Abstract
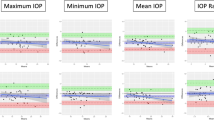
The standing potential of the eye is decreased by intravenous administration of hypertonic solutions. This hyperosmolarity-induced response has been recorded in normal subjects by the use of electro-oculography (EOG) in the dark. An intravenous administration of Fructmanit® (1.4 × 103 mOsmol) (150 ∼ 500ml, 2.37 ∼ 9.70ml/kg, 0.08 ∼ 0.36 ml/kg/min) was used to evoke the hyperosmolarity response. The amplitude of the response was expressed in percentage, V0 − Vmin/V0 × 100, where V0 is the base value of the EOG before administration of the hypertonic solution and Vmin is a minimum EOG amplitude after administration. The distribution of the amplitude of the hyperosmolarity response was approximated by the normal distribution in normal subjects. The minimum, the maximum, the mean and the standard deviation of the amplitude of the hyperosmolarity response were respectively 34.2%, 52.3%, 42.6% and 4.6% in normal subjects. The normal range of the hyperosmolarity response would be 33.4 ∼ 51.8% (M ± 2SD). The hyperosmolarity response, which originates mainly in the retinal pigment epithelium, is a useful new quantitative and specific test of the activity of the retinal pigment epithelium in clinical practice.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arden GB and Barrada A (1962) Analysis of the electro-oculograms of a series of normalsubjects. Brit J Ophthal 46:468–482
Arden GB and Kelsey JH (1962) Changes produced by light in the standing potential of the human eye. J Physiol 161:189–204
Arden GB, Barrada A and Kelsey JH (1962) New clinical test of retinal function based upon the standing potential of the eye. Brit J Ophthal 46:449–467.
Gouras P and Carr RE (1965) Light-induced DC responses of monkey retina before and after central retinal artery interruption. Invest Ophthal 4:310–317
Kawasaki K, Yamamoto S and Yonemura D (1977) Electrophysiological approach to clinical test for the retinal pigment epithelium. Acta Soc Ophthal Jpn 81:1303–1312
Madachi-Yamamoto S (1980) Abolition of the light rise by aspartate. Acta Soc Ophthal Jpn 84:607–616
Madachi-Yamamoto S (1982) Electrophysiological evaluation of retinal pigment epithelium for clinical use (1) hyperosmolarity response of the standing potential and its origin. Acta Soc Ophthal Jpn 86:374–384
Mita T, Nikara T, Inomata K and Shimazaki Y (1963) Variations in the standing potential of the human eye due to light and dark adaptation. J Iwate Med Ass 14:243–251
Mukoh S, Kawasaki K and Yonemura D (1982) Hyperosmolarity-induced changes in the transepithelial potential of the retina. Acta Soc Ophthal Jpn 86:970–975
Nilsson SEG and Skoog K-O (1975) Covariation of the simultaneously recorded c-wave and standing potential of the human eye. Acta Ophthal 53:721–730
Pernice D, Täumer R, Rohde N and Hennig J (1976) Several clinical EOG tests - an overview. Proposal of a varied EOG test. Bibl Ophthal 85:25–34
Takahashi Y, Otsuka T, Sasamori H, Takamatsu T, Inomata K, Mita T and Tazawa Y (1979) DC-registered c-wave in human normal eyes and possibility of its clinical application. Proc 16th ISCEV Symp. Jpn J Ophthal Suppl:113–118
Yonemura D, Kawasaki K, Usukura H, Yanagida T and Yamamoto S (1977) Electroretinogram and electro-oculogram in occlusion of the central retinal artery. Acta Soc Ophthal Jpn 81:323–329
Yonemura D and Kawasaki K (1979) New approaches to ophthalmic electrodiagnosis by retinal oscillatory potential, drug-induced responses from retinal pigment epithelium and cone potential. Docum Ophthal 48:163–222
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Madachi-Yamamoto, S., Yonemura, D. & Kawasaki, K. Hyperosmolarity response of ocular standing potential as a clinical test for retinal pigment epithelium activity normative data. Doc Ophthalmol 57, 153–162 (1984). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00143079
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00143079