Abstract
Whilst wing size measurements are often used in Drosophila to discriminate between groups of individuals, the choice of the particular characters measured is generally not justified.
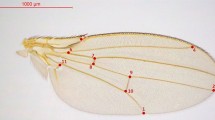
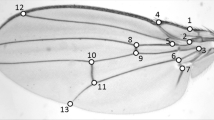
Statistical and genetical properties of 8 characters measured on the left wing, in three stocks of Drosophila melanogaster were analysed. A multivariate analysis is done by studying correlations between characters and by interpreting the first factor of a principal component analysis.
The results shows that only one measurement is sufficient in order to discriminate between the stocks, as far as mean values are concerned; wing length is, in that case, the best character since its variance has a relatively high genetic component. When dealing with correlation among characters as a way of estimating shape, four measurements are needed and sufficient. This shows the necessity of choosing the characters to be measured.
Similar content being viewed by others
Références
Alonso, A. & Munoz, A., 1984. Biometric characterisation of some wing measurement in Drosophila melanogaster. Dres. Inf. Serv. 60: 47–48.
Atchley, W. R., 1980. M-statistics and morphometric divergence. Science 208: 1059–1060.
Biemont, C., 1986. Transposition of the mobile element mdg-1 in Dropophila melanogaster populations selected for viability (soumis pour publication).
Blackith, R. E. & Reyment, R. A., 1971. Multivariate morphometrics. Academic press. London-New York.
Cavicchi, S., Giorgi, G. & Mochi, M., 1978. Investigation on carly divergence between populations of Drosophila melanogaster kept at different temperatures. Genetics 48: 81–87.
Cavicchi, S., Ouerra, D., Glorgi, G. & Pezzoli, C., 1988. Temperature-related divergence in experimental populations of Drosophila melanogaster. I. Genetic and developmental basis of wing size and shape variation. Genetics 109: 665–689.
David, J., Boequet, C. & De Scheemacker-Louis, M., 1977, Genetic latitudinal adaptation of Drosophila melanogaster: new discriminative biometrical traits between European and equatorial African populations. Genet. Res., Camb. 30: 247–255.
David, J. & Clavel, M. F., 1965. Interaction entre le génotype et le milleu d'élevage: conséquence sur les caractéristiques du dévelopment de la drosophile. Bull. biol. Fr. Belg. 94: 369–378.
Falconer, D. S., 1981. Introduction to quantitative genetics. Longman, New York.
Harter, H. L., 1960. Critical values for Dunean's new multiple range test. Biometrics 16: 671–685.
James, J. W., 1964. Comparing regression and correlation coefficients Appl. Statist. 13: 127–132.
Lefebvre, J., 1980. Introduction aux analyses statistiques multidimensionelles. Masson (2ième édit.).
Pontier, J., 1964. Une méthode d'analyse factorielle. Quelques applications à la Biologie. Thèse 3ième cycle, Lyon.
Prevosti, A., 1955. Geographical variability in quantitative traits in populations of Drosophila subobscura. Cold Spring Harb. Symp. quant. Biol. 20: 294–299.
Rao, C.R., 1953. Discriminant function for genetic differentíation and selection. Sankhya 12: 229–246.
Reeve, E. C. R. & Robertson, F. W., 1953. Studies in quantitative inheritance. II Analysis of a strain of Drosophila melanogaster selected for long wings. J. Genet. 51: 276–316.
Robertson, F. W. & Reeve, E. C. R., 1952. Studies in quantitative inheritance. I. The effects of selection of wing and thorax length in Drosophila melanogaster. J. Genet. 56: 416–448.
Rochetta, G., Alicchio, R. & Palenzone, D. L., 1974. Multivariate response to disruptive selection. Monitore zool, Ital. 10: 253–264.
Rouvier, R., 1966. L'analyse en composantes principaless son utilisation en génétique et ses rapports avec l'analyse diseriminatoire. Biometrics 22: 343–357.
Schluter, D., 1984. Morphological and phylogenetle relation among the Darwin's finches. Evolution 38: 921–930.
Takanashi, E. & Kitagawa, O., 1977. Quantitative analysis of genetic differentiation among geographical strains of Drosophila melanogaster. Dros. Inf. Serv. 52: 28.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Terzian, C. De l'optimisation du nombre de variables morphologiques dans la discrimination entre populations (le cas de l'aile chez Drosophila melanogaster). Genetica 69, 219–225 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00133525
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00133525