Abstract
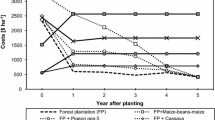
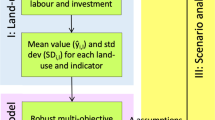
Input/output data from tree growing experiments in Southeast Asia were analysed within the framework of a model of a smallholder farm. Data on cropping were obtained from surveys of farmers. Prior to formulating a whole farm model, this input/output data were modified in two ways: (a) a yield penalty was imposed upon a continuous cropping regime to reflect the impact of land degradation; (b) an agroforestry (intercropping) activity was synthesised by reference to an existing agroforestry bioeconomic model. The modelling framework was conventional linear programming. The interplay of land area availability, land and labour productivity, and interest rates lead to a relatively complex picture, even for the simplified farming systems that were examined. Model results showed a clear indication of the potential role of trees, but this potential role decreased with increasing interest rates. The analysis suggested that smaller farms will be less inclined towards tree growing. A mixture of trees and crops appears attractive, on purely economic grounds, over a wide range of interest rates and land areas. Consideration of factors outside the model, such as risk aversion objectives of smallholders, and their limited opportunities to borrow for investments in tree planting, reinforce the tendency to combine trees and crops.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barnard, CW and Nix, JS (1979) Farm Planning and Control. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK
Betters, DR (1988) Planning optimal economic strategies for agroforestry systems. Agroforestry Systems 7: 17–31
ICRAF (1993) Annual Report. ICRAF, Nairobi, Kenya
Kuusipalo J and Hadi TS (1995) Forest plantation approach in rehabilitation of Imperata grasslands: research in Riam Kiwa, South Kalimantan. Workshop on agroforestry innovations for Imperata grassland rehabilitation, January 23–27, Banjarmasin, Indonesia
Menz, KM, O'Brien, GC and Parilla, LS (1995) A profile of upland farming systems on sloping land in the Philippines. ACIAR Working Paper 46, ACIAR, Canberra, Australia
Nelson, R, Grist, P, Menz, K, Paningbatan, E and Mamicpic, M (1996) A cost-benefit analysis of hedgerow intercropping in the Philippine uplands using SCUAF. Imperata project paper 1996/2. Centre for Resource and Environmental Studies, Australian National University, Canberra, Australia
Rae, AN (1994) Agricultural Management Economics: Activity Analysis and Decision Making. CAB International, Wallingford, UK
Raintree, J and Warner, K (1986) Agroforestry pathways for the intensification of shifting cultivation. Agroforestry Systems 4: 39–54
Sabarnurdin, MS, Iswantoro, H and Adjers, G (eds) (1991) Forestation of Alang-alang Grassland: Lessons from South Kalimantan. Gadjah Mada University, Yogyakarta, Indonesia
Tambupolon, A, Otsamo, A, Kuusipalo, J and Jaskari, H (1995) From Grasslands to Forests: Profitable and Sustainable Reforestation of Alang-alang Grasslands in Indonesia. ENSO Forest Development Oy Ltd, Banjabaru, South Kalimantan, Indonesia
Thomas, TH, Willis, RW, Bezkorowajnyj, PG, Sangkul, S and Ng, AP (1993) A Compendium of Technical Overviews for the BEAM Spreadsheet Models: TANZMOD, RRYIELD, POPMOD, and ROWECON4. The BEAM Project School of Agricultural and Forest Sciences, University of Wales, Bangor, Gwynedd, UK
Turvey, ND (1995) Afforestation of Imperata Grasslands in Indonesia. ACIAR technical reports 33, ACIAR, Canberra, Australia
Verinumbe, I, Knipscheer, HC and Enabor, GE (1984) The economic potential for leguminous tree crops in zero-tillage cropping in Nigeria: a linear programming model. Agroforestry Systems 2: 129–138
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Menz, K., Grist, P. Economic opportunities for smallholders to combine pulpwood trees and food crops. Agroforest Syst 36, 221–232 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00142875
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00142875