Summary
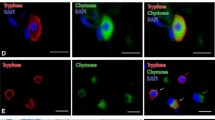
During investigations of murine and human mast cell immunoreactivity with potential anti-interleukin-4 antibodies, non-specific, non-immunological labelling of mouse and human mast cells became apparent. Non-specific, non-immunological labelling was identified by (i) immunolabelling of mast cells when using control isotype primary antibodies, (ii) ability of conjugated secondary antibodies to label mast cells without prior mast cell exposure to a primary antibody, (iii) extinction of the non-specific labelling and retention of specific labelling when the pH of the diluting and washing buffers is shifted from pH 7.2 to pH 6.0, and (iv) reduction/extinction of the labelling when the antibodies are pre-incubated with soluble heparin prior to immunostaining. The site of the reactivity on the electron microscope level was shown to be confined to the mast cell secretory granules. The results of this study support the hypothesis that non-specific labelling of mast cells results from an ionic interaction between the F(ab′)2 segments of antibodies and the heparin constituent of the mast cell secretory granules. This study points out the necessity of stringent controls when using immunohistochemistry to determine mast cell reactivity to various antibodies.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Benjamini, E. & Leskowitz, S. (1991) Immunology: a Short Course. 2nd edn. New York: Wiley-Liss.
Buffa, R., Crivelli, O., Fiocca, R., Fontana, P. & Solcia, E. (1979a) Complement-mediated unspecific binding of immunoglobulins to some endocrine cells. Histochemistry 63, 15–21.
Buffa, R., Solcia, E., Fiocca, R., Crivelli, O. & Pera, A. (1979b) Complement-mediated binding of immunoglobulins to some endocrine cells of the pancreas and gut. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 27, 1279–80.
Bussolati, G. & Gugliotta, P. (1983) Nonspecific staining of mast cells by avidin-biotin-peroxidase complexes (ABC). J. Histochem. Cytochem. 33, 1419–21.
Claman, H., Giorno, R. & Seibold, J. (1991) Endothelial and fibroblastic activation in scleroderma: the myth of the ‘uninvolved’ skin. Arthritis Rheumatism 34, 1495–1501.
Duhamel, R. & Whitehead, J. (1990) Prevention of nonspecific binding of avidin. Meth. Enzymol. 184, 201–7.
Giorno, R., Lee Choi, K. & Claman, H. N. (1987) Simultaneous in situ detection of IgE receptors and cytoplasmic granules in murine cutaneous mast cells. J. Immunol. Meth. 99, 163–6.
Grube, D. (1980) Immunoreactivities of gastrin (G-) cells. II. Nonspecific binding of immunoglobulins to G-cells by ionic interactions. Histochemistry 66, 149–67.
Horny, H.-P., Reimann, O. & Kaiserling, E. (1988) Immunoreactivity of normal and neoplastic human tissue mast cells. Am. J. Clin. Path. 89, 335–40.
Mar, H. & Wight, T. (1988) Colloidal gold immunostaining on deplasticized ultra-thin sections. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 36, 1387–95.
Pouplard, A., Bottazzo, G.-F., Doniach, D. & Roitt, I. (1976) Binding of human immunoglobulins to pituatary ACTH cells. Nature 261, 142–4.
Ruck, P., Horny, H.-P. & Kaiserling, E. (1990) Immunoreactivity of human tissue mast cells: nonspecific binding of primary antibodies against regulatory peptides by ionic linkage. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 38, 859–67.
Scheck, O., Horny, H.-P., Ruck, P., Schmelzle, R. & Kaiserling, E. (1987) Solitary mastocytoma of the eyelid. A case report with special reference to the immunocytology of human tissue mast cells, and a review of the literature. Virchows Arch. A Pathol. Anat. Histopathol. 412, 31–6.
Seibold, J., Giorno, R. & Claman, H. (1991) Dermal mast cell degranulation in systemic sclerosis. Arthritis Rheumatism 33, 1702–9.
Uvnas, B., Aborg, C.-H. & Bergendorff, A. (1970) Storage of histamine in mast cells. Evidence for an ionic binding of histamine to protein carboxyls in the granule heparin- protein complex. Acta Physiol. Scand. 336, (Suppl) 1–26.
Uvnas, B., Aborg, C.-H., Lyssarides, L. & Thyberg, J. (1985) Cation exchanger properties of isolated rat peritoneal mast cell granules. Acta Physiol. Scand. 125, 25–31.
Uvnas, B., Aborg, C.-H., Lyssarides, L., Thyberg, J. & Danielsson, L.-G. (1986) Rat mast cells superfused with isotonic solutions release histamine, probably via intracellular cation exchange K+ ↔ Hi+ ions. Acta Physiol. Scand. 128, 657–8.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schiltz, P.M., Lieber, J., Giorno, R.C. et al. Mast cell immunohistochemistry: non-immunological immunostaining mediated by non-specific F(ab′)2-mast cell secretory granule interaction. Histochem J 25, 642–647 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00157878
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00157878