Abstract
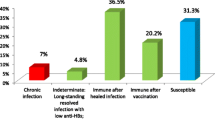
A cross-sectional study was performed to obtain risk factors for hepatitis B disease, HBsAg carriers and immunised personnel, among 2470 workers in a general hospital in Madrid, Spain. The data obtained were analyzed with multiple logistic regression to obtain β coefficients for variables. The results of the analysis show that being a nurse or being regularly exposed to blood are the most important risk factors for hepatitis B acquisition. The length of time working at the same job activity was also a risk factor. The resulting β coefficients allow the construction of a predictive equation for non-immunised, HBsAg carrier and immunised HBV status, which can select subjects for a hepatitis B vaccination program.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dandoy S., Kirkman-Liff B. and Brakowsky F. (1984): Multiple exposures of hospital employees to Hepatitis B - Arch. Inter. Med. 144: 720–723.
DeJuanes Pardo J.R., Fuertes A., Lago E. et al. (1986): Estudio de la prevalencia de marcadores de VHB y VHLT III, ante una campaña de vacunación contra la hepatitis B, en el personal sanitario extrahospitalario- Rev. Esp. Microbiol. Clin. 1: 230–234.
DeJuanes Pardo J.R., García Delgado I., Rodríguez Agulló J.L. and Corres Pireti M.A. (1987): Seguimiento de las hepatitis virales agudas, come enfermedad profesional, en el hospital general durante un periodo de 7 años - Rev. Esp. Microbiol. Clin. 2: 71–76.
Dienstag J.L. and Ryan D.M. (1982): Occupational exposures to hepatitis B virus in hospital personnel: infection or immunization? - Am. J. Epidemiol. 115: 26–39.
Enmanuel J.C., Bassett M.T. and Smith H.J. (1988): Risk of hepatitis B infection among medical and paramedical workers in a general hospital in Zimbabwe - J. Clin. Pathol. 41: 334–336.
Follet E.A., Symington I.S. and Cameron M.G. (1987): Experience with hepatitis B vaccination in nurses in a hospital for the mentally handicapped - Lancet ii: 728–731.
Galambos J.T. (1986): Transmission of hepatitis B from providers to patients: How big is the risk? Hepatology 6: 320–325.
Gerety R.J. and Tabor E. (1985): The Epidemiology of Hepatitis B. In: Hepatitis B, Gerety R.J. - Academic Press. Inc., Florida pp. 77–79.
Gustafson T.L. (1991): TRUE EPISTAT. 4th ed. Richardson T.X. Epistat services.
Hadley W.K. (1989): Infection of the health care worker by HIV and other blood-borne viruses: risks, protection and education - Am. J. Hosp. Pharm. 46 (Suppl): 54–57.
Hicks C.K., Hargiss C.O. and Harris J.R. (1985): Prevalence survey for hepatitis B in high-risk university hospital employees - Am. J. Infect. Control. 13: 1–16.
Hosmer D.W. and Lemeshow S. (1989): The multiple logistic regression model. In: Applied logistic regression. John Wiley and Sons - New York, pp. 25–36.
Johnson C.D., Evans R., Shanson D.C. and Wastell C. (1989): Attitudes of operating theatre staff to inoculation-risk cases - Br. J. Surg. 76: 195–197.
Malo González L.C., Herruzo-Cabrera R., García Caballero J. and Rey Calero J. (1990): Encuesta epidemiológica sobre la infección por el virus de la Hepatitis B (VHB) en personal sanitario, en consulta de Medicina Laboral - Ciencia Médica 7: 207–213.
Mulley A.G., Silverstein M.D. and Dienstag J.L. (1982): Indications for use of hepatitis B vaccine, based on cost-effectiveness analysis - New Engl. J. Med. 307: 644–652.
Pattison C.P., Maynard J.E., Berquist D.R. and Webster H.M. (1975): Epidemiology of hepatitis B in hospital personnel - Am. J. Epidemiol. 101: 59–64.
Tsega E., Horton J., Nordenfelt E., Hanson B.G. and Wolde-Hawariat G. (1989): Do hospital personnel in hyperendemic areas require immunization against hepatitis B virus infection? Is vertical transmission of HVB infection common in this group? - Eth. Med. J. 27: 101–106.
Williams R. and Fagan E. (1988): Viral hepatitis in hospitals a clinical overview - J. Hosp. Infect. 11: 142–149.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Herruzo-Cabrera, R., Malo-González, L., Purón, M.E.C. et al. Predictive equation for acquisition of hepatitis B in hospital workers in a general hospital. Eur J Epidemiol 9, 442–446 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00157404
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00157404