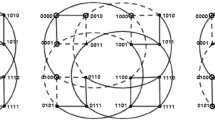
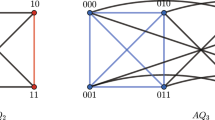
Abstract
The interconnection network in large-scale parallel/distributed supercomputer systems is a crucial component. Three networks are overviewed here. Multistage cube networks represent an important family of networks, which includes the omega, n-cube, multistage shuffle-exchange, delta, baseline, SW-banyan, and Generalized Cube. This family has been used or proposed for use in such systems as staran, pasm, Ultracomputer, the BBN Butterfly, the IBM RP3, and data-flow machines. The multistage cube topology, distributed routing control, and ability to be partitioned into independent subnetworks are examined. The Extra Stage Cube (ESC), a single-fault-tolerant multistage cube network, is described. The structure, control, and partitionability of the ESC, and how it functions when multiple faults occur, are presented. The Dynamic Redundancy (DR) network, a fault-tolerant multistage cube network that supports the incorporation of spare processors for fault tolerance, is discussed. Its structure, control, and partitionability into single-fault-tolerant subnetworks are explained.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams III, G. B., and Siegel, 39–01 J. 1982. The extra stage cube: a fault-tolerant interconnection network for supersystems. IEEE Trans. Comput. C-31 (May), 443–454.
Adams III, G. B., and Agrawal, D. P., and Siegel, H. J. 1987. A survey and comparison of faul-ttolerant multistage interconnection networks. Computer (in press).
Adams III G. B., and Siegel, H. J. 1984. Modifications to improve the fault tolerance of the extra stage cube interconnection network. In 1984 International Conference on Parallel Processing (August), pp. 169–173.
Barnes, G. H., and Lundstrom, S. F. 1981. Design and validation of a connection network for manyprocessor multiprocessor systems. Computer, 14 (December), 31–41.
Batcher, K. E. 1974. Staran parallel processor system hardware. In AFIPS 1974 National Computer Conference (May), pp. 405–410.
Batcher, K. E. 1976. The flip network in Staran. In 1976 International Conference on Parallel Processing (August), pp. 65–71.
Batcher, K. E. 1977. Staran series E. In 1977 International Conference on Parallel Processing (August), pp. 140–143.
Batcher, K. E. 1980. Design of a massively parallel processor. IEEE Trans. Comput., C-29 (September), 836–844.
Batcher, K. E. 1982. Bit serial parallel processing systems. IEEE Trans. Comput., C-31 (May), 377–384.
Briggs, F. A., Fu, K.-S., Hwang, K., and Wah, B. W. 1982. Pumps architecture for pattern analysis and image database management. IEEE Trans. Comput., C-31 (October), 969–982.
Broomell, G., and Heath, J. R. 1983. Classification categories and historical development of circuit switching topologies. ACM Comput. Surveys, 15 (June), 95–133.
Crowther, W., Goodhue, J., Starr, E., Thomas, R., Williken, W., and Blackadar, T. 1985. Performance measurements on a 128-node Butterfly parallel processor. In 1985 International Conference on Parallel Processing (August), pp. 531–540.
Davis IV, N. J., Hsu, W. T.-Y., and Siegel, H. J. 1985. Fault location techniques for distributed control interconnection networks. IEEE Trans. Comput., (October), 902–910.
Delp, E. J., Siegel, H. J., Whinston, A., and Jamieson, L. H. 1985. An intelligent operating system for executing image understanding tasks on a reconfigurable parallel architecture. In IEEE Computer Society Workshop on Computer Architecture for Pattern Analysis and Image Database Management (November), pp. 217–224.
Dennis, J. B., Boughton, G. A., and Leung, C. K. C. 1980. Building blocks for data flow prototypes. In Seventh Annual Symposium on Computer Architecture (May), pp. 1–8.
Feng, T. Y. 1981. A survey of interconnection networks. Computer, 14 (December), 12–27.
Feng, T. Y., and Wu, C.-L. 1981. Fault-diagnosis for a class of multistage interconnection networks. IEEE Trans. Comput., C-30 (October), 743–758.
Feng, T. Y., and Zhang, Q. 1985. Fault diagnosis of multistage interconnection networks with four valid states. In Fifth International Conference on Distributed Computing Systems (May), pp. 218–226.
Filip, A. E. 1982. A distributed signal processing architecture. In Third International Conference on Distributed Computing Systems (October), pp. 49–55.
