Summary
The effect of Hoe 140, a potent bradykinin B2 receptor antagonist, on the micturition reflex and detrusor hyperreflexia induced by chemical cystitis has been investigated in anaesthetized rats. Hoe 140 (1–100 nmol/kg i. v.) produced a dose-dependent blockade of the contraction of the rat urinary bladder induced by i. v. administration of bradykinin (100 nmol/kg) without affecting the response produced by the selective tachykinin NK-1 receptor agonist, [Sar9] substance P (SP) sulfone (1 nmol/kg i. v.). At doses which produce selective and long-lasting blockade of bradykinin receptors in the urinary bladder, Hoe 140 did not modify urodynamic parameters in normal rats.
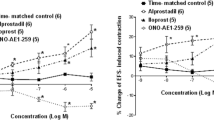
Intravesical instillation of xylene in female rats decreased bladder capacity and increased micturition frequency. These effects also occurred in rats pretreated with capsaicin as adults. Hoe 140 did not modify xylene-induced cystitis. Intraperitoneal administration of cyclophosphamide (150 mg/kg, 48 h before) decreased bladder capacity and increased micturition frequency. These effects of cyclophosphamide were abolished in rats pretreated with capsaicin as adults. Hoe 140 increased bladder capacity and decreased micturition frequency in rats pretreated with cyclophosphamide.
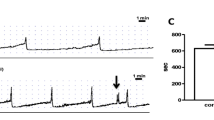
Addition of bradykinin (10 µmol/l) to the medium in the superfused rat urinary bladder preparation evoked a prompt increase in the outflow of calcitonin gene-related peptide like immunoreactivity (CGRP-LI). Hoe 140 (3 µmol/l) inhibited (by about 50%) the CGRP-LI outflow stimulated by bradykinin.
These findings demonstrate the participation of bradykinin, through 132 receptors, in the genesis of detrusor hyperreflexia during cyclophosphamide-induced cystitis. Capsaicin-sensitive primary afferent neurons are a likely target for Hoe 140 action in this model of experimental cystitis, as exemplified by its ability to prevent CGRP-LI outflow by bradykinin.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bathon JM, Proud D (1991) Bradykinin antagonists. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 31:129–162
Bhoola KD, Figueroa CD, Worthy K (1992) Bioregulation of kinins, kallikreins, kininogens and kininases. Pharmacol Rev 44:4–80
Cervero F, Sann H (1989) Mechanically evoked responses of afferent fibres innervating the guinea-pig's ureter: an in vitro study. J Physiol (Lond) 412:245–266
Dion S, D'Orleans-Juste P, Drapeau G, Rhaleb NE, Rouissi N, Tousignant C, Regoli D (1987) Characterization of neurokinin receptors in various isolated organs by the use of selective agonists. Life Sci 41:2269–2276
Field JL, Hall JM, Morton IKM (1992) Bradykinin receptors in the guinea-pig taenia caeci are similar to proposed BK 3 receptors in the guinea-pig trachea, and are blocked by Hoe 140. Br J Pharmacol 105:293–296
Foad BS, Hess EV (1976) Urinary bladder complications with cyclophosphamide therapy. Arch Intern Med 136:616–622
Griesbacher T, Lembeck F (1992) Analysis of the antagonistic actions of HOE 140 and other novel bradykinin analogues on the guinea-pig ileum. Eur J Pharmacol 211:393–398
Grinberg-Funes DJ, Sheldon C, Weiss M (1990) The use of prostaglandin F2 alpha for the prophylaxis of cyclophosphamide induced cystitis in rats. J Urol 144:1500–1504
Hock FJ, Wirth K, Albus U, Linz W, Gerhards HJ, Wiemer G, Henke St, Breipohl G, Konig W, Knolle J, Scholkens BA (1991) Hoe 140, a new potent and long acting bradykinin antagonist: in vitro studies. Br J Pharmacol 102:769–773
Lembeck F, Griesbacher T, Eckhardt M, Henke S, Breipohl G, Knolle J (1991) New, long-acting, potent bradykinin antagonists. Br J Pharmacol 102:297–304
Maggi CA (1991) The role of peptides in the regulation of the micturition reflex: an update. Gen Pharmacol 22:1–24
Maggi CA, Abelli L, Giuliani S, Santicioli P, Geppetti P, Somma V, Frilli S, Meli A (1988) The contribution of sensory nerves to xyleneinduced cystitis in rats. Neuroscience 26:709–723
