Abstract
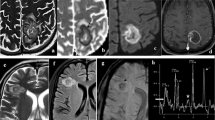
A case of phaeohyphomycosis caused by Bipolaris spicifera involving the brain and sinuses is presented. The patient survived following surgery and ketoconazole therapy, which successfully treated both the sinus and the brain infections.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
AdamR.D., PaquinM.L., PetersenE.A., SaubolleM.A., RinaldiM.G., CorcoranJ.G., GalgianiJ.N. and SobonyaR.E. (1986): Phaeohyphomycosis caused by the fungal genera Bipolaris and Exserohilum. A report of 9 cases and review of the literature - Medicine 65: 203–217.
AjelloL., GeorgL.K., SteigbigelR.T. and WangC.J.K. (1974): A case of phaeohyphomycosis caused by a new species of Phialophora - Mycologia 66: 490–498.
BiggsP.J., AllenR.L., PowersJ.M. and HolleyH.P. (1986): Phaeohyphomycosis complicating compound skull fracture - Surg. Neurol. 25: 393–396.
ChandlerF.W. and WattsJ.C. (1987): Pathologic Diagnosis of Fungal Infections - American Society of Clinical Pathology Press - Chicago.
FaderR.C. and McGinnisM.R. (1988): Infections caused by dematiaceous fungi: Chromoblastomycosis and phaeohyphomycosis - Clin. Infect. Dis. 2: 925–938.
FusteF.J., AjelloL., ThrelkeldR. and HenryJ.E.J. (1973): Drechslera hawaiiensis: Causative agent of a fatal fungal meningo-encephalitis - Sabouraudia 11: 59–63.
GourleyD.S., WhismanB.A., JorgensenN.L., MartinM.E. and ReidM.J. (1990): Allergic Bipolaris sinusitis: Clinical and immunopathologic characteristics - J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 85: 583–591.
McGinnisM.R. (1983): Chromoblastomycosis and phaeohyphomycosis: New concepts, diagnosis, and mycology - J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 8: 1–16.
McGinnisM.R. and FaderR.C. (1988): Mycetoma: A contemporary concept - Clin. Infect. Dis. 2: 939–954.
McGinnisM.R., RinaldiM.G. and WinnR. (1986): Emerging agents of phaeohyphomycosis: Pathogenic species of Bipolaris and Exserohilum - J. Clin. Microbiol. 24: 250–259.
MilroyC.M., BlanshardJ.D., LucasS. and MichaelsL. (1989): Aspergillosis of the nose and paranasal sinuses - J. Clin. Pathol. 42: 123–127.
MortonS.J., MidthunK. and MerzW. (1986): Granulomatous encephalitis caused by Bipolaris hawaiiensis - Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 110: 1183–1185.
MorganM.A., WilsonW.R., NeelH.B. and RobertsG.D. (1984): Fungal sinusitis in healthy and immunocompromised individuals - Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 82: 597–601.
VeressB., MalikO.A., ElTayebA.A., ElDaoudS., MahgoubE.S. and ElHassenA.M. (1973): Further observations on the primary paranasal Aspergillus granuloma in the Sudan - Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 22: 765–772.
WaxmanJ.E., SpectorJ.G., SaleS.R. and KatzensteinA.L. (1987): Allergic Aspergillus sinusitis: Concepts in diagnosis and treatment of a new clinical entity -Laryngoscope 97: 261–266.
YoshimoriR.N., ItabashiH.H. and FujikawaD.G. (1982): Phaeohyphomycosis of brain. Granulomatous encephalitis caused by Drechslera spicifera - Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 77: 363–370.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
McGinnis, M.R., Campbell, G., Gourley, W.K. et al. Phaeohyphomycosis caused by Bipolaris spicifera: An informative case. Eur J Epidemiol 8, 383–386 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00158572
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00158572