Summary
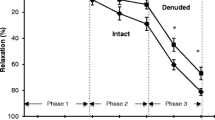
Tetrandrine is an alkaloid from a Chinese herb which has been used to treat hypertension in humans. The mechanism(s) of its antihypertensive action is not clear. The goal of this study was to examine the direct effects of a derivative of tetrandrine, 7-O-ethyl tetrandrine (TD), on vascular smooth muscle. In particular, the goals were to study (1) the involvement of the endothelium in the responses of isolated aortic rings to TD, and (2) the effects of TD at intracellular sites involved in muscle contraction in skinned aortic strips treated with saponin. TD (1–100 µmol/l) decreased noradrenaline (NA) and K+-evoked contraction of isolated aortic rings with or without endothelium in a concentration-dependent manner although to a lesser degree with the K+-evoked contraction. In NA-contracted rings, the IC50 for TD was approximately 28–30 µ mol/l, at which a 20% decrease in K+-force development of aortic rings was observed. The slope of the concentration-relaxation curve was steeper in aortic rings with endothelium than without endothelium (1.09 vs. 0.88) in NA-contracted rings. TD increased tone in acetylcholine (ACh)-relaxed rings but did not change the force in aortic rings relaxed by sodium nitroprusside (NaNP) or ATP. In TD pretreated rings, TD blocked ACh-induced relaxation, but not NaNP or ATP-induced relaxation. In skinned aortic strips, TD decreased Ca2+ uptake by the SR (IC50 ≈ 77.4 µmol/l slope = 0.88), did not affect Ca2+ release from the SR, and decreased Ca2+-activation of the contractile proteins at 300 µmol/l TD. The conclusions are that TD prevented endothelium-dependent ACh relaxation by blocking muscarinic receptors, and that the endothelium-independent relaxation is caused by blocking Ca2+ entry through the sarcolemma and by the decreased Ca2+ uptake by the SR.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Endo M, Iino M (1980) Specific perforation of muscle cell membranes with preserved SR functions by saponin treatment. J Muscle Res Cell Motil 1:89–100
Furchgott RF (1988) Endothelium-dependent relaxation in systemic arteries. In: Vanhoutte PM (ed) Relaxing and contracting factors, biological and clinical research. Humana Press, Clifton, NJ, pp 1–26
Furchgott RF, Zawadzki JV (1980a) The obligatory role of endothelial cells in the relaxation of arterial smooth muscle by acetylcholine. Nature 288:373–376
Furchgott RF, Zawadzki JV (1980b) ATP relaxes rabbit aortic smooth muscle by both an indirect action via endothelial cells and a direct action. Pharmacologist 22:271
Guardabasso V, Rodbard D, Munson PJ (1987) A model-free approach to estimation of relative potency in dose-response curve analysis. Am J Physiol 252:E351-E364
Hu WS, Pang XB, Wang Y, Hu CJ, Lu FH (1983) Mode of action of tetrandrine on vascular smooth muscle. J Tradit Chin Med 3:7–12
Kamm KE, Stull JT (1985) The function of myosin and myosin light chain kinase phosphorylation in smooth muscle. Ann Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 25:539–620
Kerrick WGL, Donaldson SKB (1972) The effects of Mg2+ on submaximum Ca2+-activated tension in skinned fibers of frog skeletal muscle. Biochim Biophys Acta 275:117–122
Kawashima K, Hayakawa T, Miwa Y, Oohata H, Suzuki T, Fujimoto K, Ogino T, Cehn Z (1990) Structure and hypotensive activity relationships of tetrandrine derivatives in stroke-prone spontaneously hypertensive rats. Gen Pharmacol 21:343–347
King VF, Garcia ML, Himmel D, Reuben JP, Lam YT, Pan J, Han G, Kaczorowski GJ (1988) Interaction of tetrandrine with slowly inactivating calcium channels — Characterization of calcium channel modulation by an alkaloid of Chinese medicinal herb origin. J Biol Chem 263:2238–2244
Martin W (1988) Basal release of endothelium-derived relaxing factor. In: Vanhoutte PM (ed) Relaxing and contracting factors, biological and clinical research. Humana Press, Clifton, NJ, pp 159–178
Snedecor GW, Cochran WG (1967) Statistical methods. Iowa University Press, Ames, Iowa, pp 59–62, 93–99
Su J, Zhang CC (1989) Intracellular mechanisms of halothane's effect on isolated aortic strips of the rabbit. Anesthesiology 71:409–417
Van Breemen C (1989) Cellular mechanisms regulating [Ca2+]i smooth muscle. Ann Rev Physiol 51:315–329
Vanhoutte PM (1988) Endothelium-dependent contractions in veins and arteries. In: Vanhoutte PM (ed) Relaxing and contracting factors, biological and clinical research. Humana Press, Clifton, NJ, pp 27–40
Waldmon SA, Murad F (1988) Biochemical mechanisms underlying vascular smooth muscle relaxation: the guanylate cyclase-cyclic GMP system. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 12:5115–5118
Winquist RJ, Bunting PB, Baskin BP, Wallace AA (1984) Decreased endothelium-dependent relaxation in New Zealand genetic hypertensive rats. J Hypertens 2:541–545
Zeng F, Shaw DH, Ogilvie RI (1985) Kinetic disposition and hemodynamic effects of tetrandrine in anesthetized dogs. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 7:1034–1039
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Correspondence to Judy Y. Su at the above address
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Su, J.Y. Mechanisms of action of 7-O-ethyl tetrandrine in isolated vascular smooth muscle of the rabbit aorta. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 347, 445–451 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00165397
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00165397