Flynn, M. J. 1966. Very high-speed computing systems. Proc. IEEE, 54 (December), 1901–1909.
Goke, G. R., and Lipovski, G. J. 1973. Banyan networks for partitioning multiprocessor systems. In First Annual Symposium on Computer Architecture (December), pp. 21–28.
Gottlieb, A., Grishman, R., Kruskal, C. P., McAuliffe, K. P., Rudolph, L., and Snir, M. 1983. The NYU Ultracomputer—designing an MIMD shared-memory parallel computer. IEEE Trans. Comput., C-32 (February), 175–189.
Hillis, W. D. 1985. The Connection Machine. MIT Press, Cambridge, MA.
Hockney, R. W., and Jesshope, C. R. 1981. Parallel Computers. Adam Hilger, Bristol, England.
Hwang, K., and Briggs, F. A. 1984. Computer Architecture and Parallel Processing. McGraw-Hill, New York, NY.
Intel Corporation. 1985. A New Direction in Scientific Computing. Order 28009-001, Intel Corporation.
Jeng, M., and Siegel, H. J. 1986a. A fault-tolerant multistage interconnection network for multiprocessor systems using dynamic redundancy. In Sixth International Conference on Distributed Computing Systems (June), pp. 70–77.
Jeng, M. and Siegel, H. J. 1986b. Implementation approach and reliability estimation of dynamic redundancy networks. In 1986 Real-Time Systems Symposium (December), pp. 79–88.
Jones, A. K., Chansler, R. J., Jr., Durham, I., Feiler, P., and Schwans, K. 1977. Software management of Cm*—a distributed multiprocessor. In AFIPS 1977 National Computer Conference (June), pp. 657–663.
Kapur, R. N., Premkumar, U. V. and Lipovski, G. J., 1980. Organization of the TRAC processor-memory subsystem. In AFIPS 1980 National Computer Conference (June), pp. 623–629.
Lawrie, D. H. 1975. Access and alignment of data in an array processor. IEEE Trans. Comput., C-24 (December), 1145–1155.
Malek, M., and Myre, W. W. 1981. A description method for interconnection networks. IEEE Technical Committee Distrib. Processing Quart., (February), 1–6.
Masson, G. M., Gingher, G. C., and Nakamura, S. 1979. A sampler of circuit switching networks. Computer, 12 (June), 32–48.
McMillen, R. J., and Siegel, H. J. 1980. The hybrid cube network. In Distributed Data Acquisition, Computing, and Control Symposium (December), pp. 11–22.b
McMillen, R. J., and Siegel, H. J. 1985. Evaluation of cube and data manipulator networks. J. Parallel Distrib. Comput., 2 (February), 79–107.
McMillen, R. J., Adams III G. B., and Siegel, H. J. 1981. Performance and implementation of 4 × 4 switching nodes in an interconnection network for Pasm. In 1981 International Conference on Parallel Processing (August), pp. 229–233.
McDonald, W. C., and Williams, J. M. 1978. The advanced data processing test bed. In IEEE Computer Society Second International Computer Software and Applications Conference (March), pp. 346–351.
Nutt, G. J. 1977a. Microprocessor implementation of a parallel processor. In Fourth Annual Symposium on Computer Architecture (March), pp. 147–152.
Nutt, G. J. 1977b. A parallel processor operating system comparison. IEEE Trans. Software Eng., SE-3 (November), 467–475.
Patel, J. H. 1981. Performance of processor-memory interconnections for multiprocessors. IEEE Trans. Comput., C-30 (October), 771–780.
Pease III, M. C. 1977. The indirect binary n-cube microprocessor array. IEEE Trans. Comput., C-26 (May), 458–473.
Pfister, G. F., Brantley, W. C., George, D. A., Harvey, S. L., Kleinfelder, W. J., McAuliffe, K. P., Norton, V. A. and Weiss, J. 1985. The IBM Research Parallel Processor Prototype (RP3): introduction and architecture. In 1985 International Conference on Parallel Processing (August), pp. 764–771.
Premkumar, U. V., Kapur, R. N., Malek, M., Lipovski, G. J., and Horne, P. 1980. Design and implementation of the Banyan interconnection network in Trac. In AFIPS 1980 National Computer Conference (June), pp. 643–653.
