P in the vagus nerve. Naunyn Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 306:37–44]
Ghatei MA, Gu J, Mulderry PK, Blank MA, Allen JM, Morrison JFB, Polak JM, Bloom SR (1985) Calcitonin gene-related peptide in the female rat urogenital tract. Peptides 6:809–815
Holzer P, Bucsics A, Lembeck F (1982) Distribution of capsaicinsensitive nerve fibres containing immunoreactive substance P in cutaneous and visceral tissues of the rat. Neurosci Letters 31:253–257
Holzer-Petsche U, Lembeck F (1984) Systemic capsaicin treatment impairs the micturition reflex in rat. Brit J Pharmacol 83:935–941
Kahan M, Goldberg PD, Mandell EE (1970) Neurogenic vesical dysfunction and diabetes mellitus. NY State J Med 2:2448–2455
Kolta MG, Wallace LJ, Gerald MC (1985) Streptozotocin-induced diabetes affects rat urinary bladder response to autonomic agents. Diabetes 34:917–921
Lincoln J, Haven AJ, Sawyer M, Burnstock G (1984a) The smooth muscle of rat bladder in the early stages of streptozotoc-ininduced diabetes. Brit J Urol 56:24–30
Lincoln J, Crockett M, Haven AJ, Burnslock G (1984b) Rat bladder in the early stages of streptozotocin-induced diabetes: adrenergic and cholinergic innervation. Diabetologia 26:81–87
Maggi CA, Santicioli P, Meli A (1984a) The effect of topical capsaicin on rat urinary bladder motility in vivo. Eur J Pharmacol 103:41–50
Maggi CA, Evangelista S, Grimaldi G, Santicioli P, Giolitti A, Meli A (1984b) Evidence for the involvement of arachidonic acid metabolites in spontaneous and drug-induced contractions of rat urinary bladder. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 230:500–513
Maggi CA, Meli A (1986) The role of neuropeptides in the regulation of the micturition reflex. J Anton Pharmacol 6:133–162
Maggi CA, Santicioli P, Meli A (1985) Evidence for the involvement of endogenous substance P in the motor effects of capsaicin on the rat urinary bladder. J Pharm Pharmacol 37:203–204
Maggi CA, Santicioli P, Borsini F, Giuliani S, Meli A (1986a) The role of the capsaicin-sensitive innervation of the rat urinary bladder in the activation of micturition reflex. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 332:276–283
Maggi CA, Santicioli P, Giuliani S, Furio M, Meli A (1986b) The capsaicin-sensitive innervation of the rat urinary bladder: further studies on mechanisms regulating micturition threshold. J Urol 136:696–700
Maggi CA, Santicioli P, Meli A (1986c) Postnatal development of micturition reflex in rats. Am J Physiol 250 (Regulatory Integrative Comp Physiol 19):R926-R931
Maggi CA, Santicioli P, Meli A (1986d) Somatovesical and vesicovesical excitatory reflexes in urethane-anaesthetized rats. Brain Res 380:83–93
Maggi CA, Giuliani S, Santicioli P, Meli A (1986e) Analysis of factors involved in determining urinary bladder voiding cycle in urethan-anesthetized rats. Am J Physiol 251:R250-R257
Maggi CA, Santicioli P, Meli A (1986f) The nonstop transvesical cystometrogram in urethane-anesthetized rats. J Pharm Meth 15:157–167
Mordes JP, Rossini AA (1981) Animals models of diabetes. Amer J Med 70:353–360
Mulderry PK, Ghatei MA, Rodrigo J, Allen JM, Rosenfeld MG, Polak JM, Bloom SR (1985) CGRP in cardiovascular tissues of the rat. Neuroscience 14:947–954
Santicioli P, Maggi CA, Meli A (1985) The effect of capsaicin pretreatment on the cystometrograms of urethane-anesthetized rats. J Urol 133:700–703
Santicioli P, Maggi CA, Meli A (1986) Functional evidence for the existence of a capsaicin-sensitive innervation in the rat urinary bladder. J Pharm Pharmacol 38:446–451
Schmidt RE, Plurad SB, Moderat CW (1983) Experimental diabetic autonomic neuropathy characterization in streptozotocin-diabetic Sprague-Dawley rats. Lab Invest 49:538–552
Sharkey KA, Williams RG, Schultzberg M, Dockray GJ (1983) Sensory substance P innervation of the urinary bladder: possible site of action of capsaicin in causing urine retention in rats. Neuroscience 10:861–868
Slein HW (1974) Methods of enzymatic analysis. Bergmeyer HV (ed) Academic Press, New York, pp 1196–1201
Theodorsson-Norheim E, Brodin E, Norheim I, Rosell S (1984) Antisera raised against eledoisin and kassinin detect immunoreactive material in rat tissue extracts: tissue distribution and chromatographic characterization. Regul Pept 9:229–244
Yokokawa K, Sakanaka M, Shiosaka S, Tchyama M, Shiotani Y, Sonoda T (1985) Three dimensional distribution of sustance P-like immunoreactivity in the urinary bladder of rat. J Neural Transm 63:209–222
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Send offprint requests to P. Santicioli at the above address
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Santicioli, P., Gamse, R., Maggi, C.A. et al. Cystometric changes in the early phase of streptozotocin-induced diabetes in rats: evidence for sensory changes not correlated to diabetic neuropathy. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 335, 580–587 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00169128
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00169128