Abstract
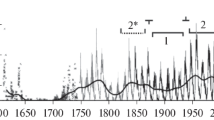
Series of 110 years of sunspot numbers and indices of geomagnetic activity are used with 17 years of solar wind data in order to study through solar cycles both stream and shock event solar activity. According to their patterns on Bartels diagrams of geomagnetic indices, stable wind streams and transient solar activities are separated from each other. Two classes of stable streams are identified: equatorial streams occurring sporadically, for several months, during the main phase of sunspot cycles and both polar streams established, for several years, at each cycle, before sunspot minimum. Polar streams are the first activity of solar cycles. For study of the relationship between transient geomagnetic phenomena and sunspot activity, we raise the importance of the contribution, at high spot number, of severe storms and, at low spot number, of short lived and unstable streams. Solar wind data are used to check and complete the above results. As a conclusion, we suggest a unified scheme of solar activity evolution with a starting point every eleventh year, a total duration of 17 years and an overlapping of 6 years between the first and the last phase of both successive series of phenomena: first, from polar field reversal to sunspot minimum, a phase of polar wind activity of the beginning cycle is superimposed on the weak contribution of shock events of the ending cycle; secondly, an equatorial phase mostly of shock events is superimposed on a variable contribution of short lived and sporadic stable equatorial stream activities; and thirdly a phase of low latitude shock events is superimposed on the polar stream interval of the following cycle.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Avignon, Y. and Pick-Gutman, M.: 1959, Compt. Rend. Acad. Sci. Paris 249, 2276.
Bohlin, J. D.: 1977, Solar Phys. 51, 377.
Bohlin, J. D. and Sheeley, N. R.: 1978, Solar Phys. 56, 125.
Boller, B. R. and Stolov, H. L.: 1970, J. Geophys. Res. 75, 6073.
Bridge, H. S.: 1976, in D. J. Williams (ed.), Physics of Solar Planetary Environments, A.G.U. Publication, p. 47.
Broussard, S. M., Sheeley, N. R., Tousey, R., and Underwood, J. H.: 1978, Solar Phys. 56, 161.
Burlaga, L. F. and King, J. H.: 1979, J. Geophys. Res. 84, 6633.
Caroubalos, C.: 1964, Ann. Astrophys. 27, 333.
Chernosky, E. J.: 1966, J. Geophys. Res. 71, 965.
Dodson, H. W., Hedeman, E. R., and Mohler, O. C.: 1974, Rev. Geophys. Space Phys. 12, 329.
Eddy, J. A.: 1976, Science 192, 1189.
Feldman, W. C., Asbridge, J. R., Bame, S. J., and Gosling, J. T.: 1978, J. Geophys. Res. 83, 2177.
Feldman, W. C., Asbridge, J. R., Bame, S. J., and Gosling, J. T.: 1979, J. Geophys. Res. 84, 7371.
Feynman, J.: 1980, in R. F. Donnelly (ed.), Solar Terrestrial Prediction Proceedings, Vol. 4, U.S. Department of Commerce Publication, Washington, D.C., p. A-8.
Feynman, J. and Crooker, N. U.: 1978, Nature 275, 626.
Fraser-Smith, A. C.: 1972, J. Geophys. Res. 77, 4209.
Gosling, J. T., Asbridge, J. R., Bame, S. J., and Feldman, W. C.: 1976, J. Geophys. Res. 81, 5061.
Hansen, R. T., Hansen, S. F., and Sawyer, C.: 1976, Planetary Space Sci. 24, 381.
Howard, R. and LaBonte, B. J.: 1980, Astron. Phys. Letters 239, L33.
Hundhausen, A. J.: 1977, in Jack B. Zirker (ed.), Coronal Holes and High Speed Wind Streams, Colorado Associated University Press, Boulder, p. 225.
Kane, R. P.: 1978, Nature 274, 139.
King, J. H.: 1977, Interplanetary Medium Data Book, NSSDC/WDC-A-R and S.77–04, Nat. Space Sci. Data Center, Greenbelt, Md.
Link, F.: 1977, Astron. Astrophys. 54, 857.
Livshits, M. A., Valchuk, T. E., and Feistein, Y. I.: 1979, Nature 278, 241.
Mayaud, P. N.: 1973, IAGA Bulletin No. 33.
Nolte, J. T., Gerassimenko, M., Krieger, A. S., and Solodyna, C. V.: 1978, Solar Phys. 56, 153.
Ohl, A. I.: 1966, Soln. Dann., No. 12, 84.
Ohl, A. I.: 1976, Soln. Dann., No. 9, 73.
Russel, C. T. and McPherron, R. L.: 1973, J. Geophys. Res. 78, 92.
Schatten, K. H., Scherrer, P. H., Svalgaard, L., and Wilcox, J. M.: 1978, Geophys. Res. Letters 5, 411.
Sheeley, N. R.: 1976, J. Geophys. Res. 81, 3462.
Sime, D. G. and Rickett, B. J.: 1978, J. Geophys. Res. 83, 5757.
Simon, P. A.: 1979, Solar Phys. 63, 399.
Siscoe, G. L.: 1976, J. Geophys. Res. 81, 4782.
Snyder, C. W., Neugebauer, M., and Rao, U. R.: 1963, J. Geophys. Res. 68, 6361.
Svalgaard, L.: 1976, Institute for Plasma Research, Stanford University, California, Report No. 648.
Švestka, Z.: 1966, Bull Astron. Inst. Czech. 17, 62.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Legrand, J.P., Simon, P.A. Ten cycles of solar and geomagnetic activity. Sol Phys 70, 173–195 (1981). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00154399
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00154399