Abstract
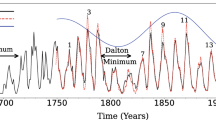
The discovery of 680-million year old varves by George Williams in South Australia, recording several millennia of fossil solar cycles, is a most exciting development that is bound to make an impact on solar physics. Already new problems of physical understanding have been posed by the 315-year Elatina cycle and the separate 350-year cycle, or undulation (Williams, 1985, 1986; Williams and Sonett, 1985). The Elatina cycle evidences itself multiplicatively in the form of amplitude modulation with a distinctive nonsinusoidal envelope, while the undulation is additive and quasisinusoidal (Bracewell and Williams, 1986). Both of these periodic phenomena are present in historical records of sunspots, but would not have been discerned from modern solar observations, which do not date back far enough. The explanation of two such sharply defined periods, in addition to the less sharply defined 22-year magnetic cycle, will require an understanding of solar physics that we do not yet have. Examples of the impact that the varve discovery is beginning to make are given, and a previously proposed mechanism for driving the activity cycle is extended in terms of a magnetic wave propagated radially outward from a deep torsional oscillator.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Babcock, H. W.: 1961, Astrophys. J. 133, 572.
Bjerknes, V.: 1926, Astrophys. J. 64, 93.
Bracewell, R. N.: 1953, Nature 171, 649.
Bracewell, R. N.: 1985, Australian J. Phys. 38, 1009.
Bracewell, R. N.: 1986, Nature 323, 516.
Bracewell, R. N.: 1987, Monthly Notices Roy. Astron. Soc. (in press).
Bracewell, R. N. and Williams, G. E.: 1986, Monthly Notices Roy. Astron. Soc. 223, 457.
Cole, T. W.: 1973, Solar Phys. 30, 103.
Dicke, R. H.: 1970, in A. Slettebak (ed.), ‘The Rotation of the Sun’, Stellar Rotation, D. Reidel Publ. Co., Dordrecht, Holland.
Dicke, R. H.: 1978, Nature 276, 676.
LaBonte, B. J.: 1986, Presentation at the First Solar Cycle Workshop, August 1986.
Menzel, D. H.: 1959, Our Sun, Harvard University Press, Cambridge.
Parker, E. N.: 1979, Cosmical Magnetic Fields, Clarendon Press, Oxford.
Ribes, E., Mein, P., and Mangeney, A.: 1985, Nature 318, 170.
Richardson, R. S. and Schwarzschild, M.: 1949, Proc. 11th Volta Conf., Rome 1953.
Waldmeier, M.: 1935, Astron. Mitteilungen Zürich 14, No. 133, 105.
Walén, C.: 1949, in T. Kuiper (ed.), The Sun, Chicago University Press, Chicago.
Williams, G. E.: 1985, Australian J. Phys. 38, 1027.
Williams, G. E.: 1981, Nature 291, 624.
Williams, G. E.: 1986, Sci. Am. 254, 88.
Williams, G. E. and Sonett, C. P.: 1985, Nature 318, 523.
Wilson, P. R.: 1987a, Solar Phys. 110, 1.
Wilson, P. R.: 1987b, Solar Phys. 110, 59.
Yule, G. U.: 1927, Phil. Trans. Roy. Soc. A226, 267.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Invited Talk to the 2nd Solar Cycle Workshop.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bracewell, R.N. The impact of varves on solar physics. Sol Phys 117, 261–267 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00147247
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00147247