Abstract
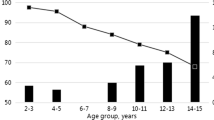
Possible hepatitis B immunization of all newborns, regardless of the mother's HBsAg status, is a strategy under consideration for selected hyperendemic areas in Italy. Sardinia is one such area. However, in 1987 in Sardinia, the prevalence of hepatitis B markers in children under 11 years was estimated at 1.7% and the prevalence of hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) at 0.2%. A much higher prevalence of HBsAg was recently observed among adults in this area: 8.7% among men and 5.2% among pregnant women. This contrasting pattern is unlikely to be due to bias: the sampling procedures adopted were appropriate and the percentage of refusals was very low (2.2%). The observed low hepatitis B marker prevalence in young age groups might be the result of a cohort effect due to the improved socio-economic conditions and changes in behaviour that have occurred in Sardinia over the last few years.
The finding of only 3 HBsAg+ individuals out of 1,826 children tested, in spite of the 5.2% HBsAg prevalence among pregnant women in that region, is probably attributable to the low proportion of HBeAg positive individuals among the HBsAg+ carrier mothers in this area.
At present, immunization of all newborns in Sardinia cannot be recommended.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barin F., Perin J. and Chotard J. (1981): Crossectional and longitudinal epidemiology of hepatitis B in Senegal. - Prog. Med. Vir., 27: 148–162.
Beasley R.P., Trepo C. and Stevens C.E. (1977): The e antigen and vertical transmission of hepatitis B surface antigen. - Am. J. Epidemiol., 105: 94–98.
Beasley R.P., Hwang L.Y. and Lin C.C. (1982): Incidence of hepatitis B virus infection in preschool children in Taiwan. - J. Infect. Dis., 146: 198–204.
Beasley R.P., Hwang L.Y. and Lin C.C. (1983): Incidence of hepatitis among students at a University in Taiwan. - Am. J. Epidemiol., - 117: 213–222.
Botha J.F., Ritchie M.J.J. and Dusheiko G.M. (1984): Hepatitis B virus carrier state in black children in Ovamboland: role of perinatal and horizontal infection. - Lancet, i: 1210–1212.
Gruppo di ricerca “HBV-Sardegna” (1986): Studio epidemiologico dell'infezione da HBV e agente delta in Sardegna. - Rec. Progr. Med., 77: 401–404.
Kahn H.A. (1983): An introduction to epidemiologic methods. - Oxford University Press., 25–28.
Lilienfeld A.M. and Lilienfeld D.F. (1980): Foundations of epidemiology. - Oxford University Press., II Edition, 326–327.
Maynard J.E (1981): Hepatitis B vaccine strategies for utilization. In: P. Maupas, P. Guesry (Eds), Hepatitis B Vaccine, INSEAM Symposium no. 18. - Elsevier-North-Holland Biomedical Press., Amsterdam, 13–19.
McCollum R.W. and Zuckerman A.J. (1981): Viral hepatitis: report on a WHO informal consultation. -J. Med. Vir., 8: 1–29.
McMahon B.J., Alward W.L.M. and Hall D.B. (1985): Acute hepatitis B virus infection: relation of age to the clinical expression of disease and subsequent development of the carrier state. - J. Infect. Dis., 151: 599–603.
Papaevangelou G. (1987): The Greak national hepatitis B vaccination programme. In: “Up-date and prospects in the control of hepatitis B: vaccines and antivirals” - Padua (Italy), October 13–14.
Prince A.M., White T. and Pollock N. (1981): Epidemiology of hepatitis B infection in Liberian infants. - Infect. Immunol., 32: 675–680.
Scarpa B. (1986): Personal communication. - Rome, May.
Stevens C.E., Beasley R.P. and Tsui J. (1975): Vertical transmission of hepatitis B antigen in Taiwan. - N. Engl. J. Med., 292: 2771–774.
Stevens C.E., Neurath R.A. and Beasley R.P. (1979): HBeAg and anti-HBe detection by radioimmunoassay: correlation with vertical transmission of hepatitis B virus in Taiwan. - J. Med. Vir., 3: 237–241.
Stroffolini T., Pasquini P. and Mele A. (1988): HBsAg prevalence among pregnant women in Italy. - Public Health, 102: 329–333.
Szmuness W. and Prince A.M. (1971): The epidemiology of serum hepatitis (SH) infections: a controlled study in two closed institutions. - Am. J. Epidemiol., 94: 585–595.
Szmuness W., Prince A.M. and Dieholt G. (1973): The epidemiology of hepatitis B infections in Africa: results of a pilot survey in the Republic of Senegal. -Am. J. Epidemiol., 98: 104–110.
Szmuness W. (1975): Recent advances in the study of the epidemiology of hepatitis B. - Am. J. Pathol., 81: 629–649.
Szmuness W., Harley E.J. and Ikram H. (1978): Sociodemographic aspects of the epidemiology of hepatitis B. In: G.N. Vyas, S.N. Cohen, R. Schmid (Eds). - Viral Hepatitis, Franklin Institute Press, Philadelphia, 297–320.
Tabor E. and Gerety R.J. (1979): Hepatitis B virus infection in infants and toddless in Nigeria: the need for early intervention. - J. Pediatr., 95: 647–650.
Tanaka T., Nagai M. and Yoshihara S. (1986): Changing pattern of age specific prevalence of hepatitis B surface antigen and corresponding antibody in Japan. - Am. J. Epidemiol., 124: 368–371.
Tassopoulos N.C., Papaevangelou G.J. and SjogrenM.H. (1987): Natural history of acute hepatitis B surface antigen-positive hepatitis in Greek adults. -Gastroenterology, 92: 1844–1850.
Whittle H.C., Bradley A.K. and McLanchlan K. (1983): Hepatitis B virus infection in two Gambian villages. -Lancet, i: 1203–1206.
Zanetti A.R., Ferroni P. and Magliano E.M. (1982): Perinatal transmission of the hepatitis B virus and of the HBV-associated delta agent from mothers to offspring in Northern Italy. - J. Med. Vir., 9: 139–148.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stroffolini, T., Franco, E., Romano, G. et al. Hepatitis B virus infection in children in Sardinia, Italy. Eur J Epidemiol 5, 202–206 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00156831
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00156831