Summary
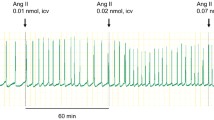
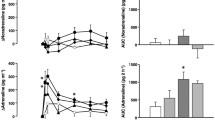
In the conscious freely moving rat, the intrathecal (i.t.) injection of neuropeptide K (NPK; 0.65 to 6.5 nmol), at T-9 spinal cord level, produced dose-dependent and prolonged (> 3 h) increases in mean arterial blood pressure (MAP) and heart rate (HR). The cardiovascular response to 3.25 nmol NPK was less sustained when injected at T-2 level. The cardiovascular response to 3.25 nmol NPK (T-9 level) was correlated with increases in plasma levels of noradrenaline, adrenaline and neuropeptide Y (NPY), and was significantly reduced by the prior i.v. administration of inhibitors of either α-adrenoceptors (1 mg/kg, phentolamine), α1-adrenoceptors (1 mg/kg, prazosin), β1-adrenoceptors (1 mg/kg, metoprolol) or angiotensin converting enzyme (10 mg/kg, captopril). The cardiovascular response to NPK was also significantly reduced in rats that had undergone, 48 h earlier, bilateral adrenalectomy or to a greater extent sympathectomy with 6-hydroxydopamine. Whereas NPK-induced release of adrenaline was abolished by adrenalectomy, that of neuropeptide Y and noradrenaline was blunted by either treatment. The results suggest that the cardiovascular effect of i.t. NPK is mediated by the stimulation of the sympathoadrenal system and the release of angiotensin. Sympathetic fibers may play a greater role than the adrenal medulla in the cardiovascular response to NPK. It appears that neuropeptide Y derives from both sympathetic fibers and adrenal medullae. Hence, if released in the spinal cord, NPK may play an important role in cardiovascular and sympathoadrenal regulation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen JM, Polak JM, Rodrigo J, Darcy K, Bloom SR (1985) Localisation of neuropeptide Y in nerves of the rat cardiovascular system and the effect of 6-hydroxydopamine. Cardiovasc Res 19:570–577
Aubert JF, Burnier M, Waeber B, Nussberger J, Dipette DJ, Burris JF, Brunner HR (1988) Effects of a nonpressor dose of neuropeptide Y on cardiac output, regional blood flow distribution and plasma renin, vasopressin and catecholamine levels. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 244:1109–1115
Bacon SJ, Smith AD (1988) Preganglionic sympathetic neurones innervating the rat adrenal medulla: immunocytochemical evidence of synaptic input from nerve terminals containing substance P, GABA or 5-hydroxytryptamine. J Anton Nerv Syst 24:97–122
Cushman DW, Ondetti MA (1980) Inhibitors of angiotensin-converting enzyme. Prog Med Chem 174:41–104
Davis BM, Krause JE, McKelvy JF, Cabot JB (1984) Effects of spinal lesions on substance P levels in the rat sympathetic preganglionic cell column: evidence for local spinal regulation. Neuroscience 13:1311–1326
Décarie A, Couture R (1992) Characterization of the peripheral action of neuropeptide K on the rat cardiovascular system. Eur J Pharmacol 213:125–131
De Luca A, Rand MJ (1988) Involvement of alpha-1 adrenoceptors in chronotropic responses to endogenously released amines in the pithed rat. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 15:33–41
Dibona GF (1982) The functions of the renal nerves. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol 94:75–181
Duggan AW, Hendry IA, Morton CR, Hutchison WD, Zhao ZQ (1988) Cutaneous stimuli releasing immunoreactive substance P in the dorsal horn of the cat. Brain Res 451:261–263
Duggan AW, Hope PJ, Jarrott B, Schaible H-G, Fleetwood-Walker SM (1990) Release, spread and persistence of immunoreactive neurokinin A in the dorsal horn of the cat following noxious cutaneous stimulation. Studies with antibody microprobes. Neuroscience 35:195–202
Edvinsson L, Ekblad E, Hakanson R, Wahlestedt C (1984) Neuropeptide Y potentiates the effect of various vasoconstrictor agents on rabbit blood vessels. Br J Pharmacol 83:519–525
Haass M, Cheng B, Richardt G, Lang RE, Schömig A (1989) Characterization and presynaptic modulation of stimulation-evoked exocytotic co-release of noradrenaline and neuropeptide Y in guinea pig heart. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 339:71–78
Hasséssian H, Couture R (1989) Cardiovascular responses induced by intrathecal substance P in the conscious freely moving rat. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 13:594–602
Hasséssian H, Drapeau G, Couture R (1988) Spinal action of neurokinins producing cardiovascular responses in the conscious freely moving rat: evidence for a NK-1 receptor mechanism. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 338:649–654
