Abstract
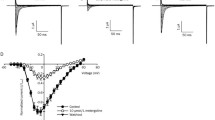
The effects of bivalent lead on ion channels activated by kainate and α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolpropionate (AMPA) were studied using Xenopus oocytes microinjected with mRNA from rat brain. Lead reduced kainate-induced membrane currents in a reversible and dose-dependent manner, without affecting membrane currents induced by AMPA. Lead decreased the kainate currents with a concentration of 0.1 μmol/l to 0.93 ± 0.01 and with a concentration of 100 μmol/l to 0.41 ± 0.04 of the control values. The blocking effect of lead on kainate responses was voltage dependent. The inhibition was strongest at - 90 mV to - 70 mV and became weaker at more positive membrane potentials. The effect of lead on the kainate-induced membrane currents remained unchanged when the concentration of kainate was increased. Hence lead probably represents a noncompetitive channel-blocking agent for non-N-methyl-d-aspartate (NMDA) receptor channels activated by kainate.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alkondon M, Costa ACS, Radhakrishnan V, Aronstam RS, Albuquerque EX (1990) Selective blockade of NMDA-activated channel currents may be implicated in learning deficits caused by lead. FEBS Lett 261:124–130
Bellinger D, Leviton A, Waternaux C, Needleman H, Rabinowitz M (1987) Longitudinal analyses of prenatal and postnatal lead exposure and early cognitive development. N Engl J Med 316:1037–1043
Cathala G, Savouret J-F, Mendez B, West BL, Karin M, Martial JA, Baxter JD (1983) A method for isolation of intact translationally active ribonucleic acid. DNA 2:239–335
Cavalleri A, Minoia C, Ceroni M, Polom M (1984) Lead in cerebrospinal fluid and its relationship to plasma lead in humans. J Appl Toxicol 4:65
Dumont JN (1972) Oogenesis in Xenopus laevis (Daudin). Stages of oocyte development in laboratory maintained animals. J Morphol 136:153–180
Guilarte TR, Miceli RC, Jett DA (1994) Neurochemical aspects of hippocampal and cortical Pb2+ neurotoxicity. Neurotoxicology 15:459–466
Kiss T, Osipenko N (1994) Toxic effects of heavy metals on ionic channels. Pharmacol Rev 46:245–267
Lerma J, Paternain AV, Naranjo JR, Mellström B (1993) Functional kainate-selective glutamate receptors in cultured hippocampal neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90:11688–11692
MacDonald RL, Nowak LM (1990) Mechanisms of blockade of excitatory amino acid receptor channels. Trends Pharmacol Sci 11:167–172
Madeja M, Mußhoff U, Speckmann E-J (1991) A concentration-lamp system allowing two-electrode voltage-clamp investigations in oocytes of Xenopus laevis. J Neurosci Methods 38:267–269
Massaro EJ, Massaro TF (1986) The effects of lead exposure during development on higher order cognitive functioning in the rat. Neurotoxicology 7:515–526
Mußhoff U, Binding N, Madeja M, Witting U, Speckmann E-J (1995) Actions of lead on non-NMDA receptors expressed in Xenopus oocytes. Pflügers Arch 429 [Suppl 6]: R31
Needleman HL, Schell A, Bellinger D, Leviton A, Allred EN (1990) The long-term effects of exposure to low doses of lead in childhood. N Engl J Med 322:83–88
Partin KM, Patneau DK, Winters CA, Mayer ML, Buonanno A (1993) Selective modulation of desensitization at AMPA versus kainate receptors by cyclothiazide and concanavalin A. Neuron 11:1069–1082
Paternain AV, Morales M, Lerma J (1995) Selective antagonism of AMPA receptors unmasks kainate receptor-mediated responses in hippocampal neurons. Neuron 14:185–189
Simons TJB (1993) Lead transport and binding by human erythorcytes in vitro. Pflügers Arch 423:307–313
Sommer B, Seeburg PH (1992) Glutamate receptor channels: novel properties and new clones. Trends Pharmacol Sci 13:291–296
Ujihara H, Albuquerque EX (1992) Developmental change of the inhibition by lead of NMDA-activated currents in cultured hippocampal neurons. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 263:868–875
Uteshev V, Büsselberg D, Hass HL (1993) Pb2+ modulates the NMDA-receptor-channel complex. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 347:209–213
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mußhoff, U., Madeja, M., Binding, N. et al. Lead-induced blockade of kainate-sensitive receptor channels. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 353, 42–45 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00168914
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00168914