Summary
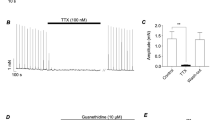
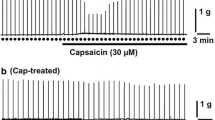
To find out whether, and which type of, adrenoceptors mediate prejunctional inhibition of sensory neurotransmitter release from trigeminal fibres, the modulation of twitch response to electrical field stimulation on rabbit isolated iris was investigated. Evoked iris sphincter contractions consisted of a minor fast cholinergic and a large slow component. The latter was unaffected by atropine and guanethidine, hence nonadrenergic noncholinergic in nature (NANC), but nearly completely abolished by capsaicin pretreatment and by the neurokinin receptor antagonist spantide. The response was probably not mediated by NK2 receptors as SR 48,968, an NK2 selective nonpeptide antagonist, failed to reduce the response to the release of the endogenous neurokinin(s) (and exogenous substance P), but in part due to NK1 receptor activation as shown by a reduction of response by CP 96,345, an NK1 selective non-peptide antagonist, and in part perhaps mediated by NK3 receptors. A small neurokinin receptor antagonist- and capsaicin-insensitive NANC contraction is probably not mediated by CGRP receptors.
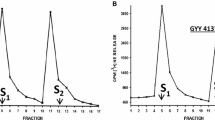
The α2-adrenoceptor agonist oxymetazoline inhibited the evoked NANC response (22 nmol/1, IC20; about 40%, maximum inhibition) without affecting the cholinergic response (up to 1 μmol/1) or the postjunctional iris sensitivity to exogenous substance P. The inhibition was antagonized by rauwolscine (apparent -log KB 8.04) and by the relatively α2B-adrenoceptor selective antagonist ARC-239 (-log KB 8.51).
The α2- and imidazoline receptor agonist aganodine inhibited the evoked NANC response (0.25 μmol/l, IC20; about 30%, maximum inhibition) without affecting the postjunctional substance P responses. Rauwolscine 0.3 μmol/l failed to antagonize this effect.
It is concluded that the release of sensory neurotransmitter(s) from trigeminal fibres in the rabbit eye may be inhibited by α2B-adrenoceptors and by a non-α2-receptor, perhaps an imidazoline receptor.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amann R, Lembeck F (1991) Capsaicin-induced desensitization in rat and rabbit. Ann NY Acad Sci 632:363–365
Beding-Barnekow B, Brodin E, Håkanson R (1988) Substance P, neurokinin A and neurokinin B in the ocular response to injury in the rabbit. Br J Pharmacol 95:259–267
Beresford IJM, Birch PJ, Hangan RM, Ireland SJ (1991) Investigation into species variants in tachykinin NK1 receptors by use of the nonpeptide antagonist, CP-96,345. Br J Pharmacol 104:292–293
Bognar IT, Baretti R, Fischer S, Veldet C, Fuder H (1990) Alpha-adrenoceptor mediated facilitation of acetylcholine release in the rat perfused heart. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 254:702–710
Butler JM, Powell D, Unger WG (1980) Substance P levels in normal and sensorily denervated rabbit eyes. Exp Eye Res 30:311–313
Bylund DB, Ray-Prenger C (1989) Alpha-2A and alpha-2B adrenergic receptor subtypes: attenuation of cyclic AMP production in cell lines containing only one receptor subtype. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 251:640–644
Bylund DB, Ray-Prenger C, Murphy TJ (1988) Alpha-2A and alpha-2B adrenergic receptor subtypes: antagonist binding in tissues and cell lines containing only one subtype. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 245:600–607
Bylund DB, Blaxall HS, Iversen LJ, Caron MG, Lefkowitz RJ, Lomasney JW (1992) Pharmacological characteristics of α2-adrenergic receptors: comparison of pharmacologically defined subtypes with subtypes identified by molecular cloning. Mol Pharmacol 42:1–5
Bynke G, Wahlestedt C, Beding B, Håkanson R (1985) Pupillary supersensitivity to substance P following prolonged treatment with tetrodotoxin or substance P antagonists. Eur J Pharmacol 108:217–223
Chiba T, Yamaguchi A, Yamatani T, Nakamura A, Morishita T, Inui T, Fukase M, Noda T, Fujita T (1989) Calcitonin gene-related peptide receptor antagonist human CGRP-(8–37). Am J Physiol 256:E331-E335