Sejnowski, M. C., Upchurch, E. T., Kapur, R. N., Charlu, D. P. S., and Lipovski, G. J. 1980. An overview of the Texas Reconfigurable Array Computer. In AFIPS 1980 National Computer Conference (June), pp. 631–641.
Siegel, H. J. 1977. Analysis techniques for SIMD machine interconnection networks and the effects of processor address masks. IEEE Trans. Comput., C-26 (February), 153–161.
Siegel, H. J. 1979. Interconnection networks for SIMD machines. Computer, 12 (June), 57–65.
Siegel, H. J. 1980. The theory underlying the partitioning of permutation networks. IEEE Trans. Comput., C-29 (September), 791–801.
Siegel, H. J. 1985. Interconnection Networks for Large-Scale Parallel Processing: Theory and Case Studies. Lexington Books, D. C. Heath and Company, Lexington, MA.
Siegel, H. J., and McMillen, R. J. 1981. The multistage cube: a versatile interconnection network. Computer, 14 (December), 65–76.
Siegel, H. J., and Smith, S. D. 1978. Study of multistage SIMD interconnection networks. In Fifth Annual Symposium on Computer Architecture (April), pp. 223–229.
Siegel, H. J., McMillen, R. J., and Mueller, P. T. Jr. 1979. A survey of interconnection methods for reconfigurable parallel processing systems. In AFIPS 1979 National Computer Conference (June), pp. 529–542.
Siegel, H. J., Mueller, P. T. Jr. and Smalley, H. E. Jr 1978. Control of a partitionable multimicroprocessor system. In 1978 International Conference on Parallel Processing (August), pp. 9–17.
Siegel, H. J., Schwederski, T., Davis IV, N. J., and Kuehn, J. T. 1984. pasm: a reconfigurable parallel system for image processing. In Workshop on Algorithm-guided Parallel Architectures for Automatic Target Recognition (July), 263–291. (Also appears in the ACM sigarch newsletter: Comput. Architect. News, 12, 4 (September), 7–19.)
Siegel, H. J., Siegel, L. J., Kemmerer, F. C., Mueller, P. T. Jr., Smalley, H. E. Jr. and Smit, S. D. 1981. Pasm: a partitionable simd/mimd system for image processing and pattern recognition. IEEE Trans. Comput., C-30 (December), 934–947.
Smith, S. D., and Siegel, H. J. 1978. Recirculating, pipelines, and multistage simd interconnection networks. In 1978 International Conference on Parallel Processing (August), pp. 206–214.
Stone, H. S. 1980. Parallel computers. In H. S. Stone (ed.), Introduction to Computer Architecture, 2nd ed. Science Research Associates, Chicago, IL, 363–425.
Swan, R. J., Bechtolsheim, A., Lai, K. W., and Ousterhout, J. K. 1977a. The implementation of the Cm* multimicroprocessor. In AFIPS 1977 National Computer Conference (June), pp. 645–655.
Swan, R. J., Fuller, S., and Siewiorek, D. P. 1977b. Cm*: a modular multimicroprocessor. In AFIPS 1977 National Computer Conference (June), pp. 637–644.
Thanawastien, S., and Nelson, V. P. 1981. Interference analysis of shuffle/exchange networks. IEEE Trans. Comput. C-30 (August), 545–556.
Thurber, K. J. 1976. Large Scale Computer Architecture: Parallel and Associative Processors. Hayden Book Company, Rochelle Park, NJ.
Thurber, K. J. 1979. Parallel processor architectures—part 1: general purpose systems. Comput. Design, 18 (January), 89–97.
Thurber, K. J., and Masson, G. M. 1979. Distributed-Processor Communication Architecture. Lexington Books, D. C. Heath and Company, Lexington, MA.
Wu, C.-L., and Feng, T. Y. 1980. On a class of multistage interconnection networks. IEEE Trans. Comput., C-29 (August), 694–702.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This research was supported by the Air Force Office of Scientific Research under grant F49620-86-K-0006, the Rome Air Development Center under grant F30602-83-K-0119, and the Purdue Research Foundation David Ross Grant 1985/86 no. 0857.
currently with the Supercomputing Research Center, 4380 Forbes Blvd., Lanham, MD 20706 (as of June 1, 1987).
currently with Computer Science Department, University of Illinois, Urbana-Champaign, IL 61801.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Siegel, H.J., Tsun-Yuk Hsu, W. & Jeng, M. An introduction to the multistage cube family of interconnection networks. J Supercomput 1, 13–42 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00138604
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00138604