Summary
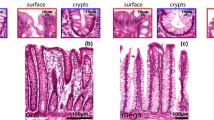
The application of an antibody against tumour necrosis factor-alpha (TNF) to thin sections of plastic-embedded mouse tissue has identified sites of TNF activity in normal and endotoxin-treated C3N/HeN mice. Prior to endotoxin treatment, TNF was observed in the secretory granules of the antibacterial Paneth cell and one type of crypt endocrine cell. Four hours after endotoxin treatment, these two types of intestinal cell were found to have degranulated. In addition, endotoxin treatment resulted in the appearance of TNF in the secretory granules of all eosinophils, neutrophils and monocytes in the bone marrow, spleen, lung and the proximal intestine. TNF was also observed in the internal elastic lamina (IEL) of arterioles. These results suggest that the process of TNF induction specifically targets the immune system and the vasculature. An invasive stimulus, such as circulating endotoxin, can provoke the immune cells to be armed with TNF. That same stimulus may cause arteriole smooth muscle cells to secrete TNF. TNF secretion in the presence of arteriole smooth muscle cells may play a role in the adjustment of arteriole tone. In the venules, TNF may be responsible for platelet and neutrophil accumulation which leads to embolism formation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beutler, B. & Cerami, A. (1986) Cachectin and tumor necrosis factor as two sides of the same biological coin. Nature 320, 584–8.
Chensue, S. W., Terebuh, P. D., Remick, D. G., Scales, W. E. & Kunkel, S. L. (1991) In vivo biologic and immunohistochemical analysis of interleukin-1 alpha, beta and tumor necrosis factor during experimental endotoxemia. Kinetics, Kupffer cell expression, and glucocorticoid effects. Am. J. Pathol. 138, 395–402.
Djeu, J. Y., Serbousek, D. & Blanchard, D. K. (1990) Release of tumor necrosis factor by human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Blood 76, 1405–9.
Dubravec, D. B., Spriggs, D. R., Mannick, J. A. & Rodrick, M. L. (1990) Circulating human peripheral blood granulocytes synthesize and secrete tumor necrosis factor α. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 87, 6758–61.
Hauptman, S. P. & Tomasi, T. B. (1976) The secretory immune system. In Basic and Clinical Immunology (edited by Fudenberg, H. H., Stites, D. P., Caldwell, D. P. & Wells, J. V.) pp. 170–81. Los Altos, CA: Lange Medical Publications.
Havell, E. A. (1989) Evidence that tumor necrosis factor has an important role in antibacterial resistance. J. Immunol. 143, 2894–9.
Hinshaw, L. B., Tekamp-Olson, P., Chang, A. C. K., Lee, P. A., Taylor, F. B. JR, Murray, C. K., Peer, G. T., Emerson, T. E., Passey, R. B. & Kuo, G. C. (1990) Survival of primates in LD100 septic shock following therapy with antibody to tumor necrosis factor (TNFα). Circulatory Shock 30, 279–92.
Kettelhut, I. C., Fiers, W. & Goldberg, A. L. (1987) The toxic effects of tumor necrosis factor in vivo and their prevention by cyclooxygenase inhibitors. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 84, 4273–7.
Luedke, E. S. & Humes, J. L. (1989) Effect of tumor necrosis factor on granule release and LTB4 production in adherent human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Agents Actions 27, 451–4.
Messina, E. J., Weiner, R. & Kaley, G. (1976) Prostaglandins and local circulatory control. Fed. Proc. 35, 2367–75.
Mozes, T., Zijlstra, F. J., Heiligers, J. P. C., Tak, C. J. A. M., Ben-Efraim, S., Bonta, I. L. & Saxena, P. R. (1991) Sequential release of tumor necrosis factor, platelet activating factor and eicosanoids during endotoxin shock in anaesthetized pigs; protective effects of indomethacin. Br. J. Pharmacol. 104, 691–9.
Natanson, C., Danner, R. L., Elin, R. J., Hosseini, J. M., Peart, K. W., Banks, S. M., Macvittie, T. J., Walker, R. I. & Parrillo, J. E. (1989) Role of endotoxemia in cardiovascular dysfunction and mortality. Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus challenges in a canine model of human septic shock. J. Clin. Invest. 83, 243–51.
Rodning, C. B., Wilson, I. D. & Erlandsen, S. L. (1976) Immunoglobulins within human small-intestinal Paneth cells. Lancet 1, 984–7.
Rothstein, J. L. & Schreiber, H. (1988) Synergy between tumor necrosis factor and bacterial products causes hemorrhagic necrosis and lethal shock in normal mice. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 85, 607–11.
Schmauder-Chock, E. A. & Chock, S. P. (1989) Localization of cyclo-oxygenase and prostaglandin E2 in the secretory granule of the mast cell. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 37, 1319–28.
Schmauder-Chock, E. A. & Chock, S. P. (1992) Protaglandin E2 localization in the rat ileum. Histochem. J. 24, 663–72.
Sisson, J. H., Prescott, S. M., Mcintyre, T. M. & Zimmerman, G. A. (1987) Production of platelet-activating factor by stimulated human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. J. Immunol. 138, 3918–26.
Tracey, K. J., Beutler, B., Lowry, S. F., Merryweather, J., Wolpe, S., Milsark, I. W., Hariri, R. J., Fahey, T. J. III, Zentella, A., Albert, J. D., Shires, G. T. & Cerami, A. (1986) Shock and tissue injury induced by recombinant human cachectin. Science 234, 470–4.
Varani, J., Bendelow, M. J., Sealey, D. E., Kunkel, S. L., Gannon, D. E., Ryan, U. S. & Ward, P. A. (1988) Tumor necrosis factor enhances susceptibility of vascular endothelial cells to neutrophil-mediated killing. Lab. Invest. 59, 292–5.
Wakabayashi, G., Gelfand, J. A., Jung, W. K., Connolly, R. J., Burke, J. F. & Dinarello, C. A. (1991) Staphylococcus epidermidis induces complement activation, tumor necrosis factor and interleukin-1, a shock-like state and tissue injury in rabbits without endotoxemia. Comparison to Escherichia coli. J. Clin. Invest. 87, 1925–35.
Warren, J. S., Barton, P. A., Mandel, D. M. & Matrosic, K. (1990) Intrapulmonary tumor necrosis factor triggers local platelet-activating factor production in rat immune complex alveolitis. Lab. Invest. 63, 746–54.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schmauder-Chock, E.A., Chock, S.P. & Patchen, M.L. Ulstrastructural localization of tumour necrosis factor-alpha. Histochem J 26, 142–151 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00157963
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00157963