Summary
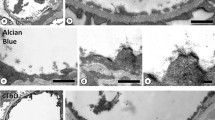
Glomerular capillary wall anionic sites have been demonstrated by cationic gold staining of archived renal biopsy tissue (up to 10 years old), obtained from six patients, originally embedded in paraffin wax, and subsequently reprocessed into LR gold resin. The staining patterns at pH 2.5 and pH 7.0, demonstrating different glomerular basement membrane (GBM) anionic constituents, were compared in three patients from whom tissue directly processed into LR gold and reprocessed tissue was available. Ultrastructural preservation was poorer and shrinkage artefact greater in paraformaldehyde-lysine periodate (PLP) as opposed to formol saline-fixed reprocessed tissue. However, GBM anionic site expression was well preserved, or even enhanced (lamina rara externa, pH 7.0) in reprocessed tissue, using either fixative. Although it may not be possible to compare subtle changes in anionic site distribution in variously fixed and processed tissues, due to these artefacts, the technique enables retrospective study of charge status in archived material from disease groups in which there are distinct anionic site aberrations.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barnes, J. L., Radnik, R. A., Gilchrist, E. P. & Venkatachalam, M. A. (1984) Size and charge selectivity defects induced in glomerular basement membrane by a polycation. Kidney Int. 25, 11–19.
Bendayan, M., Benhamou, N. & Desjardins, M. (1990) Ultrastructural distribution of lectin-binding sites in the glomerular wall of streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. J. Submicrosc. Cytol. Pathol. 22, 173–84.
Bertolatus, J. A. & Hunsicker, L. G. (1987) Polycation binding to glomerular basement membrane: effect of biochemical modification. Lab. Invest. 56, 170–9.
Brenner, B. M., Hostetter, T. H. & Humes, H. D. (1978) Molecular basis of proteinuria of glomerular origin. New Eng. J. Med. 15, 826–33.
Chen, K. & Wight, T. N. (1984) Proteoglycans in arterial smooth muscle cell cultures: an ultrastructural histochemical analysis. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 32, 347–57.
Fox, C. H., Johnson, F. B., Whiting, J. & Roller, P. P. (1985) Formaldehyde fixation. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 33, 845–53.
Goode, N. P., Shires, M., Crellin, D. M. & Davison, A. M. (1991a) Detection of glomerular anionic sites in post-embedded ultrathin sections using cationic colloidal gold. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 39, 965–72.
Goode, N. P., Shires, M., Aparicio, S. R. & Davison, A. M. (1991b) Cationic colloidal gold - a novel marker for the demonstration of glomerular polyanion status in routine renal biopsies. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 6, 923–30.
Goode, N. P., Shires, M., Dyson, E. H. & Davison, A. M. (1991c) Glomerular charge detection in rat and human using cationic colloidal gold. J. Pathol. 163, 166A.
Goode, N. P., Shires, M. & Davison, A. M. (1992) Preparation and use of the poly-l-lysine-gold probe: a differential marker of glomerular anionic sites. Histochemistry 98, 67–72.
Hunsicker, L. G., Shearer, T. P. & Shaffer, S. J. (1981) Acute reversible proteinuria induced by infusion of the polycation hexadimethrine. Kidney Int. 20, 7–17.
Kanwar, Y. S., Linker, A. & Farquhar, M. G. (1980) Increased permeability of the glomerular basement membrane to ferritin after removal of glycosaminoglycans (heparan sulphate) by enzyme digestion. J. Cell Biol. 86, 688–93.
Lelongt, B., Marino, H. & Kanwar, Y. S. (1987) Status of glomerula proteoglycans in aminonucleoside nephrosis. Kidney Int. 31, 1299–310.
Londono, I. & Bendayan, M. (1988) High-resolution cytochemistry of neuraminic and hexuronic acid-containing macromolecules applying the enzyme-gold approach. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 36, 1005–14.
Londono, L., Coulombe, P. A. & Bendayan, M. (1989) Brief review of progresses in enzyme gold cytochemistry. Scan. Microsc. (suppl) 3, 7–14.
Mcclean, I. W. & Nakane, P. K. (1974) Periodate-lysineparaformaldehyde fixative: a new fixative for immunoelectron microscopy. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 22, 1077–83.
Moss, J., Woodrow, D. F., Shore, I., Gower, P., Philips, M. & Spiro, R. G. (1990) Ultrastructural immunogold studies of heparan sulphate proteoglycan in normal human glomeruli and glomerulonephritis. J. Pathol. 161, 137–43.
Pilia, P. A., Swain, R. P., Williams, A. V., Loadholt, C. B. & Ainsworth, S. K. (1985) Glomerular anionic site distribution in nonproteinuric rats: a computer assisted morphometric analysis. Am. J. Pathol. 121, 474–85.
Rosenzweig, L. J. & Kanwar, Y. S. (1982) Removal of sulfated (heparan sulphate) or nonsulfated (hyaluronic acid) glycosaminoglycans results in increased permeability of the glomerular basement membrane to 125I-bovine albumin. Lab. Invest. 47, 177–84.
Shires, M., Goode, N. P., Crellin, D. M. & Davison, A. M. (1990) Immunogold-silver staining of mesangial antigen in Lowicryl K4M- and LR gold-embedded renal tissue using epipolarization microscopy. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 38, 287–9.
Spicer, S. S. & Schulte, B. A. (1992) Diversity of cell glycoconjugates, shown histochemically: a perspective (review). J. Histochem. Cytochem. 40, 1–38.
Vehaskari, M., Root, E. R., Germuth, F. G. & Robson, A. M. (1982) Glomerular charge and urinary protein excretion: effects of systemic and intrarenal polycation infusion in the rat. Kidney Int. 22, 127–35.
Vorbrodt, A. W. (1989) Ultracytochemical characterization of anionic sites in the wall of brain capillaries. J. Neurocytol. 18, 359–68.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Goode, N.P., Shires, M., Aparicio, S.R. et al. Cationic gold staining of glomerular anionic sites in archived tissue, reprocessed from paraffin wax into LR gold resin. Histochem J 25, 401–405 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00159505
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00159505