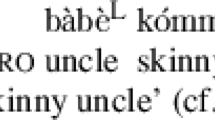This paper proposes a phonological analysis of the Bengali intonational system, using a descriptive framework developed by Pierrehumbert (1980) and others. Our analysis bears on a number of theoretical points. We argue that the Bengali facts support a typology of intonational tones that includes only pitch accents and boundary tones, and that the docking sites for boundary tones are the phrase edges provided under the theory of the Prosodic Hierarchy (Selkirk 1980). We show that Bengali intonational contours are governed by the obligatory Contour Principle (OCP), which forbids adjacent identical tones. Underlying contours that violate the OCP are converted to permissible surface forms by a phonological rule. We also bring Bengali data to bear on a long-standing controversy concerning phrasal stress: Bengali can be shown to have a default, phonologically assigned phrasal stress pattern; thus phrasal stress assignment cannot be reduced exclusively to focus and other semantic factors.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beckman, Mary and Janet Pierrehumbert: 1986, ‘Intonational Structure in Japanese and English’, Phonology Yearbook 3, 255–309.
Bolinger, Dwight: 1951, ‘Intonation: Levels vs. Configurations’, Word 7, 199–210.
Bolinger, Dwight: 1972, ‘Accent is Predictable (If You're a Mind Reader)’, Language 48, 633–644.
Bruce, Gösta: 1977, Swedish Word Accents in Sentence Perspective, Gleerup, Lund.
Chatterji, Suniti Kumar: 1921, ‘Bengali Phonetics’, Bulletin of the School of Oriental and African Studies 2, 1–25.
Cho, Young-mee: 1990, ‘Syntax and Phrasing in Korean’, in Inkelas and Zec (1990), pp. 47–62.
Clements, George N. and Kevin Ford: 1979, ‘Kikuyu Tone Shift and its Synchronic Consequences’, Linguistic Inquiry 10, 179–210.
Condoravdi, Cleo: 1990, ‘Sandhi Rules of Greek and Prosodic Theory’, in Inkelas and Zec (1990), pp. 63–84.
Culicover, Peter and Michael Rochemont: 1983, ‘Stress and Focus in English’, Language 59, 123–165.
Dell, François: 1986, ‘L'accentuation des phrases en français’, in François Dell, Daniel Hirst, and Jean-Roger Vergnaud (eds.), Forme sonore du language, Hermann, Paris, pp. 65–122.
Ferguson, Charles A. and Munier Chowdhury: 1960, ‘The Phonemes of Bengali’, Language 36, 22–59.
Goldsmith, John: 1976, Autosegmental Phonology, MIT dissertation. [Published 1979 by Garland Press, New York.]
Gussenhoven, Carlos: 1984, On the Grammar and Semantics of Sentence Accents, Foris, Dordrecht.
Gussenhoven, Carlos: 1990, ‘Tonal Association Domains and the Prosodic Hierarchy in English’, in Susan Ramsaran (ed.), Studies in the Pronunciation of English: A Commemorative Volume in Honour of A. C. Gimson, Routledge, London, pp. 27–37.
Inkelas, Sharon: 1988, ‘Prosodic Effects on Syntax: Hausa “fa”’, in Proceedings of the Seventh West Coast Conference on Formal Linguistics. Stanford Linguistics Association, Stanford, CA.
Inkelas, Sharon and Draga Zec (eds.): 1990, The Phonology-Syntax Connection, University of Chicago Press, Chicago.
Kaisse, Ellen: 1985, Connected Speech: The Interaction of Syntax and Phonology, Academic Press, Orlando, FL.
Kanerva, Jonni: 1990, ‘Focusing on Phonological Phrases in Chichewa’, in Inkelas and Zec (1990), pp. 145–161.
Klaiman, M. H.: 1987, ‘Bengali’, in Bernard Comrie (ed.), The World's Major Languages, Croon Helm, London and Sydney, pp. 490–513.
