Abstract
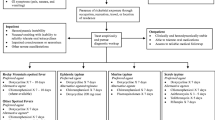
The author reviews the recent advances in the treatment of Mediterranean Spotted Fever and Q fever. In mediterranean spotted fever (M.S.F.), in vitro and preliminary in vivo data support the place of quinolones and josamycin in the treatment of M.S.F. In children josamycin could become the first choice drug as well as in pregnant woman. In Q fever chronic disease should be treated using a combination of antibiotic (doxycycline + quinolones) for a minimum of 3 years.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
BarkerCF. (1986): Determination of antibiotic susceptibility of Rickettsiae and Chlamydiae in BS-C-1 cell cultures. - Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1969: 1968: 425–428.
BellaF., FontB., UrizS., Munoz EspinT., Espejo ArenasE., TraveriaJ., SerranoJ.A. and SeguraF. (1990): Randomized trial of Doxycycline versus Josamycin for Mediterranean Spotted Fever. -Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 34: 937–938.
Bella CuetoF., Font CreusB., Segura PortaF., Espejo ArenasE., Lopez ParesP. and Munoz EspinT. (1987): Comparative, randomized trial of one day Doxycycline versus 10/day Tetracycline therapy for Mediterranean Spotted Fever. - J. Infect. Dis. 155: 1056–1058.
BertrandA., JambonF., JonquetO. and ReynesJ. (1988): Infections par les rickettsiales et fluoroquinolones. - Path. Biol. 36: 493–495.
DrancourtM. and RaoultD. (1989): In vitro susceptibilities of Rickettsia rickettsii and Rickettsia conorii to Roxithromycin and Pristinamycin.. -Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 33: 2146–2148.
FishbeinD.B., FrontiniM. G., GilesR. and VernonL.L. (1990): Fatal cases of Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever in the United States, 1981–1988. - Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sc. 590: 246–247.
FreemanR. and HodsonM. (1972): Q fever endocarditis treated with Trimethoprimsulfamethoxazole.- Br. Med. J. 1: 419.
GuchiolF., PallaresR., CarratalaJ., BolaoF., ArizaJ., RuftG. and ViladrichRE (1989): Randomized Double-blind evaluation of Ciprofloxacin and Doxycycline for Mediterranean Spotted Fever. -Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 33: 987–988.
HackstadtT. and WilliamsJ.C. (1981): Biochemical stratagem for obligate parasitism of eukaryotic cells by Coxiella burnetii. - Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 78: 3240–3244.
HuebnerR.J., HottleG.A. and RobinsonE.B. (1948): Action of Streptomycin in experimental infection with Q fever. - Publ. Health Rept. 63: 357.
JacksonE.B. (1951): Comparative efficacy of several antibiotics on experimental Rickettsial infections in embryonated eggs. - Antibiotics and Chemotherapy. 1: 231–241.
KimbroughR.C. III, OrmsbeeA., PeacockN., RogersW.R., BennettsR.W., RaafJ., KrauseA. and GardnerC. (1979): Q fever in the United States. - Ann. Inter. Med. 91: 400–402.
LangleyJ.M., MarrieT.J., CovertA., WaagD.M. and WilliamsJ.C. (1988): Poker players' pneumonia. An urban outbreak of Q fever following exposure to a parturient cat. - N. Engl. J. Med. 319: 354–357.
LevyP.J., DrancourtM., EtienneJ., AuvergnatJ.C., BeytoutJ., SaintyJ.M., GoldsteinF. and RaoultD. (1991): Antibiotic therapy of 32 cases of Q fever endocarditis: comparison of different regimens. -Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 35: 88–91.
LevyP.Y., RaoultD. and RazonglesJ.J. (1989): Q fever and autoimmunity. - Eur. J. Epidemiol. 5: 447–452.
Munoz EspinT., Lopez-ParesP., Espejo ArenasE., Font CreusB., Martinez VilaI., Traveria-CasanovaJ., Segura-PortaF. and Bella-CuetoF. (1986): Erythromycin versus Tetracycline for treatment of Mediterranean Spotted Fever. - Arch. Dis. Child. 61: 1027–1029.
OrmsbeeR.A. and PickensE. G. (1951): A comparative by means of the complement-fixation test of the relative potencies of chloramphenicol, aureomycin, and terramycin in esperimental Q fever infections in embryonated eggs. - J. Immunol. 67: 437–447.
OrmsbeeR.A., ParkerH. and PickensE. G. (1955): The comparative effectiveness of aureomycin, terramycin, chloramphenicol, erythromycin and thiomycetin in suppressing experimental rickettsial infections in chick embryos. - J. Infect. Dis. 96: 162–169.
PowellO.W., KennedyK.P., McIverM. and SilverstoneH. (1962): Tetracycline in the treatment of “Q” fever. Australian Annals of Medecine. 11: 184.
RaoultD. (1990): Host factors in the severity of Q fever. - Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. 590: 33–38.
Raoult D. and Drancourt M. (1988): Macrolides et rickettsioses dans Macrolides et Synergistine. Pocidalo J.J., Vachon J., Coulaud J.P., Vilde J.L. Librairie Arnette-Paris. - 183–186.
RaoultD., DrancourtM. and VestrisG. (1990): Bactericidal effect of Doxycycline combined with lysosomotropic agents against Coxiella burnetii. -Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 34: 1512–1514.
RaoultD., GallaisH., DeMiccoPh. and CasanovaP. (1986): Ciprofloxacin therapy in Mediterranean Spotted Fever. - Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 30: 606–607.