Maggi CA, Lecci A, Santicioli P, Del Bianco E, Giuliani S (1992b) Cyclophosphamide-cystitis in rats: involvement of capsaicin-sensitive primary afferents. J Anton Nerv Syst 38:201–208
Maggi CA, Meli A (1988) The sensory and ‘efferent’ function of capsaicin-sensitive sensory neurons. Gen Pharmacol 19:1–43
Maggi CA, Patacchini R, Santicioli P, Geppetti P, Cecconi R, Giuliani S, Meli A (1989) Multiple mechanisms in the motor responses of the guinea-pig urinary bladder to bradykinin. Br J Pharmacol 98:619–629
Maggi CA, Santicioli P, Borsini F, Giuliani S, Meli A (1986) The role of capsaicin-sensitive innervation of the rat urinary bladder in the activation of micturition reflex. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 332:276–285
Maggi CA, Santicioli P, Del Bianco E, Giuliani S (1992a) Local motor responses to bradykinin and bacterial chemotactic peptide formylmethionyl-leucyl-phenylalanine (FMLP) in the guinea-pig isolated renal pelvis and ureter. J Urol 148:1944–1950
Manning DC, Snyder SH (1989) Bradykinin receptors localized by quantitative autoradiography in kidney, ureter and bladder. Am J Physiol 256:F909-F915
Marceau F, Barabe J, St Pierre S, Regoli D (1980) Kinin receptors in experimental inflammation. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 58:536–542
Marceau F, Lussier A, Regoli D, Giroud JP (1983) Pharmacology of kinins: their relevance to tissue injury and inflammation. Gen Pharmacol 14:209–229
Oza NB (1988) A new direct radioimmunoassay of rat urinary kininogen. Biochem Pharmacol 37:1965–1970
Phillips FS, Sternberg SS, Cronin AP, Vidal PN (1961) Cyclophosphamide and urinary bladder toxicity. Cancer Res 21:1577–1586
Pisano JJ, Yates K, Pierce JV (1978) Kininogen in human urine. Agents Actions 8:153–156
Regoli D, Barabe J (1980) Pharmacology of bradykinin and related kinins. Pharmacol Rev 32:1–46
Rhaleb NE, Rouissi N, Jukic D, Regoli D, Henke S, Breipohl G, Knolle J (1992) Pharmacological characterization of a new highly potent B2 receptor antagonist (Hoe 140: D-Arg[Hyp3, Thi5, DTic7, Oic8]bradykinin). Eur J Pharmacol 210:115–120
Santicioli P, Maggi CA, Geppetti P, Del Bianco E, Theodorsson E, Meli A (1988) Release of CGRP-like immunoreactivity from organs of the genitourinary tract in rats. Neurosci Lett 92:197–200
Saria A, Lundberg JM, Skofitsch G, Lembeck F (1983) Vascular protein leakage in various tissues induced by substance P, capsaicin, bradykinin, serotonin, histamine and by antigen challenge. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 324:212–218
Stillwell TJ, Benson RC Jr (1988) Cyclophosphamide induced hemorrhagic cystitis — a review of 100 patients. Cancer 61:451–457
Su HC, Wharton J, Polak JM, Mulderry PK, Ghatei MA, Gibson SJ, Terenghi G, Morrison JFB, Ballesta J, Bloom SR (1986) CGRP immunoreactivity in afferent neurons supplying the urinary tract: combined retrograde tracing and immunohistochemistry. Neuroscience 3:727–747
Watson NA, Notley RG (1973) Urological complications of cyclophosphamide. Br J Urol 45:606–611
Wirth K, Hock FJ, Albus U, Liinz W, Alpermann HG, Anagnostopoulos H, Henke St, Breipohl G, Konig W, Knolle J, Scholkens BA (1991) Hoe 140 a new potent and long acting bradykinin antagonist: in vivo studies. Br J Pharmacol 102:774–777
Yamasu A, Oh-ishi S, Hayashi I, Hayashi K, Hayashi M, Yamaki K, Nakano T, Sunahara N (1989) Differentiation of kinin fractions in ureter, urine and bladder urine of normal and kininogen deficient rats. J Pharmacobiodyn 12:287–292
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Correspondence to C. A. Maggi at the above address
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Maggi, C.A., Santicioli, P., Del Bianco, E. et al. Evidence for the involvement of bradykinin in chemically-evoked cystitis in anaesthetized rats. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 347, 432–437 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00165395
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00165395