Abstract
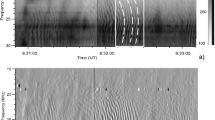
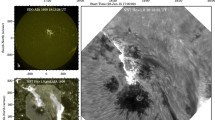
The two-element interferometer at Hat Creek Observatory was used at 1.3 cm wavelength to study the fine structure of the radio emissive regions on the Sun. Observations of the quiet Sun at 1.3 cm show sudden changes in the fringe amplitude and phase, lasting for typically about 5–8 min. Assuming that these events are identical in nature, a plot of peak amplitude vs the projected baseline at the time of the event suggests emission from a region of angular size of about 10″. The corresponding brightness temperature is 50000 K. It is possible that these events may be related to the appearance and disappearance of groups of spicules or mottles.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beckers, J. M.: 1972, Ann. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 10, 73.
Hills, R., Janssen, M., Thornton, D. D., and Welch, W. J.: 1973, IEEE Special Issue on Radio and Radar Astronomy, in press.
Leighton, R. B., Noyes, R. W., and Simon, G. W.: 1962, Astrophys. J. 135, 474.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kundu, M.R., Velusamy, T. Fine structure of the Sun at 1.3 cm wavelength. Sol Phys 34, 125–131 (1974). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00149604
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00149604