Abstract
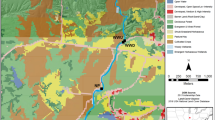
In an attempt to assess the influence of tertiary-treated sewage influx on bacterial metabolism in the Danube River, bacterial abundance, ectoenzymatic activity, faecal coliforms, faecal streptococci, chlorophyll a (chl a), concentrations of dissolved (DOC) and total organic carbon (TOC) and inorganic nutrients were measured upstream of the sewage influx and compared with sampling sites downstream. Additional samples were taken near the outlet of the sewage treatment plant. Bacterial abundance as determined by epifluorescence microscopy was compared with plate counts of total heterotrophic bacteria. Significantly higher values were obtained at the stations downstream from the sewage influx only for faecal coliforms and faecal streptococci, for glucuronidase activity and bacterial biovolume. All the other parameters were not significantly different from values obtained at the upstream sampling site. Strong seasonal dependence was detectable for nitrate with high concentrations during the winter (≈ 250 µM) and low concentrations during summer (≈ 100 µM). A distinct spring phytoplankton bloom was noticeable in the river reaching chl a concentrations of ≈ 70 µg 1−1; during the remaining seasons chl a concentrations were <20 µg 1−1. Highly significant correlations were found between faecal coliform counts and glucuronidase activity. C:N:P ratios of 13.9:10.7:1 (for the upstream station) and 11.7:9.2:1 (for the downstream stations) of dissolved nutrients are rather low indicating severe carbon limitation of bacterioplankton. Based on our results we conclude that the heterotrophic bacterial community is not significantly effected by the input of treated sewage but faecal contamination is readily detectable over a comparatively long reach of 30 km.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Admiraal, W. & W. Van Zanten, 1988. Impact of biological activity on detritus transported in the lower river Rhine: an exercise in ecosystem analysis. Freshwat. Biol. 20: 215–290.
Ammerman, J. W., 1991. Role of Ecto-Phosphohydrolases in Phosphorus Regeneration in Estuarine and Coastal Environments. In R. D. Chrost (ed.), Microbial Enzymes in Aquatic Environments, Springer-Verlag, New York, 1991: 165–183.
Barcina, I., I. Arana, J. Iriberri & L. Egea, 1986. Factors affecting the survival of E. coli in a river. Hydrobiologia 141 (Dev. Hydrobiol. 36): 249–253.
Berg, J. D. & L. Fiksdal, 1988. Rapid detection of total and fecal coliforms in water by enzymatic hydrolysis of 1202 1119 V 2 4-methylumbelliferone-,β-D-galactosidase. Appl. Envir. Microbiol. 54: 2118–2122.
Billen, G., P. Servais & S. Bequevort, 1990. Dynamics of bacterioplankton in oligotrophic and eutrophic aquatic environments: bottom-up or top-down control? Hydrobiologia 207 (Dev. Hydrobiol. 62): 27–32.
Boon, P.I., 1991. Enzyme Activities in Billabongs of Southeastern Australia. In R. J. Chrost (ed.), Microbial Enzymes in Aquatic Environments, Springer-Verlag, New York, 1991: 286–297.
Boon, P. I., 1993. Organic matter degradation and nutrient regeneration in Australian fresh waters: 111. Size fractionation of phosphatase activity. Arch. Hydrbiol. 126: 339–360.
Cembella, A. D., N. J. Anita & P. J. Harrison, 1984. The utilization of inorganic and organic phosphorus compounds as nutrients of eucaryotic microalgae: a multidisciplinary perspective. In R. J. Chrost (ed.), Microbial Enzymes in Aquatic Environments. Springer-Verlag, New York: 1991.
Chang, G. W. & J. Brill & R. Lum, 1989. Proportion of β-D-Dglucuronidase-negative Escherichia coli in human fecal samples. Appl. envir. Microbiol. 55: 335–339.
Chrost, R. J., (ed.) 1991. Microbial enzymes in aquatic environments. New York, 310 pp.
Chrost, R. J., U. Münster, H. Rai, D. Albrecht, P. K. Witzel & J. Overbeck, 1989. Photosynthetic production and exoenzymatic degradation of organic matter in the euphotic zone of a eutrophic lake. J. Plankton Res. 11: 223–242.
Chrost, R. J. & J. Overbeck, 1987. Kinetics of alkaline phosphatase activity and phosphorus availability for phytoplankton and bacterioplankton in Lake Plußsee (North German eutrophic lake). Microb. Ecol. 13: 229–248.
Clark, D. L., B. B. Milner, M. H. Stewart, R. L. Wolfe & B. H. Olson, 1991. Comparative study of commercial 4-methylumbelliferyl, β-D-glucuronide preparations with the Standard Methods membrane filtration fecal coliform test for detection of Escherichia coli in water samples. Appl. envir. Microbiol. 57: 1528–1534.
