Abstract
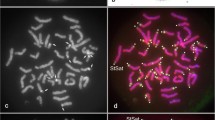
An unusual large heterochromatic segment around the pericentromeric region of the X-chromosome is reported. In normal circumstances, the pericentromeric region of the X-chromosome is negative by the restriction endonuclease AluI/Giemsa technique. However, this unusual X-chromosome was found to have AluI resistant (positive) chromatin. The evolution of extra heterochromatin is a postzygotic event as substantiated by the presence of a normal cell line.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Babu, A., A. K., Agarwal & R. S., Verma, 1988. A new approach in recognition of heterochromatin regions of human chromosomes by means of restriction endonucleases. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 42: 60–65.
Brutlag, D. L., 1980. Molecular arrangement and evolution of heterochromatic DNA. Ann. Rev. Genet. 14: 121–144.
Durfy, S. J. & H. F., Willard, 1989. Patterns of intra and interarray sequence variation in the alpha satellite from the human X chromosome: Evidence for short-range homogenization of tandemly repeated DNA sequences. Genomic 5: 810–821.
Dyer, K. A., T. K., Canfield & S. M., Gartler, 1989. Molecular cytological differentiation of active from inactive X domains in interphase: implications for X-chromosome inactivation. Cytogenet. Cell Genet. 50: 116–120.
Fantes, J., J., Gosden & J., Piper, 1988. Use of an alphoid satellite sequence to locate the X-chromosome automatically with particular reference to identification of the fragile X. Cytogenet. Cell Genet. 48: 142–147.
Greig, G. M., S. B., Englang, M., Bedford & H. F., Willard, 1989. Chromosome specific alpha satellite DNA from the centromere of human chromosome 16. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 45: 862–872.
Jabs, E. W. & M. G., Persico, 1987. Characterization of human centromeric regions of specific chromosomes by means of alphoid DNA sequences. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 41: 374–390.
Jabs, E. W. & N., Carpenter, 1988. Molecular cytogenetic evidence for amplification of chromosome-specific alphoid sequences at enlarged C-band on chromosome 6. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 43: 69–74.
Singer, M. F., 1982. Highly repeated sequences in mammalian genomes. Int. Rev. Cytol. 76: 67–112.
Verma, R. S. & H., Dosik, 1980. Human chromosomal heteromorphisms: Nature and clinical significance. Int. Rev. Cytol. 62: 361–383.
Verma, R. S., 1988. Heterochromatin: Molecular and Structural Aspects. Cambridge University Press, New York.
Verma, R. S. & A., Babu, 1989. Human Chromosomes: Manual of Basic Techniques. Pergamon Press, New York.
Waye, J. S. & H. F., Willard, 1985. Chromosome-specific alpha satellite DNA: Nucleotide sequence analysis of the 2.0 kilobasepair respeat from the human X chromosome. Nucleic acids Res. 13: 2731–2743.
Willard, H. F., 1985. Chromosome-specific organization of human alpha satellite DNA. AM. J. Hum. Genet. 37: 524–532.
Willard, H. F., K. D., Smith & J., Sutherland, 1983. Isolation and characterization of a major tandem repeat family from the human X chromosome. Nucleic Acids Res. 11: 2017–2033.
Yang, T. P., S. K., Hansen, K. K., Oishi, O. A., Ryder & B. A., Hamkalo, 1982. Characterization of a cloned repetitive DNA sequence concentrated on the human X chromosome. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 79: 6593–6597.
Yurov, Y. B., S. P., Mitkevich & A. I., Alexandrov, 1987. Application of cloned satellite DNA sequence to molecular cytogenetic analysis of constitutive heterochromatin heteromorphisms in man. Hum. Genet. 76: 157–164.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Luke, S., Mathews, T. & Verma, R.S. Evolution of pericentromeric heterochromatin of human X chromosome. Genetica 87, 63–64 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00128774
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00128774