Abstract
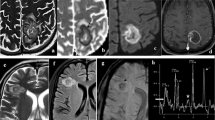
A 76-year-old male with chief complaints of back and right leg sciatica was hospitalized. His abdominal CT scan revealed lumber spondylitic stenosis. A laminectomy was performed. Postoperatively, he became febrile, aphasic and had grand mal seizure. A left craniotomy of the front abscess, seen in the CT scan, was performed. H and E stained smears of drainage revealed dematiaceous, septate hyphae. Cultures of the abscess drainage grew an olivaceous-grey fungus. Based on macro- and micro-morphological characters, growth at 42° C, and exoantigenic analysis, the patient's fungus was identified as Xylohypha bantiana. Treatment with amphotericin B and 5-fluorocytosine was initiated. Despite surgical procedures and antifungal therapy, the patient's condition deteriorated and he died a few weeks later due to cerebral edema. The case reported here is the first microscopically, culturally, histopathologically and exoantigenically proven case of phaeohyphomycosis caused by X. bantiana in the province of Alberta and from Canada. A review of the literature on cases of X. bantiana infections has also been presented.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
AjelloL. (1969): A comparative study of pulmonary mycoses of Canada and the United States - Public Health Reports (Wash., D.C.) 84:869–877.
BobraS.T. (1958): Mycotic abcess of the brain probably due to Cladosporium trichoides: Report of the fifth case - Can. J. Med. Assoc. 79: 657–659.
DixonD.M., MerzW.G., ElliottH.L. and MacleayS. (1987): Experimental central nervous system phaeohyphomycosis following intranasal inoculation of Xylohypha bantiana in cortisone-treated mice -Mycopathologia100: 145–153.
DixonD.M., WalshT.J., MerzW.G. and McGinnisM.R. (1989): Infections due to Xylohypha bantiana (Cladosporium trichoides) - Rev. Infect. Dis. 11: 515–525.
HonboS., StandardP.G., PadhyeA.A., AjelloL. and KaufmanL. (1984): Antigenic relationships among Cladosporium species of medical importance - J. Med. Vet. Mycol. 22: 301–310.
HornL.H., WilanskyD.L. and HarlandW.A. (1960): Neurogenic hypernatremia with mycotic brain granulomas due to Cladosporium trichoides - Can. J. Med. Assoc. 83: 1314–1317.
McGinnisM.R. and BorelliD. (1981): Cladosporium bantiana and its synonym Cladosporium trichoides -Mycotaxon 13: 127–136.
McGinnisM.R., BorelliD., PadhyeA.A. and AjelloL. (1986): Reclassification of Cladosporium bantianum to the genus Xylohypha - J. Clin. Microbiol. 23:1148–1151.
SekhonA.S., BannerjeeS.N., MielkeB.W., IdikioH., WoodG. and DixonJ.M.S. (1990): Current status of cryptococcosis in Canada - Mycoses 33: 73–80.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sekhon, A.S., Galbraith, J., Mielke, B.W. et al. Cerebral phaeohyphomycosis caused by Xylohypha bantiana, with a review of the literature. Eur J Epidemiol 8, 387–390 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00158573
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00158573