Emonds-Alt X, Vilain P, Goulaouic P, Proietto V, Van Broeck D, Advenier C, Naline E, Neliat G, Le Fur G, Brelière JC (1992) A potent and selective non-peptide antagonist of the neurokinin A (NK2) receptor. Life Sci 50:PL101-PL106
Folkers K, Håkanson R, Hörig J, Jie-Cheng X, Leander S (1984) Biological evaluation of substance P antagonists. Br J Pharmacol 83:449–456
Fuder H, Braun H-J, Schimkus R (1986) Presynaptic alpha-2 adrenoceptor activation and coupling of the receptor-presynaptic effector system in the perfused rat heart: affinity and efficacy of phenethylamines and imidazoline derivatives. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 237:237–245
Geppetti P, Patacchini R, Cecconi R, Tramontana M, Meini S, Romani A, Nardi M, Maggi CA (1990) Effects of capsaicin, tachykinins, calcitonin gene-related peptide and bradykinin in the pig iris sphincter muscle. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 341:301–307
Gleason MM, Hieble JP (1992) The α2-adrenoceptors of the human retinoblastoma cell line (Y79) may represent an additional example of the α2c-adrenoceptor. Br J Pharmacol 107:222–225
Göthert M, Molderings GJ (1991) Involvement of presynaptic imidazoline receptors in the α2-adrenoceptor-independent inhibition of noradrenaline release by imidazoline derivatives. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 343:271–282
Grundström N, Anderson RGG (1985) In vivo demonstration of alpha-2-adrenoceptor-mediated inhibition of the excitatory non-cholinergic neurotransmission in guinea pig airways. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 328:236–240
Gustafsson LE, Wiklund NP (1986) Adenosine-modulation of cholinergic and non-adrenergic non-cholinergic neurotransmission in the rabbit iris sphincter. Br J Pharmacol 88:197–204
Håkanson R, Beding B, Ljungqvist A, Chi J-Y, Leander S, Trojnar J, Folkers K (1988) Blockade of sensory nerve mediated contraction of the rabbit iris sphincter by a series of novel tachykinin antagonists. Reg Peptid 20:99–105
Hall JM, Mitchell D, Morton IKM (1991) Neurokinin receptors in the rabbit iris sphincter characterised by novel agonist ligands. Eur J Pharmacol 199:9–14
Hisayama T, Shinkai M, Takayanagi I, Morimoto S-I, Ishida K (1988) Mechanism of action of nicotine in isolated iris sphincter preparation of rabbit. Br J Pharmacol 95:459–464
Holzer P (1988) Local effector functions of capsaicin-sensitive sensory nerve endings: involvement of tachykinins, calcitonin gene-related peptide and other neuropeptides. Neuroscience 24:739–768
Holzer P (1991) Capsaicin: cellular targets, mechanisms of action, and selectivity for thin sensory neurons. Pharmacol Rev 43:143–201
Hosoki R, Hisayama T, Takayanagi I (1987) Pharmacological evidence for the possible coexistence of multiple receptor sites for mammalian tachykinins in rabbit iris sphincter smooth muscle. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 335:290–295
Krootila K, Oksala O, Zschauer A, Palkama A, Uusitalo H (1992) Inhibitory effect of methysergide on calcitonin gene-related peptide-induced vasodilatation and ocular irritative changes in the rabbit. Br J Pharmacol 106:404–408
Leander S, Håkanson R, Rosell S, Folkers K, Sunder F, Tornqvist K (1981) A specific substance P antagonist blocks smooth muscle contractions induced by non-cholinergic, non-adrenergic nerve stimulation. Nature (London) 294:467–469
Legat FJ, Griesbacher T, Lembeck F (1992) CP-96,345, a non-peptide antagonist of substance P: I. Effects on the actions mediated by substance P and related tachykinins on the guinea-pig ileum and rabbit jejunum. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 346:315–322
Limberger N, Mayer A, Zier G, Valenta B, Starke K, Singer EA (1989) Estimation of pA2 values at presynaptic α2-autoreceptors in rabbit and rat brain cortex in the absence of autoinhibition. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 340:639–647
Limberger N, Spath L, Starke K (1991) Subclassification of the presynaptic α2-autoreceptors in rabbit brain cortex. Br J Pharmacol 103:1251–1255
Limberger N, Trendelenburg A-U, Starke K (1992) Pharmacological characterization of presynaptic α2-autoreceptors in rat submaxillary gland and heart atrium. Br J Pharmacol 107:246–255
