Abstract
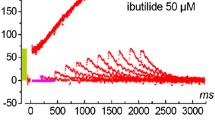
We have studied the inhibitory influence of the class III antiarrhythmic drug ambasilide (LU 47110) on the transient outward current I to1 and the sustained current T so following inactivation of I to1 in human atrial myocytes. The two currents are separated by a mathematical procedure based on the amplitudes and time constants of the biexponential inactivation of the total outward current. The frequency dependence, the recovery from inactivation and the kinetics of activation and inactivation are described. Ambasilide reversibly and concentration dependently inhibited I to1, I so and the sodium current I Na. Concentration required for half maximal inhibition (IC50) for the effects on I to1 and I so were 23.3 μmol/l and 45.7 μmol/l respectively, concentrations shown by others to be effective in terminating and preventing fibrillation in a dog atrial arrhythmia model. Ambasilide not only reduced the amplitude of I to1 and I so but also accelerated the time course of inactivation from 14.22 to 6.69 ms and from 202.3 to 87.9 ms respectively. The amplitude of I to1 showed only a small dependence on stimulation frequency characteristic for human atrial myocytes, whereas I so was reduced significantly at higher stimulation frequencies. Ambasilide did not change these relationships (0.1–4 Hz) and therefore did not show the reverse use-dependence known from other class III antiarrhythmic agents and which is an important property for a prospective antiarrhythmic drug. The lack of an effect of ambasilide on both steady-state activation and inactivation of I to1, and the time constant of recovery from inactivation, suggests that ambasilide acts by changing conductance rather than by influencing the gating mechanism. The described characteristics make ambasilide an interesting substance in the group of class III antiarrhythmic drugs.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amos GJ, Wettwer E, Li Q, Himmel HM, Ravens U (1994) Differences in outward currents of human atrial and ventricular myocytes (abstract). Circulation 90:1–581
Amos GJ, Li Q, Wettwer E, Himmel HM, Metzger F, Ravens U (1995) Kinetics of clofilium block of human atrial outward currents (abstract). Naunyn Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 351 (suppl): R105
Berger F, Borchard U, Hafner D (1989) Effects of the calcium entry blocker bepridil on repolarizing and pacemaker currents in sheep cardiac Purkinje fibres. Naunyn Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 339:638–646
Beuckelmann DJ, Näbauer M, Erdmann E (1993) Alterations of K+ currents in isolated human ventricular myocytes from patients with terminal heart failure. Circ Res 73:379–385
Colatsky TJ, Follmer CH, Starmer CF (1990) Channel specificity in antiarrhythmic drug action. Mechanism of potassium channel block and its role in suppressing and aggravating cardiac arrhythmias. Circulation 82:2235–2242
Coraboeuf E, Nargeot J (1993) Electrophysiology of human cardiac cells. Cardiovasc Res 27:1713–1725
Duan D, Fermini B, Nattel S (1993) Potassium channel blocking properties of propafenone in rabbit atrial myocytes. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 264:1113–1123
Dukes ID, Cleemann L, Morad M (1990) Tedisamil blocks the transient and delayed rectifier K+ currents in mammalian cardiac and glial cells. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 254:560–569
Escande D, Coulombe A, Faivre J-F, Deroubaix E, Coraboeuf E (1987) Two types of transient outward currents in adult human atrial cells. Am J Physiol 252:H142-H148
Fermini B, Wang Z, Duan D, Nattel S (1992) Differences in rate dependence of transient outward current in rabbit and human atrium. Am J Physiol 263:H1747-H1754
Himmel HM, Li Q, Amos GH, Wettwer E, Metzger F, Ravens U (1995) Pharmacological modulation of the transient outward current in human ventricular myocytes (abstract). Naunyn Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 351 (suppl):R105
Hondeghem LM, Snyders DJ (1990) Class III antiarrhythmic agents have a lot of potential but a long way to go. Reduced effectiveness and dangers of reverse use dependence. Circulation 81:686–690
Jacobson SL, Altschuld RA, Hohl CM (1990) Muscle cell cultures from human heart. In: Piper HM (ed) Cell culture techniques in heart and vessel research. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 75–98
Jahnel U, Klemm P, Nawrath H (1994) Different mechanisms of the inhibition of the transient outward current in rat ventricular myocytes. Naunyn Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 349:87–94
