Summary
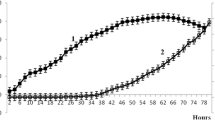
A segregationally stable host-plasmid system, E. coli DH5α (pTKW106), was used to study the effect of induction on the accumulation rate of cells and gene expression in biofilm cultures. Isopropyl β-D-thiogalactoside (IPTG) was used to induce the expression of β-galactosidase from the plasmid. The biofilm cell net accumulation rates decreased with increasing induction levels. At 0.17 and 0.34 mM of IPTG, the biofilm cell net accumulation rates ranged between 17 and 30% when compared to the uninduced case. At 0.51 mM of IPTG, the biofilm cell density never increased. At 0.17 and 0.34 mM of IPTG, β-galactosidase contents reached maxima 36 hours after induction with both amounts representing about 7.5% of total protein. At 0.51 mM of IPTG, β-galactosidase production reached its maximum, about 16% of total protein, 48 hours after induction. The β-galactosidase mRNA synthesis rates increased with increasing inducer levels. Maximum β-galactosidase mRNA synthesis rates were reached 36 hours after induction for each IPTG concentration.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bentley, W. E., Davis, R. H. and Kompala, D. S. (1991). Dynamics of induced CAT expression in Escherichia coli. Biotechnology and Bioengineering 38, 749–760.
Bryers, J. D. (1990). Biofilms in Biotechnology. In: Biofilms, pp. 733–773. Edited by W. G. Characklis & K. C. Marshall. New York, NY: John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
Cannistraro, V. J. and Kennell, D. (1979). Escherichia coli lac operator mRNA affects translation initiation of β-galactosidase mRNA. Nature 277:407–409.
Dwyer, D. F. & Timmis, K. N. (1990). Engineering microbes for function and safety in the environment. In Introduction of modified organisms into the environment, pp. 79–98. Edited by H. A. Mooney & G. Bernardi. New York, NY: John Wiley and Sons, Ltd.
Gausing, K. (1980). Regulation of ribosome biosynthesis in E. coli. In Ribosomes: Structure, Function and Genetics, pp. 693–718. Edited by G. Chambliss, G. R. Craven, J. Davies, K. Davis, L. Kahan & M. Nomura. Baltimore, MD: University Park Press.
Gerdes, K. (1988). The parB (hok/sok) locus of plasmid R1: a general purpose plasmid stabilization system. Bio/Technology 6, 1402–1405.
Glick, B. R. & Whitney, G. K. (1987). Factors affecting the expression of foreign proteins in Escherichia coli. Journal of Industrial Microbiology 1, 277–282.
Huang, C.-T., Peretti, S. W. & Bryers, J. D. (1993). Plasmid retention and β-galactosidase expression in suspended and biofilm cultures of recombinant E. coli DH5α (pMJR1750). Biotechnology and Bioengineering 41, 211–220.
Huang, C.-T. (1993) Plasmid retention and gene expression in bacterial biofilm cultures. Ph.D. Dissertation, Duke University, Durham, North Carolina, U. S. A.
Melo, L. F., Bott, T. R., Fletcher, M. & Capdeville, B. (eds.) (1992) Biofilms-Science and Technology, NATO ASI Series. Boston, MA: Kluwer Academic Publishers.
Miller, J. H. (1972). Experiments in Molecular Genetics, pp. 352–355. Cold Spring Harbor, NY: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory.
Nüβlein, K., Maris, D., Timmis, K. & Dwyer, D. F. (1992) Expression and transfer of engineered catabolic pathways harbored by Pseudomonas spp. introduced into activated sludge microcosms. Applied and Environmental Microbiology 58, 3380–3386.
Wood, T. K., Kuhn, R. H. & Peretti, S. W. (1990). Enhanced plasmid stability through post-segregational killing plasmid-free cells. Biotechnology/Technique 4, 39–44.
Wood, T. K. & Peretti, S. W. (1991). Effects of chemically-induced, cloned-gene expression on protein synthesis in E. coli. Biotechnology Bioengineering 38, 397–412.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, CT., Peretti, S.W. & Bryers, J.D. Effects of inducer levels on a recombinant bacterial biofilm formation and gene expression. Biotechnol Lett 16, 903–908 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00128622
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00128622