Summary
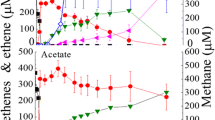
A consortium of anaerobic microorganisms was grown on acetate, ethanol, glucose or methanol and dechlorinated 50 umol 2,4,6-trichlorophenol, through 2,4-dichlorophenol, to 4-chlorophenol. The highest rate of dechlorination of 2,4,6-trichlorophenol was observed when ethanol was used as a growth substrate.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Armanante, P. M. Kafkewitz, D., Lewandowski, G., Kung, C. M. Environ Prog. 11, 113 (1992)
Criddle, C.S. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 41 (1993)
Krumme M. L., Boyd, S. A. Water Research, 22, 171 (1988)
Steiert, J.G., Crawford, R. L. Trends in Biotechnology, 3, 300 (1985)
Wu, W. M., Bhatnagar, L., Zeikus, J. G. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 59, 389 (1993)
Zhang, X., Wiegel, J. Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 56, 1119 (1990)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pak, D. Enhanced dechlorination of 2,4,6-trichlorophenol by anaerobic microbial populations in the presence of ethanol. Biotechnol Lett 18, 981–984 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00154634
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00154634