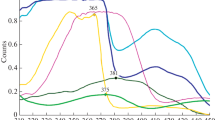
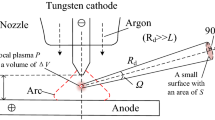
Summary
Measurements are described as a basis for specifications of protective glasses in welding operations.
§ 2 deals with measurements of the thresholds of ultraviolet and infrared radiation, which produce a just perceptible change in the eye. These measurements were carried out by Fischer, Ver-meulen and Eymers for monochromatic radiation. By means of a harm-factor the equivalent dose of radiation with an arbitrary spectral distribution is calculated.
In § 3 measurements of the ultraviolet and infrared radiant flux in welding operations are described and the maximum permissible transmission factor in these spectral regions is determined.
§ 4 deals with measurements of the visible radiation and the maximum and minimum, values of the visible transmission factor.
In § 5a comparison has been made with American, British and German Specifications.
Zusammenfassung
Es werden Messungen beschrieben, welche die Basis sind für die Bestimmung der richtigen Durchlässigkeit von Schutzgläsern für Schweisser.
Par. 2 beschäftigt sich mit Schwellenwertmessungen für das Ultraviolett und Infrarot, wobei als Mass der Schwelle die eben merkbare Veränderung im Auge gewählt wurde. Solche Messungen haben Fischer, Vermeulen und Eymers ausgeführt. Mittels eines Schädigungsfaktors wurde die Aequivalentdosis bei arbiträrer spektraler Verteilung berechnet.
In Par. 3 wird über Messungen der ultravioletten und infraroten Strahlung des Schweissbogens berichtet und der Faktor der maximalen Durchlässigkeit in diesen Spektralgebieten ermittelt.
Der Par. 4 beschäftigt sich in gleicher Weise mit dem sichtbaren Teil der Schweissbogenstrahlung und mit der Beleuchtung der Werkstätte.
Im Par. 5 endlich werden die amerikanischen, englischen und deutschen Vorschriften für Schweisserschutzgläser mit einander verglichen.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Federal Specifications GGG-G 541 (goggles) and GGG-H 191a (helmets) 1930, 32.
Britisch Standard Specification - No. 676, 1936.
Deutsche Normen DIN 4646, 4647 - 1933, 37.
Rapport over Ultravioletverlichting. - 1932. Ned. Tijdschr. Geneesk. 76, 34.
Cogan, D. C. and Kinsey, V. E. (1946) - Arch. of Ophth. 35, 670.
Fischer, F. P., Vermulden, D. and Eymers, J. G. (1935) - Arch. f. Augenheilk. 109, 462.
Heel, van A. C. S. (1933) - Polytechnic Weekblad 27, 584.
Rooks, R. (1945) - Iowa Med. Soc. 35, 141 (after Ronge, H. E.Ultraviolet radiation with artificial illumination. Upsala 1948, 54).
Rutgers, G. A. W. (1942 a) - Electrotechniek 20, 219.
—, (1942 b) - Electrotechniek 20, 287.
—, (1946) - Electrotechniek 24, 249.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Investigation carried out under the auspices of the Dutch National Committee on Illumination in the KEMA Laboratory under the guidance of Dr. D. Ver-meulen, to whom the author is much indebted.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rutgers, G.A.W. Protective glasses for welding. Doc Ophthalmol 4, 320–334 (1950). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00141320
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00141320