Le Grand B, Hatem S, Deroubaix E, Couétil J-P, Coraboeuf E (1994) Depressed transient outward and calcium currents in dilated human atria. Cardiovasc Res 28:548–556
Li Q, Himmel HM, Ravens U (1995) Effects of the antiarrhythmic drug clofilium on the transient outward current in rat and human ventricular myocytes (abstract). Naunyn Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 351 (suppl):R105
Mansourati J, Le Grand B (1993) Transient outward current in young and adult diseased human atria. Am J Physiol 265: H1466-H1470
Näbauer M, Beuckelmann DJ (1992) Block of transient outward current by class Ic antiarrhythmic agents propafenone and flecainide in human ventricular myocytes (abstract). Circulation 86:1–697
Näbauer M, Beuckelmann DJ, Erdmann E (1993) Characteristics of transient outward current in human ventricular myocytes from patients with terminal heart failure. Circ Res 73:386–394
Ohler A, Ravens U (1994) Effects of E-4031, almokalant and tedisamil on postrest action potential duration of human papillary muscles. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 270:460–465
Pelzmann B, Schaffer P, Mächler H, Rigler B, Koidl B (1995) Adenosine inhibits the L-type calcium current in human atrial myocytes. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 351: 293–297
Schaffer P, Pelzmann B, Bernhart E, Lang P, Mächler H, Rigler B, Koidl B (1995) Effects of propafenone on outward currents in human atrial myocytes. In: Vereecke J, Bogaert PP van, Verdonck F (eds) Potassium channels in normal and pathological conditions. Leuven University Press, Leuven, pp 396–399
Shibata EF, Drury T, Refsum H, Aldrete V, Giles W (1989) Contributions of a transient outward current to repolarization in human atrium. Am J Physiol 257:H1773–1781
Slawsky MT, Castle NA (1994) K+ channel blocking actions of flecainide compared with those of propafenone and quinidine in adult rat ventricular myocytes. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 269:66–74
Takanaka C, Sarma JSM, Singh BN (1992) Electrophysiologic effects of ambasilide (LU 47110), a novel class III antiarrhythmic agent, on the properties of isolated rabbit and canine cardiac muscle. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 19:290–298
Tseng G-N, Hoffman BF (1989) Two components of transient outward current in canine ventricular myocytes. Circ Res 64: 633–647
Varró A, Nánási PP, Lathrop DA (1993) Potassium currents in isolated human atrial and ventricular cardiocytes. Acta Physiol Scand 149:133–142
Wang J, Feng J, Nattel S (1994) Class III antiarrhythmic drug action in experimental atrial fibrillation. Differences in reverse use dependence and effectiveness between d-sotalol and the new antiarrhythmic drug ambasilide. Circulation 90:2032–2040
Wang Z, Fermini B, Nattel S (1993a) Delayed rectifier outward current and repolarization in human atrial myocytes. Circ Res 73:276–285
Wang Z, Fermini B, Nattel S (1993b) Sustained depolarization-induced outward current in human atrial myocytes. Circ Res 73:1061–1076
Wang Z, Fermini B, Nattel S (1995) Effects of flecainide, quinidine, and 4-aminopyridine on transient outward and ultrarapid delayed rectifier currents in human atrial myocytes. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 272:184–196
Wettwer E, Amos G, Gath J, Zerkowski H-R, Reidemeister J-C, Ravens U (1993) Transient outward current in human and rat ventricular myocytes. Cardiovasc Res 27:1662–1669
Wettwer E, Amos GJ, Posival H, Ravens U (1994) Transient outward current in human ventricular myocytes of subepicardial and subendocardial origin. Circ Res 75:473–482
Zhang Z-H, Follmer CH, Sarma JSM, Chen F, Singh BN (1992) Effect of ambasilide, a new class III agent, on plateau currents in isolated guinea pig ventricular myocytes: block of delayed outward potassium current. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 263:40–48
Zhang Z-H, Boutjdir M, El-Sherif N (1994) Ketanserin inhibits depolarization-activated outward potassium current in rat ventricular myocytes. Circ Res 75:711–721
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Koidl, B., Flaschberger, P., Schaffer, P. et al. Effects of the class III antiarrhythmic drug ambasilide on outward currents in human atrial myocytes. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 353, 226–232 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00168761
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00168761