Summary
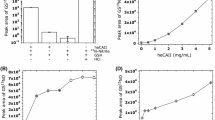
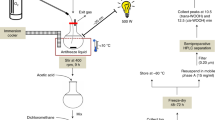
The molecular mechanism(s) underlying the vasodilator activity of CAS 936 (3-(cis-2,6-dimethylpiperidino)-N-(4-methoxybenzoyl)-sydnonimine) and its metabolites 3-(cis-2,6-dimethylpiperidino)-sydnonimine (C87 3754) and N-(cis-2,6-dimethylpiperidino)-N-nitroso-2-aminoacetonitril (C873786) was investigated. These compounds were tested for their relaxant activity in isolated rabbit arterial segments, activation of purified soluble guanylyl cyclase and release of nitric oxide (NO) in vitro and in vivo. C873754 and C873786 inhibited the noradrenalin-induced contraction and increased the cyclic GMP content of endothelium-denuded rabbit aortic and femoral segments, whereas CAS 936 was without effect. Similarly, both metabolites, but not CAS 936, activated purified soluble guanylyl cyclase (EC50 about 30 μM) and released NO in buffered aqueous solutions, as detected by electron spin resonance (esr) spectrometry. Both in vitro and in vivo an accumulation of NO was detected by esr spectrometry in vascular tissues exposed to the metabolites of CAS 936, whereas a significant release of NO from CAS 936 was only detected in the isolated rabbit liver, but not in vascular tissue. It is conceivable, therefore, that the metabolites of CAS 936 appearing in the systemic circulation after hepatic biotransformation induce vasodilatation by release of NO and activation of soluble guanylyl cyclase in vascular smooth muscle. Moreover, the activation of soluble guanylyl cyclase in vitro by the metabolites of CAS 936 was significantly enhanced by co-incubation with certain particulate fractions from bovine aortic endothelial and smooth muscle cells. Thus, an enzymic release of NO from these metabolites in addition to their spontaneous decomposition may play a significant role for their vasodilator activity in vivo.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bohn H, Schönafinger K (1989) Oxygen and oxidation promote the release of nitric oxide from sydnonimines. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 14 [Suppl 11]: S6-S12
Bohn H, Beyerle R, Martorana PA, Schönafinger K (1991) CAS 936, a novel sydnonimine with direct vasodilating and nitric oxide-donating properties: effects on isolated blood vessels. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 18:522–527
Bohn nH, Martorana PA, Schönafinger K (1992) Cardiovascular effects of the new NO donor pirsidomine. Hemodynamic profile and tolerance studies in anesthetized and conscious dogs. Eur J Pharmacol (in press)
Busse R, Pohl U, Kellner C, Klemm U (1983) Endothelial cells are involved in the vasodilatory response to hypoxia. Pflügers Arch 397:78–80
Busse R, Pohl U, Mülsch A, Bassenge E (1989) Modulation of the vasodilator action of SIN-1 by the endothelium. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 14 [Suppl 11]: S81-S85
Feelisch M, Ostrowski J, Noack E (1989) On the mechanism of NO release from sydnonimines. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 14 [Suppl 11]:S13-S22
Harper JF, Brooker G (1975) Femtomole sensitive radioimmunoassay for cyclic AMP and cyclic GMP after 2′O acetylation by acetic anhydride. J Cyc Nucleotide Res 1:207–218
Hecker M, Walsh DT, Vane JR (1991) On the substrate specificity of nitric oxide synthase. FEBS Lett 294:221–224
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ (1951) Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193:265–275
Lückhoff A, Busse R (1990) Activators of potassium channels enhance calcium influx into endothelial cells as a consequence of potassium currents. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 342:94–99
Lückhoff A, Busse R, Winter I, Bassenge E (1987) Characterization of vascular relaxant factor released from cultured endothelial cells. Hypertension 9:295–303
Mordvintcev PI, Mülsch A, Busse R, Vanin AF (1991) On-line detection of nitric oxide formation in liquid aqueous phase by electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopy. Anal Biochem 199:142–146
Mülsch A, Busse R (1990) NG-nitro-{spl-arginine (N5-[imino(nitramino)methyl]-l-ornithine) impairs endothelium-dependent dilations by inhibiting cytosolic nitric oxide synthesis from l-arginine}. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 341:143–147
Mülsch A, Gerzer R (1991) Purification of heme-containing soluble guanylyl cyclase. In: Jonson JA, Corbin JD (eds) Methods enzymol 195: Adenylyl cyclase, G proteins, and guanylyl cyclase. Academic Press, San Diego, pp 377–383
Mülsch A, Busse R, Winter I, Bassenge E (1989) Endothelium- and sydnonimine-induced responses of native and cultured aortic smooth muscle cells are not impaired by nitroglycerin tolerance. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 339:568–574
Mülsch A, Mordvintcev PI, Vanin AF, Busse R (1991) The potent vasodilating and guanylyl cyclase activating dinitrosyl-iron(II) complex is stored in a protein-bound form in vascular tissue and is released by thiols. FEBS Lett 294:252–256
Mülsch A, Vanin AF, Mordvintcev PI, Hauschildt S, Busse R (1992) NO accounts completely for the oxygenated nitrogen species generated by enzymic l-arginine oxygenation. J Biochem 288:597–603
Steiner AL, Parker CW, Kipnis DM (1972) Radioimmunoassay for cyclic nucleotides. I. Preparation of antibodies and iodinated cyclic nucleotides. J Biol Chem 247:1106–1113
Tanayama S, Nakai Y, Fujita T, Suzuoki T (1974) Biotransformation of molsidomine (N-ethoxycarbonyl-morpholinosydnonimine), a new antianginal agent, in rats. Xenobiotica 4:175–191
Vanin AF (1987) Sources of iron capable of forming nitrosyl complexes in animal tissues. Biofizika 31:128–131
Woolum JC, Tiezzi E, Commoner B (1968) Electron spin resonance of iron-nitric oxide complexes with amino acids, peptides and proteins. Biochem Biophys Acta 160:311–320
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Correspondence to A. Mülsch at the above address
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mülsch, A., Hecker, M., Mordvintcev, P.I. et al. Enzymic and nonenzymic release of NO accounts for the vasodilator activity of the metabolites of CAS 936, a novel long-acting sydnonimine derivative. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 347, 92–100 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00168778
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00168778