Ladd, D. Robert: 1980, The Structure of Intonational Meaning, Indiana University Press, Bloomington and London.
Ladd, D. Robert: 1983, ‘Phonological Features of Intonational Peaks’, Language 59, 721–759.
Ladd, D. Robert: forthcoming, ‘Metrical Representation of Pitch Register’, to appear in John Kingston and Mary Beckman (eds.), Papers in Laboratory Phonology I, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge.
Leben, William: 1973, Suprasegmental Phonology, Doctoral dissertation, MIT. [Distributed by Indiana University Linguistics Club, Bloomington.]
Liberman, Mark: 1975, The Intonational System of English, MIT dissertation. [Reproduced 1978 by the Indiana University Linguistics Club, Bloomington.]
Liberman, Mark and Janet Pierrehumbert: 1984, ‘Intonational Invariance under Changes in Pitch Range and Length’, in Mark Aronoff and Richard Oehrle (eds.), Language Sound Structure: Studies Presented to Morris Halle by his Teacher and Students, MIT Press, Cambridge, MA, pp. 157–233.
McCarthy, John: 1986, ‘OCP Effects: Gemination and Antigemination’, Linguistic Inquiry 17, 207–263.
Nespor, Marina and Irene Vogel: 1986, Prosodic Phonology, Foris, Dordrecht.
Odden, David: 1986, ‘The Role of the Obligatory Contour Principle in Phonological Theory’, Language 62, 353–383.
Odden, David: 1988, ‘Antiantigemination and the OCP’, Linguistic Inquiry 19, 451–475.
Pierrehumbert, Janet: 1980, The Phonetics and Phonology of English Intonation, MIT dissertation.
Pierrehumbert, Janet and Mary Beckman: 1988, Japanese Tone Structure, MIT Press, Cambridge, MA.
Poser, William J.: 1984, The Phonetics and Phonology of Tone and Intonation in Japanese, Doctoral dissertation, MIT, Cambridge, MA.
Prince, Alan: 1983, ‘Relating to the Grid’, Linguistic Inquiry 14, 19–100.
Schmerling, Susan: 1976, Aspects of English Sentence Stress, University of Texas Press, Austin.
Selkirk, Elisabeth: 1980, ‘Prosodic Domains in Phonology: Sanskrit Revisited’, in Mark Aronoff and Mary-Louise Kean (eds.), Juncture, Anma Libri, Saratoga, CA.
Selkirk, Elisabeth: 1984, Phonology and Syntax: The Relation between Sound and Structure, MIT Press, Cambridge.
Selkirk, Elisabeth and Tong Shen: 1990, ‘Prosodic Domains in Shanghai Chinese’, in Inkelas and Zec (1990), pp. 313–337.
Selkirk, Elisabeth and Koichi Tateishi: forthcoming, ‘Major Phrases in Japanese’, to appear in Carol Georgopoulos and Roberta Ishihara (eds.), Interdisciplinary Approaches to Language: Essays in Honor of S.-Y. Kuroda, Kluwer, Dordrecht.
Trager, George and Henry L. Smith: 1951, An Outline of English Structure, Battenburg Press, Norman, Oklahoma.
Yip, Moira: 1988, ‘The Obligatory Contour Principle and Phonological Rules: A Loss of Identity’, Linguistic Inquiry 19, 65–100.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
We would like to express our appreciation to D. Bolinger, C. Gussenhoven, M. Halle, P. Keating, D. R. Ladd, E. Selkirk, and three reviewers for NLLT for very helpful comments on earlier versions of this paper. The pitch tracks below were made using software by Henning Reetz, to whom many thanks. Our research was made possible by Visiting Research Fellowships for Hayes in 1986 and 1988 from the Max-Planck-Institut für Psycholinguistik, Nijmegen.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hayes, B., Lahiri, A. Bengali intonational phonology. Nat Lang Linguist Theory 9, 47–96 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00133326
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00133326