RaoultD., PiquetPh., GallaisH., DeMiccoPh., DrancourtM. and CasanovaP. (1986): Coxiella burnetii infection of a vascular prosthesis. - N. Engl. J. Med. 315: 1358.
RaoultD., RazaA. and MarrieT. (1990): Q fever endocarditis and other forms of Chronic Q fever in T.J. Marrie. Q fever. The disease. - Volume I. - CRC Book (Boca Raton, FLA. - USA) p. 179–200.
RaoultD., RoussellierP., GalicherV., PerezR. and TamaletJ. (1986): In vitro susceptibility of Rickettsia conorii to Ciprofloxacin as determined by suppressing lethality in chicken embryos and by plaque assay. - Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 29: 424–425.
RaoultD., RoussellierP. and TamaletJ. (1988): In vitro evaluation of Josamycin, Erythromycin and Spiramycin against Rickettsia rickettsii and Rickettsia conorii. - Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 32: 255–256.
RaoultD., RoussellierP., VestrisG., GalicherV., PerezR. and TamaletJ. (1987): In vitro and in ovo susceptibility of Rickettsia conorii and Rickettsia rickettsii to pefloxacin. - J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 19: 303–305.
RaoultD., RoussellierP., VestrisG. and TamaletJ. (1987): In vitro susceptibility of Rickettsia rickettsii and Rickettsia conorii as determined by plaque assay and by microplaque colorimetric assay. - J. Infect. Dis. 155: 1059–1062.
RaoultD. and WalkerD.H. (1990): Rickettsia rickettsii (Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever and other Spotted Fevers). In: Mandell, Douglas, Bennett. Principles and Practice of Infections disease. - Churchill Livingstone (New York) p. 1465–1470.
RaoultD., YeamanM.R. and BacaO. (1989): Susceptibility of Coxiella burnetii to Pefloxacin and Ofloxacin in ovo and in persistently infected L929 cells. - Antimicrob. Agent Chemother. 33: 621–623.
RaoultD., YeamanM.R. and BacaO. (1989): Susceptibility of Rickettsia and Coxiella burnetii to quinolones in vitro. - Rev. Infect. Dis. Vol. 11 Supplements 1989. p. S986.
SawyerL.A., FishbeinD.A. and McDadeJ.E. (1987): Q fever: current concepts. - Rev. Infect. Dis. 9: 935–940.
ShakedY., SamraM., MaeirK. and RubinsteinE. (1988): Murine typhus and Spotted Fever in Israel in the eighties: retrospective analysis. - Infection. vol. 16, 5: 283–287.
SmadelJ.E., JacksonE.B. and CruiseA.B. (1949): Chloromycetin in experimental rickettsial infections. -J. Immunol. 62: 49–57.
SpelmanD.W. (1982): Q fever. A study of 111 consecutive cases. - Med. J. Aust. 1: 547–557.
SpicerA.J., PeacockM.G. and WilliamsJ.C. (1981): Effectiveness of several antibiotics in suppressing chick embryo lethality during experimental infections by Coxiella burnetii, Rickettsia typhi and R. rickettsii. In: W. Burgdorfer and R.L. Anaker. Rickettsiae and Rickettsial Diseases. - Academic Press, edit. New York. p. 375.
SubramanyaN.I., WrightJ.S. and KhanM.A.R. (1982): Failure of rifampin and cotrimoxazole in Q fever endocarditis. - Br. Med. J. 283: 343.
TobinM.J., CahillN., GeartyG., MaurerB., BlakeS., DalyK. and HoneR. (1982): Q fever endocarditis. -Am. J. Med. 72: 396.
TunstallP. (1970): Apparent recurrence of Q fever endocarditis following homograft replacement of aortic valve. - Br. Heart J. 32: 568.
TurckW.P.G., HowittG., TurnbergL.A., FoxH., LongsonM., MattewsM.B. and DasMguptaR. (1976): Chronic Q fever. Q. J. Med. 45: 193–197.
VarmaM.P.S., AdgeyA.A.J. and ConnollyJ.H. (1980): Chronic Q fever endocarditis. - Br. Heart J. 43: 695.
WissemanC.L.Jr., SilvermanD.J., WaddellA. and BrownD.T. (1982): Penicillin-induced unstable intracellular formation of sheroplasts by Rickettsiae.- J. Infect. Dis. 146: 147–158.
WissemanC.L.Jr., WaddellA.D. and WalshW.T. (1974): In: vitro studies of the action of antibiotics on Rickettsia prowazekii by two basic methods of cell culture. - J. Infect. Dis. 130: 564–574.
Yagupsky P. and Gross E.M. (1984): Relapse of Israeli spotted feve treated with doxycycline. - Trop. Med. Hyg.: 139–140.
YeamanM.R., MitsherL.A. and BacaO. (1987): In vitro susceptibility of Coxiella burnetii to antibiotics, including several Quinolones. - Antimicrob. Agents Chemother 31: 1079–1084.
Yeaman M.R. and Baca O. (1990): Unexpected antibiotic susceptibility of a chronic isolate of Coxiella burnetii. - Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci.: 297–305.
YeamanM.R., RomanM.J. and BacaO.G. (1989): Antibiotic susceptibility of two Coxiella burnetii isolates implicated in distinct clinical syndromes. - Antimicrob. Agent Chemother. 33: 1052–1057.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Raoult, D. Antibiotic treatment of rickettsiosis, recent advances and current concepts. Eur J Epidemiol 7, 276–281 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00145677
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00145677