Hasséssian H, Couture R, de Champlain J (1990) Sympathoadrenal mechanisms underlying cardiovascular responses to intrathecal substance P in conscious rats. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 15:736–744
Helke CJ, Charlton CG, Keeler JR (1985) Bulbospinal substance P and sympathetic regulation of the cardiovascular system: a review. Peptides 6 [Suppl 2]:69–74
Helke CJ, Krause JE, Mantyh PW, Couture R, Bannon MJ (1990) Diversity in mammalian tachykinin peptidergic neurons: multiple peptides, receptors, and regulatory mechanisms. FASEB J 4:1606–1615
Holets V, Elde R (1982) The differential distribution and relationship of serotoninergic and peptidergic fibers to sympathoadrenal neurons in the intermediolateral cell column of the rat: a combined retrograde axonal transport and immunohistofluorescence study. Neuroscience 7:1155–1174
Hua X-Y, Theodorsson-Norheim E, Brodin E, Lundberg JM, Hökfelt T (1985) Multiple tachykinins (neurokinin A, neuropeptide K and substance P) in capsaicin-sensitive sensory neurons in the guinea-pig. Regul Peptides 13:1–19
Hua X-Y, Saria A, Gamse R, Theodorsson-Norheim E, Brodin E, Lundberg JM (1986) Capsaicin induced release of multiple tachykinins (substance P, neurokinin A and eledoisin-like material) from guinea-pig spinal cord and ureter. Neuroscience 19:313–319
Lundberg JM, Saria A, Franco-Cereceda A, Hökfelt T, Terenius L, Goldstein M (1985) Differential effects of reserpine and 6-hydroxydopamine on neuropeptide Y (NPY) and noradrenaline in peripheral neurons. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 328:331–340
Lundberg JM, Hökfelt T, Hemsén A, Theodorsson-Norheim E, Pernow J, Hamberger B, Goldstein M (1986) Neuropeptide Y-like immunoreactivity in adrenaline cells of adrenal medulla and in tumors and plasma of pheochromocytoma patients. Regul Peptides 13:169–182
Martling C-R, Theodorsson-Norheim E, Norheim I, Lundberg JM (1987 a) Bronchoconstrictor and hypotensive effects in relation to pharmacokinetics of tachykinins in the guinea-pig — evidence for extraneuronal cleavage of neuropeptide K to neurokinin A. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 336:183–189
Martling C-R, Theodorsson-Norheim E, Lundberg JM (1987 b) Occurrence and effects of multiple tachykinins; substance P, neurokinin A and neuropeptide K in human lower airways. Life Sci 40:1633–1643
Morris MJ, Russell AE, Kapoor V, Cain MD, Elliott JM, West MJ, Wing LMH, Chalmers JP (1986) Increases in plasma neuropeptide Y concentrations during sympathetic activation in man. J Auton Nerv Syst 17:143–149
Morris M, Kapoor V, Chalmers J (1987) Plasma neuropeptide Y concentration is increased after hemorrhage in conscious rats: relative contributions of sympathetic nerves and the adrenal medulla. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 9:541–545
Osnes JB, Aass H, Skomedal T (1989) Adrenoceptors in myocardial regulation: concomitant contribution from both alpha- and beta-adrenoceptor stimulation to the inotropic response. Basic Res Cardiol 84 [Suppl 1]:9–17
Peuler JD, Johnson GA (1977) Simultaneous single isotope radioenzymatic assay of plasma norepinephrine, epinephrine and dopamine. Life Sci 21:625–636
Skomedal T, Schiander IG, Osnes JB (1988) Both alpha and beta adrenoceptor-mediated components contribute to final inotropic response to norepinephrine in rat heart. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 247:1204–1210
Takeda Y, Krause JE (1989) Neuropeptide K potently stimulates salivary gland secretion and potentiates substance P-induced salivation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 86:392–396
Tatemoto K, Lundberg JM, Jörnvall H, Mutt V (1985) Neuropeptide K: isolation, structure and biological activities of a novel brain tachykinin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 128:947–953
Wahlestedt C, Edvinsson L, Ekblad E, Håkanson R (1985) Neuropeptide Y potentiates noradrenaline-evoked vasoconstriction: mode of action. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 234:735–741
Zusman RM (1984) Renin- and non-renin-mediated antihypertensive actions of converting enzyme inhibitors. Kidney Int 25:969–983
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Correspondence to R. Couture at the above address
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pham, T.M., de Champlain, J. & Couture, R. Cardiovascular and sympathoadrenal responses to intrathecal injection of neuropeptide K in the conscious rat. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 347, 42–49 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00168770
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00168770