Lomasney JW, Cotecchia S, Lefkowitz RJ, Caron MG (1991) Molecular biology of α-adrenergic receptors: implications for receptor classification and for structure-function relationships. Biochim Biophys Acta 1095:127–139
Maggi CA (1991) The pharmacology of the efferent function of sensory nerves. J Anton Pharmacol 11:173–208
Matran R, Martling C-R, Lundberg JM (1989) Inhibition of cholinergic and non-adrenergic, non-cholinergic bronchoconstriction in the guinea pig mediated by neuropeptide Y and α2-adrenoceptors and opiate receptors. Eur J Pharmacol 163:15–23
Mimeault M, Quirion R, Dumont Y, St-Pierre S, Fournier A (1992) Structure-activity study of hCGRP8–37, a calcitonin gene-related peptide receptor antagonist. J Med Chem 35:2163–2168
Molderings GJ, Hentrich F, Gothert M (1991) Pharmacological characterization of the imidazoline receptor which mediates inhibition of noradrenaline release in the rabbit pulmonary artery. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 344:630–638
Oksala O, Stjernschantz J (1988) Effects of calcitonin gene-related peptide in the eye. Inv Ophthalmol Vis Sci 29:1006–1011
Rechtman MP, Boura ALA, King RG, Olley JE, Schiller PW (1990) Effects of morphine, H Tyr-D-Arg-Phe-Lys-NH2 (DALDA) and BHT920 on non-cholinergic nerve-mediated bronchoconstriction in pithed guinea-pigs. Br J Pharmacol 101:269–272
Regoli D, Drapeau G, Dion S, Couture R (1988) New selective agonists for neurokinin receptors: pharmacological tools for receptor characterization. Trends Pharmacol Sci 9:290–295
Schwartz DD, Malik KU (1992) Characterization of prejunctional alpha-2 adrenergic receptors involved in modulation of adrenergic transmitter release in the isolated perfused rat kidney. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 261:1050–1055
Snider RM, Constantine JW, Lowe JA, Longo KP, Lebel WS, Woody HA, Drozda SE, Desai MC, Vinick FJ, Spencer RW, Hess H-J (1991) A potent nonpeptide antagonist of the substance P (NK1) receptor. Science 251:435–437
Stjernschantz J (1984) Autacoids and neuropeptides. In: Sears ML (ed) Pharmacology of the eye. Handbook of Exp Pharmacol vol 69. Springer, Heidelberg New York Tokyo pp 311–365
Ueda N, Muramatsu I, Hayashi H, Fujiwara M (1982) Trigeminal nerve: the possible origin of substance P-ergic response in isolated rabbit iris sphincter muscle. Life Sci 31:369–375
Ueda N, Muramatsu I, Fujiwara M (1984) Capsaicin and bradykinin-induced substance P-ergic responses in the iris sphincter muscle of the rabbit. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 230:469–473
Ueda N, Muramatsu I, Fujiwara M (1985) Dual effects of dynorphin-(1–13) on cholinergic and substance P-ergic transmissions in the rabbit iris sphincter muscle. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 232:545–550
Uhlén S, Xia Y, Chhajlani V, Felder CC, Wikberg JES (1992) [3H]-MK 912 binding delineates two α2-adrenoceptor subtypes in rat CNS one of which is identical with the cloned pA2d α2-adrenoceptor. Br J Pharmacol 106:986–995
Van Rossum JM (1963) Cumulative dose-responses curves. II. Technique for the making of dose-response curves in isolated organs and the evaluation of drug parameters. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Thér 143:299–330
Vaught JL (1988) Substance P antagonists and analgesia: a review of the hypothesis. Life Sci 43:1419–1431
Wang ZY, Håkanson R (1992) Effect of resiniferatoxin on the isolated rabbit iris sphincter muscle: comparison with capsaicin and bradykinin. Eur J Pharmacol 213:235–241
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This study was supported by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (Fu 163/3)
Correspondence to H. Fuder at the above address
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fuder, H., Selbach, M. Characterization of sensory neurotransmission and its inhibition via α2B-adrenoceptors and via non-α2-receptors in rabbit iris. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 347, 394–401 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00165389
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00165389