Abstract
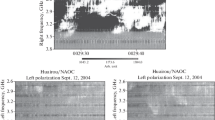
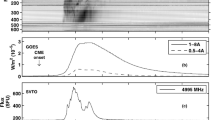
Several type III, type II, and type IV bursts were observed on April 25 and 26, 1979 with the Clark Lake Radio Observatory's E-W and N-S swept frequency interferometers in the range 20–110 MHz. The radio bursts were associated with hard X-ray bursts in the energy range 26–154 keV, as observed by ISEE-3. The type III bursts, which were associated with impulsive hard X-rays, were observed to great heights (∼ 3.1R ⊙ from disk center at 28 MHz) and their location indicates that the electron streams responsible for them were injected at the footpoints of magnetic field lines which diverge in the corona. With one exception, all the type III bursts occurred in dense coronal regions. Two gradual hard X-ray bursts were observed to occur in association with a type IV without type II, and a type IV-type II burst. For the gradual burst (observed on April 25) associated with a type IV only, it is believed that part of the energetic electrons responsible for meter-decameter type IV are trapped in a plasmoid behind a weak shock, as evidenced by the absence of a type II, while another part is located in low lying magnetic loops producing centimeter and hard X-radiation. The type II burst associated with the other gradual hard X-ray burst (observed on April 26) started approximately 9 min after the impulsive hard X-ray burst peak. This rather long delay between the type II onset and the impulsive maximum is believed to represent the time interval over which the shock becomes strong enough to produce a detectable type II higher in the corona.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arnoldy, R. L., Kane, S. R., and Winckler, J. R.: 1968, Astrophys. J. 151, 711.
Dulk, G. A.: 1973, Solar Phys. 32, 491.
Duncan, R. A.: 1979, Solar Phys. 63, 389.
Gergely, T. E. and Kundu, M. R.: 1981, Solar Phys. 71, 65.
Hudson, H. S.: 1978, Astrophys. J. 224, 235.
Kane, S. R.: 1972, Solar Phys. 27, 174.
Kane, S. R.: 1981, Astrophys. J. 247, 1113.
Kane, S. R., Anderson, K. A., Evans, W. D., Klebesadel, R. W., and Laros, J.: 1979, Astrophys. J. Letters 233, L151.
Kane, S. R., Pick, M., and Raoult, A.: 1980, Astrophys. J. Letters 241, L113.
Kane, S. R., Anderson, K. A., Evans, W. D., Klebesadel, R. W., and Laros, J.: 1981, in preparation.
Kundu, M. R.: 196l, J. Geophys. Res. 66, 3208.
Leblanc, Y.: 1973, Astrophys. Letters 14, 41.
Lin, R.: 1974, in G. Newkirk Jr. (ed.), ‘Coronal Disturbances’, IAV Symp. 57, 201.
Lin, R. P. and Hudson, H. S.: 1971, Solar Phys. 17, 412.
Newkirk, G. A., Jr.: 1967, Ann. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 5, 213.
Solar Geophysical Data: April 1979.
Solar Geophysical Data: May 1979.
Švestka, Z. and Fritzová-Švestková, L.: 1974, Solar Phys. 36, 417.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kundu, M.R., Gergely, T.E. & Kane, S.R. Positional characteristics of meter-decameter wavelength bursts associated with hard X-Ray bursts. Sol Phys 79, 107–119 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00146976
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00146976