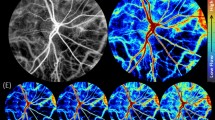
Abstract
• Background: Color Doppler imaging allows for simultaneous two-dimensional anatomical imaging and Doppler evaluation of blood flow velocity. • Methods: We examined 40 normal eyes (17 males and 23 females, aged 16 to 57 years) with this technique. The color Doppler unit used in this study had a 5.0-MHz PLF-503 ST phased-array scanning head. Each vessel examination was repeated 10 times during a single session. • Results: The following peak flow velocities were found: central retinal artery, 12.5±2.4 cm/s; central retinal vein, 4.4±0.49 cm/s; posterior ciliary arteries, 14.4±2.6 cm/s; vorticose veins, 5.5±1.0 cm/s; ophthamic artery, 36.9±7.0 cm/s. Ophthalmic artery systolic and end-diastolic velocities declined as a function of age; however, these changes were not significant (systolic: r=−0.24; diastolic, r=−0.22). • Conclusion: This noninvasive technique allows quantitative assessment of blood flow velocity in these vessels.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berger RW, Guthoff R, Helmke K, Winkler P, Draeger J (1989) Doppler sonographische Befunde der arteria and vena centralis retinae. Fortschr Ophthalmol 86:334–336
Bezzi M, Mitchell DG, Needleman L, Goldberg BB (1988) Iatrogenic aneurysmal protal-hepatic venous fistula. J Ultrasound Med 7:457–461
Duncan WJ (1988) Color Doppler in clinical cardiology. Saunders, Philadelphia, pp 1–5
Erickson SJ, Hendrix LE, Massaro BM, et al. (1989) Color Doppler flow imaging of the normal and abnormal orbit. Radiology 173:511–516
Erickson SJ, Mewissen MW, Foley WD, et al. (1989) Color Doppler evaluation of arterial stenoses and occlusions involving the neck and thoracic inlet. Radiographics 9.389–406
Feke GT, Tagawa H, Deupree DM, Goger DG, Sebag J, Weiter J (1989) Blood flow in the normal human retina. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 30:58–65
Flaharty PM, Lieb WE, Sergott RC, Bosley TM, Savino PJ (1991) Color Doppler imaging: a new noninvasive technique to diagnose and monitor carotid cavernous sinus fistulas. Arch Ophthalmol 109:522–526
Fleischer AC (1991) Ultrasound imaging 2000: assessment of uteroovarian blood flow with transvaginal color Doppler sonography. Potential clinical applications in infertility. Fertil Steril 55:684
Grant EG, Tessier FN, Perrella RR(1989) Clinical Doppler imaging. Am J Radiol 52:707–717
Guthoff RF, Berger RW, Winkler P, Helmke K, Chumbley LC (1991) Doppler ultrasonography of malignant melanomas of the uvea. 109: 537–541
Hayreh SS (1974) The choriocapillaries. Albrecht van Graefes Arch Klin Exp Ophthalmol 192:165–179
Hayreh SS (1974) Submacular choroidal vascular pattern. Experimental fluorescein fundus angiography studies. Albrecht von Graefes Arch Klin Exp Ophthalmol 192:181–196
Lieb WE, Cohen SM, Merton DA, et al. (1991) Color Doppler imaging of the eye and orbit: technique and normal vascular anatomy. Arch Ophthamol 109:527–531
Lizzi FL, Mortimer AJ (1988) Bioeffects considerations for the safety of diagnostic ultrasound. J Ultrasound Med 7 [Suppl]:1–38
Lizzi FL, Packer AJ, Coleman DJ (1978) Experimental cataract production by high frequency ultrasound. Ann Ophthalmol 10:934–942
Lizzi FL, Coleman DJ, Driller J, Fanzen LA, Leopold M (1981) Effects of pulsed ultrasound on ocular tissue. Ultrasound Med Biol 7:245–252
Merritt CR (1987) Doppler flow imaging. J Clin Ultrasound 15:591–597
Moddleton WD, Thorne DA, Melson GL (1989) Color Doppler ultrasound of the normal testis. Am J Roentgenol 152:293–297
Powis RL (1988) Color flow imaging: understanding its science and technology. J Diagn Med Sonogr 4:234–245
Rubin JM, Hatfield MK, Chandler WF, Black KL, DiPietro MA (1989) Intracerebral arteriovenous malformations: intraoperative color Doppler flow imaging. Radiology 170:219–222
Scoutt LM, Zawin ML, Taylor KJW (1990) Doppler ultrasound. II. Clinical applications. Radiology 174:309–319
Taylor KJW, Holland S (1990) Doppler ultrasound. I. Basic principles, instrumentation, and pitfalls. Radiology 174:297–307
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mendivil, A., Cuartero, V. & Mendivil, M.P. Color Doppler imaging of the ocular vessels. Graefe's Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 233, 135–139 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00166605
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00166605