Abstract
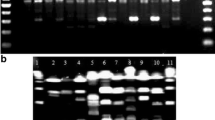
Different epidemiological markers were used to characterize 2 Staphylococcus epidermidis and 8 Staphylococcus aureus strains isolated from patients with severe infections. We compared random amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD) fingerprints, biotypes, antibiotic assays, plasmid profiles and chromosomal DNA restriction endonuclease analysis (REA). Data analysis based on numerical taxonomy methods indicates that RAPD and REA give similar results allowing a good discrimination of the two species and of each isolate. The RAPD method is easier and faster than REA, but the reproducibility of RAPD fingerprints obtained in independent experiments can be problematic. We have found simple technical devices to improve the reproducibility of the RAPD procedure which is therefore a very useful tool in epidemiology for identification and characterization of Staphylococcus spp.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Renaud F, Freney J, Etienne J, et al. Restriction endonuclease analysis of Staphylococcus epidermidis may be a useful epidemiological marker. J Clin Microbiol 1988; 26: 1729–1734.
Birnbaum D, Kelly M, Chow AW. Epidemiologic typing systems for coagulase-negative staphylococci. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol 1991; 12: 319–326.
Pfaller MA, Wakefield DS, Hollis R, et al. The clinical microbiology laboratory as an aid in infection control: The application of molecular techniques in epidemiologic studies of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis 1991; 14: 209–2174.
Goetz MB, Mulligan ME, Kwok R, et al. Management and epidemiologic analysis of an outbreak due to methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Am J Med 1992; 92: 607–614.
Kreiswirth B, Kornblum J, Arbeit RD, et al. Evidence for a clonal origin of methicillin resistance in Staphylococcus aureus. Science 1993; 259: 227–230.
van Belkum A, Bax R, Peerbooms P, et al. Comparison of phage typing and DNA fingerprinting by polymerase chain reaction for discrimination of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus strains. J Clin Microbiol 1993; 31: 798–803.
Struelens MJ, Bax R, Deplano A, et al. Concordant clonal delineation of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus by macrorestriction analysis and polymerase chain reaction fingerprinting. J Clin Microbiol 1993; 31: 1964–1970.
Saulnier P, Bourneix C, Prevost B, et al. Random amplified polymorphic DNA assay is less discriminant than pulsed-field gel electrophoresis for typing strains of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. J Clin Mocrobiol 1993; 31: 982–985.
Bingen E. Application of molecular methods to epidemiologic investigations of nosocomial infections in a pediatric hospital. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol 1994; 15: 488–493.
van Belkum A, Bax R, Prevost G. Comparison of four genotyping assay for epidemiological study of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus strains. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 1994; 13: 420–424.
Schumacher F, Jansen B, Seifert H, et al. Outbreak of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in a teaching hospital: Epidemiological and microbial surveillance. J Med Microbiol 1994; 280: 550–559.
De Lencastre H, Couto I, Melo-Cristino I, et al. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus disease in a Portuguese hospital: Characterization of clonal types by a combination of DNA typing methods. Eur J Clin Microbiol 1994; 13: 64–73.
Haertl R, Bandlow G. Genotyping of Staphylococcus epidermidis by small-fragment restriction endonuclease analysis and pulsed-field gel electrophoresis of genomic restriction fragments. Microbiol Immunol 1994; 38: 527–534.
Zambardi G, Reverdy ME, Bland S, et al. Laboratory diagnosis of oxacillin resistance in Staphylococcus aureus by a multiplex-polymerase reaction assay. Diagn Microb Infect Dis 1994; 19: 25–31.
Tenover FC, Arbeit R, Archer G, et al. Comparison of traditional and molecular methods of typing isolates of Staphylococcus aureus. J Clin Microbiol 1994; 32: 407–415.
Gurtler V, Barrie HD. Typing of Staphylococcus aureus strains by PCR-amplification of variable-length 16S-23S rDNA spacer regions: Characterization of spacer sequences. Microbiol 1995; 141: 1255–1265.
Welsh J, McClelland M. Fingerprinting genomes using PCR with arbitrary primers. Nucleic Acids Res 1990; 18: 7213–7218.
Williams JGK, Kubelik AR, Livak KJ, et al. DNA polymorphisms amplified by arbitrary primers are useful as genetic markers. Nucleic Acids Res 1990; 18: 6531–6535.
Williams JGK, Hanafey MK, Rafalski JA, et al. Genetic analysis using random amplified polymorphic DNA markers. In: Wu R (ed), Methods in enzymology. New York: Academic Press, 1993; 218: 704–740.
Almeida RJ, Jorgensen JH. Identification of coagulase-negative staphylococci with the API STAPHIDENT system. J Clin Microbiol 1983; 18: 254–257.
NCCLS Performed standards for antimicrobial susceptibility tests, 5th ed, Approved standard. M2-A5 1993; Vol. 13, No. 24.
Barsotti O, Renaud F, Freney J, et al. Rapid isolation of DNA from Actinomyces. Ann Microbiol (Inst. Pasteur) 1987; 138: 529–536.
Asubel FM, Brent R, Kingstone RE, et al. (eds). Current protocols in molecular biology. New York: J Wiley & Sons, 1987.
Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Maniatis T (eds). Molecular cloning, a laboratory manual. New York: Cold Spring Harbour Laboratory Press, 1989.
Sokal RR, Sneath PHA (eds). Principles of numerical taxonomy. San Francisco: Freeman and Co., 1973.
Mantel N. The detection of disease clustering and a generalized regression approach. Cancer Res 1967; 27: 209–220.
Rohlf FJ (ed). NTSYS-pc Version 1.70. New York: Exeter Software, 1992.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Damiani, G., Telecco, S., Comincini, S. et al. Comparison of an improved RAPD fingerprinting with different typing methods for discriminating clinical isolates of Staphylococcus spp.. Eur J Epidemiol 12, 163–169 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00145502
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00145502