Abstract
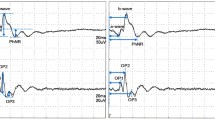
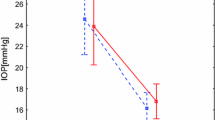
The hyperosmolarity response of the ocular standing potential was recorded in unilateral rhegmatogenous retinal detachment (8 eyes) and in the fellow ‘healthy’ eye (8 eyes). The hyperosmolarity response was greatly suppressed (M-4 SD: M and SD indicate respectively the mean and the standard deviation in normal subjects) in all affected eyes (p < 0.005), and slightly abnormal in 2 fellow eyes. The L/D ratio was normal in 2 affected eyes and in all fellow eyes. The hyperosmolarity response in the affected eyes was still greatly suppressed 14 months after successful surgical treatment.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Everett WG (1963) The fellow-eye syndrome in retinal detachment. Amer J Ophthal 56:739–748
Inahara M (1973) Studies on fine structure of experimental retinal detachment. Acta Soc Ophthal Jpn 77:1002–1019
Kawasaki K, Yamamoto S and Yonemura D (1977) Electrophysiological approach to clinical test for the retinal pigment epithelium. Acta Soc Ophthal Jpn 81:1303–1312
Kroll AJ and Machemer R (1968) Experimental retinal detachment in the owl monkey. III. Electron microscopy of retina and pigment epithelium. Amer J Ophthal 66:410–427
Madachi-Yamamoto S (1982a) Electrophysiological evaluation of retinal pigment epithelium for clinical use (I) Hyperosmolarity response of the standing potential and its origin. Acta Soc Ophthal Jpn 86:374–384
Madachi-Yamamoto S (1982b) Electrophysiological evaluation of retinal pigment epithelium for clinical use (II) Hyperosmolarity response in normal subjects. Acta Soc Ophthal Jpn 86:385–395
Madachi-Yamamoto S (1982c) Electrophysiological evaluation of retinal pigment epithelium for clinical use (III) Clinical study in several chorioretinal diseases. Acta Soc Ophthal Jpn 86:396–413
Madachi-Yamamoto S, Yonemura D and Kawasaki K (1984) Hyperosmolarity response of ocular standing potential as a clinical test for retinal pigment epithelium activity. Normative data. Docum Ophthal 57: 153–162
Makabe R (1969) Elektroretinogramm bei zu Netzhautablösung disponierten Augen. Klin Mbl Augenheilk 154:450–452
Merin S, Feiler V, Hyams S, Ivry M, Krakowski D, Landau L, Maythar B, Michaelson IC, Scharf J, Schul A and Ser I (1971) The fate of the fellow eye in retinal detachment. Amer J Ophthal 71:477–481
Mori T, Tazawa Y, Obara Y, Takahashi Y and Sasamori H (1982) ERG c-wave changes in fellow eyes of retinal detachment. Folia Ophthal Jpn 33:1578–1584
Okuma M (1972) Ultrastructural observations of the choroid and the pigment epithelium on experimental retinal detachment. Scanning electron microscopic observations of the retinal pigment epithelium. Acta Soc Ophthal Jpn 76:377–384
Tazawa Y (1980) Human ERG c-wave; its characteristics and clinical application. Folia Ophthal Jpn 31:1223–1248
Yonemura D and Kawasaki K (1979) New approaches to ophthalmic electrodiagnosis by retinal oscillatory potential, drug-induced responses from retinal pigment epithelium and cone potential. Docum Ophthal 48:163–222
Yonemura D, Kawasaki K, Kawasaki C and Usukura H (1972) The oscillatory potential of the ERG in idiopathic detachment of the retina. Acta Soc Ophthal Jpn 76:267–270
Yonemura D, Kawasaki K, Tanabe J and Yamamoto S (1978) Susceptibility of the standing potential of the eye to acetazolamide and its clinical application. Folia Ophthal Jpn 29:408–416
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kawasaki, K., Madachi-Yamamoto, S. & Yonemura, D. Hyperosmolarity response of ocular standing potential as a clinical test for retinal pigment epithelium activity rhegmatogenous retinal detachment. Doc Ophthalmol 57, 175–180 (1984). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00143081
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00143081