Cotner, J. B. & R. G. Wetzel, 1991. Bacterial Phosphatases from Different Habitats in a Small Hardwater Lake. In R. D. Chrost (ed.), Microbial Enzymes in Aquatic Environments, Springer-Verlag, New York, 1991: 187–202.
Covert, T. C., L. C. Shadix, E. W. Rice, J. R. Haines & R. W. Freyberg, 1989. Evaluation of the autoanalysis Colilert test for detection and enumeration of total coliforms. Appl. envir. Microbiol. 55: 2443–2447.
Findlay, S., M. L. Pace, D. Lints, J. J. Cole, N. F. Caraco & B. Peierls, 1991. Weak coupling of bacterial and algal production in a heterotrophic ecosystem: The Hudson River estuary. Limnol. Oceanogr. 36: 268–278.
Francko, D. A., Filtration and Buoyant Density Characterization of Algal Alkaline Phosphatase. In R. D. Chrost (ed.). Microbial Enzymes in Aquatic Environments, Springer-Verlag, New York, 1991: 227–238.
Friedrich, G. & M. Viehweg, 1984. Recent developments of the phytoplankton and its activity in the Lower Rhine. Verh. int. Ver. Limnol. 22: 2029–2035.
Fuhrman, J. A. & F. Azam, 1980. Bacterioplankton secondary production estimates for coastal waters of British Columbia, Antarctica and California. Appl. envir. Microbiol. 39: 1085–1095.
Giammanco, G., S. Pignato & M. Biondi, 1992. An enzymatic procedure for the confirmation of total coliforms and Escherichia coli enumeration from water. Zbl. Hyg. 193: 99–105.
Goldman, J. G., D. A. Caron & M. R. Dennett, 1987. Nutrient cycling in a microflagellate food chain: IV Phytoplanktonmicrofiagellate interactions. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 38: 75–87.
Gonzalez, J. M., J. Iriberri, L. Egea & I. Barcina, 1992. Characterization of culturability, protistan grazing, and death of enteric bacteria in aquatic ecosystems. Appl. envir. Microbiol. 58: 998–1004.
Güde, H., B. Haibel & H. Müller, 1985. Development of planktonic bacterial populations in a water column of Lake Constance (Bodensee-Obersee). Arch. Hydrobiol. 105: 59–77.
Halemejko, G. Z. & R. J. Chrost, 1986. Enzymatic hydrolysis of proteinaceous particulate and dissolved material in an eutrophic lake. Arch. Hydrobiol. 107: 1–21.
Hoppe, H.-G., 1983. Significance of exoenzymatic activities in the ecology of brackish water: measurements by means of methylumbelliferyl — substrates. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 11: 299–308.
Iriberri, J., A. Begona, M. Unanue, I. Barcina & L. Egea, 1993. Channelling of bacterioplanktonic production towards phagotrophic flagellates and ciliates under different seasonal conditions in a river. Microb. Ecol. 26: 111–124.
Jones, S. E. & M. A. Lock, 1993. Seasonal determinations of extracellular hydrolytic activities in heterotrophic and mixed heterotrophiclautotrophic biofilms from two contrasting rivers. Hydrobiologia 257: 1–16.
Jørgensen, N. O. G., 1987. Free amino acids in lakes: concentrations and assimilation rates in relation to phytoplankton and bacterial production. Limnol. Oceanogr. 32: 97–111.
Karner, M., D. Fuks & G. J. Herndl, 1992. Bacterial activity along a trophic gradient. Microb. Ecol. 24: 243–257.
Kasimir, G. D., 1992. Microbial investigations in the River Danube: Measuring microbial activities and biomass. Arch. Hydrobiol. Suppl. 84: 101–114.
Kasimir, G. D. & G. Kavka, 1988. Untersuchung der zählbaren und züchtbaren Bakterien in einem Laufstauökosystem (Donaustau Altenwörth). Wasser and Abwasser 32: 57–88.
Kato, K. & H.-H. Stabel, 1984. Studies on the carbon flux from phyto- to bacterioplankton communities in Lake Constance. Arch. Hydrobiol. 102: 177–192.
Kavka, G., 1986. Zur Methodik des Fäkalstreptokokkennachweises in Abwasser und Flußwasser. Wasser and Abwasser 30: 185–203.
Kavka, G., 1987. Die bakterielle Wasserbeschaffenheit der Österreichischen Donau. Wasser and Abwasser 31: 305–344.
Kirchman, D. L., Y. Suzuki, C. Garside & H. W. Ducklow, 1991. High turnover rates of dissolved organic carbon during a spring phytoplankton bloom. Nature 352: 612–614.
Kiss, K. T. & S. I. Genkal, 1993. Winter blooms of centric diatoms in the River Danube and its side-arms near Budapest (Hungary). Hydrobiologia 269/270 (Dev. Hydrobiol. 90): 317–325.
Leff, L. G., 1994. Stream bacterial ecology: A neglected field? ASM news 60: 135–138.
