Abstract
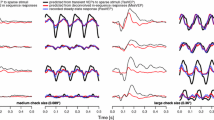
Further experiments in healthy subjects have confirmed the characteristic but variable differential effect of experimental scotomata on the pattern evoked potentials. While the waveform changes associated with different pathological scotomata also showed considerable variability, certain features common to healthy and abnormal responses could be identified. These non-specific effects of scotomata on component amplitudes and distributions frequently result in spurious delays of wide-field responses and thus have important implications for the pathophysiological interpretation of abnormal responses.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barrett G, Blumhardt LD, Halliday AM, Halliday E and Kriss A: A paradox in the lateralisation of the visual evoked response. Nature 261:252–255 1976.
Blumhardt LD: Topography of Normal and Abnormal Pattern Evoked Potentials in Man. M.D. Thesis, Otago University, 1980. University Microfilms International, Ann Arbor, Michigan. 1982.
Blumhardt LD: Do evoked potentials contribute to the early diagnosis of multiple sclerosis? In Garfield J and Warlow C (eds.). Dilemmas in the Management of the Neurological Patient, pp 18–42. Churchill-Livingstone, Edinburgh, 1984.
Blumhardt LD, Barrett G and Halliday AM: The asymmetrical visual evoked potential to pattern reversal in one half-field and its significance for the analysis of visual field defects. Br J Ophthalmol 61:454–461 1979.
Blumhardt LD, Barrett G, Halliday AM and Kriss A: The contralateral negativity of the half-field response and its association with central scotomata. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 43:286 1976.
Blumhardt LD, Barrett G, Halliday AM and Kriss A: The effect of experimental ‘scotomata’ on the ipsilateral and contralateral responses to pattern-reversal in one half-field. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 45:376–392 1978.
Blumhardt LD, Barrett G, Kriss A and Halliday AM: The pattern evoked potential in lesions of the posterior visual pathways. In Bodis-Wollner I (ed.). Evoked Potentials. Ann NY Acad Sci 388:264–289 1982.
Blumhardt LD and Halliday AM: Hemisphere contributions to the composition of the pattern-evoked potential waveform. Exp Brain Res 36:53–69 1979.
Cappin JM and Nissim S: Pattern visual evoked responses in the detection of field defects in glaucoma. Arch Ophthalmol 93:9–18 1975.
Carroll WM, Halliday AM and Kriss A: Improvements in the accuracy of pattern visual evoked potentials in the diagnosis of visual pathway disease. J Neuroophthalmol 2:237–253 1982.
Dorfman LJ, Nikoskelainan E, Rosenthal AR and Sogg RL: Visual evoked potentials in Leber's hereditary optic neuropathy. Ann Neurol 1:565–568 1977.
Ellenburger C and Siegler S: Visual evoked potentials and quantitative perimetry in multiple sclerosis. Ann Neurol 1:561–564 1978.
Halliday AM, Barrett G, Blumhardt LD and Kriss A: The macular and paramacular subcomponents of the pattern evoked response. In Lehman D and Callaway E (eds.). Human Evoked Potentials, pp 135–151. Plenum, New York, 1979.
Halliday AM: The visual evoked potential in the investigation of diseases of the optic nerve. In Halliday AM (ed.). Evoked Potentials in Clinical Testing, pp 187–234. Churchill Livingstone, London, 1982.
Harding GFA, Crews SJ and Good PA: VEP in neuro-ophthalmic disease. In Barber C (ed.). Evoked Potentials, pp 235–242. MTP Press, Lancaster 1980.
Kriss A, Carroll WM, Blumhardt LD and Halliday AM: Pattern and flash-evoked potential changes in toxic (nutritional) optic neuropathy. In Courjon J, Manguiere F and Revol M (eds.). Clinical Applications of Evoked Potentials in Neurology, pp 11–20. Raven Press, New York, 1982.
Matthews WB and Small DG: Serial recording of visual and somatosensory evoked potentials in multiple sclerosis. J Neurol Sci 40:11–21 1979.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Blumhardt, L.D. Variable effects of pathologic scotomata on wave form of pattern-reversal visual evoked response. Doc Ophthalmol 59, 107–119 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00160607
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00160607