Liepolt, R., (ed.) 1967. Die Limnologie der Donau. Schweitzerbart'sche Verlagsbuchhandlung, Stuttgart.
Martinez, J., J. Garcia-Lara & J. Vives-Rego, 1989. Estimation of Escherichia coli mortality in seawater by the decrease in 3H-label and electron transport system activity. Microb. Ecol. 17: 219–225.
Münster, U., 1994. Studies on Phosphatase Activities in Humic Lakes. Envir. Int. 20: 49–59.
Münster, U., J. Nurminen, P. Einiö & J. Overbeck, 1992. Extracellular enzymes in a small polyhumic lake: origin, distribution and activities. Hydrobiologia 243/244 (Dev. Hydrobiol. 79): 47–59.
Olsson, H., 1991. Phosphatase Activity in an Acid, Limed Swedish Lake. In R. D. Chrost (eds), Microbial Enzymes in Aquatic Environments, Springer-Verlag, New York, 1991: 206–218.
Parsons, T., Y. Maita & C. Lalli (eds), 1984. A manual for chemical and biological methods for seawater analysis. Oxford, 173 pp.
Pettersson, K., 1980. Alkaline phosphatase activity and algal surplus phosphorus as phosphorus deficiency indicator in Lake Erken. Arch. Hyrobiol. 89: 54–87.
Pettibone, G. W., 1992. The use of lauryl tryptose broth containing 4-methylumbelliferyl-β-D-glucuronide (MUG) to enumerate Escherichia coli from freshwater sediment. Letters in Applies Microbiology 15: 190–192.
Pomeroy, L. R. & D. Deibel, 1986. Temperature regulation of bas terial activity during the spring bloom in Newfoundland coasta waters. Science 233: 359–361.
Porter, K. G. & Y. S. Feig, 1980. The use of DAPI for identifying and counting aquatic microflora. Limnol. Oceanogr. 25: 943–948.
Rodinger, W., 1993. Chlorophyllgehalte des Phytoplanktons der Donau in den Jahren 1983–1990. Bericht der Bundesanstalt fair Gewässergüte, Wien 1993.
Rosso, A. L. & F. Azam, 1987. Proteolytic activity in coastal oceanic waters: depth distribution and relationship to bacterial populations. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 41: 231–240.
Scavia, D. & G. A. Laird, 1987. Bacterioplankton in Lake Michigan: dynamics, controls, and significance to carbon flux. Limnol. Oceanogr. 32: 1017–1033.
Servais, P. & G. Billen, 1991. Bacterioplankton in the Seine River (France): impact of the Parisian urban effluent. Can. J. Microbiol. 38: 56–64.
Sinasbaugh, R. L. & A. E. Linkins, 1988. Exoenzyme activity associated with lotic epilithon. Freshwat. Biol. 13: 57–72.
Somville, M., 1984. Measurement and study of substrate specificity of exoglucosidase activity in eutrophic water. Appl. envir. Microbiol. 48: 1181–1185.
Sorokin, Y. I. & T. I. Mamaeva, 1991. Role of planktonic bacteria in productivity and cycling of organic matter in the Eastern Pacific Ocean. Hydrobiologia 209: 39–50.
Stewart, A. J. & R. G. Wetzel, 1982. Phytoplankton contribution to alkaline phosphatase activity. Arch. Hydrobiol. 93: 265–271.
Talling, J. F. & J. Rzoska. 1967. The development of plankton in relation to hydrological regime in the Blue Nile. J. Ecol. 55: 637–662.
Tilzer, M. M., U. Gaedke, A. Schweizer, B. Beese & T. Weise, 1991. Interannual variability of phytoplankton productivity and related parameters in Lake Constance: no response to decreased phosphorus loading? J. Plankton Res. 13: 755–777.
Vives Rego, J., G. Billen, A. Fontigny & M. Somville, 1985. Free and attached proteolytic activity in water environments. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 21: 245–249.
Vrba, J., 1992. Seasonal extracellular enzyme activities in decomposition of polymeric organic matter in a reservoir. Arch. Hydrobiol. Beih. 37: 33–42.
Wetzel, R. G., 1981. Longterm dissolved and particulate alkaline phosphatase activity in a hardwater lake in relation to lake stability and phosphorus enrichments. Ver. int. Ver. Limnol. 21: 369–381.
Wiebe, W. J., J. W. M. Sheldon & L. R. Pomeroy, 1992. Bacterial growth in the cold: evidence for an enhanced substrate requirement. Appl. envir. Microbiol. 58: 359–364.
Wynne, D., B. Kaplan & T. Berman, 1991. Phosphatase Activities in Lake Kinneret Phytoplankton. In R. D. Chrost (ed.), Microbial Enzymes in Aquatic Environments, Springer-Verlag, New York, 1991: 220–225.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hoch, B., Berger, B., Kavka, G. et al. Influence of wastewater treatment on the microbial ecology of a large, temperate river system — the Danube River. Hydrobiologia 321, 205–218 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00143751
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00143751