Abstract
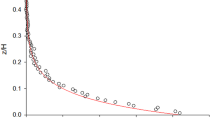
Two Langevin simulations of trajectories of marked fluid elements in inhomogenous turbulence, where the Lagrangian length and vertical velocity scales are height dependent, were compared with field data. A CO2 tracer was released from a circular line source and the concentration profiles were measured for diffusion distances of 50 and 100 cm inside and above an alfalfa canopy.
One of the simulations, suggested by Wilson et al. (1983), biases the vertical velocities by adding a mean upward drift. The second simulation proposed here by-passes this difficulty by reflecting marked particles according to a probability calculated from the gradient in vertical velocity variance between the beginning and the end of each step. This simulation also makes use of a constant time-scale within the canopy, following preliminary results from a turbulence experiment within a forest (Leclerc, 1987).
Comparing the results of these simulations with the field data shows that the simulation proposed by Wilson et al. (1983) does not correctly reproduce the difusion for the larger fetch in systems exhibiting strong gradients in vertical velocity variance. Instead, the modelled plumes exhibit a bulge at the source height whereas the field data show smooth profiles. In addition, the modelled plumes overestimate the vertical spread of the plumes, which is possibly due to the inadequacy of the approach in severely inhomogeneous systems. In contrast, the results from the tracer experiments indicate that the diffusion can be better reproduced with the use of a reflection probability calculated at each step. The discrepancies between the experimental results and the simulation using a reflection probability are attributed to stability effects.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Corrsin, S.: 1959, ‘Progress Report on Some Turbulent Diffusion Research. Atmospheric Diffusion and Air Pollution’, Adv. Geophys. 6, 161.
Denmead, O. T. and Bradley, E. F.: 1985, ‘Flux-Gradients Relationships in a Forest Canopy’, Proceedings of the Forest Environmental Measurements, Oak Ridge, Tennessee, October 23–28, D. Reidel Publ. Co., Dordrecht, Holland, p. 421.
Haugen, E.: 1972, Workshop on Micrometeorology, Am. Meteorol. Soc. Boston, Mass.
Leclerc, M. Y.: 1987, ‘Turbulence and Turbulent Diffusion Inside and above Vegetation’, Ph.D. Thesis, Chapter 1, Univ. of Guelph, Guelph, Ont. Canada.
Raupach, M. R., Coppin, P. A., and Legg, B. J.: 1986, ‘Experiments on Scalar Diffusion within a Plant Canopy, Part 2. An Elevated Plane Source’, Boundary-Layer Meteorol, 35, 21–52.
Raupach, M. R.: 1987, ‘A Lagrangian Analysis of Scalar Transfer in Vegetation Canopies’, Quart. J. Roy. Meteorol. Soc. 113, 107–120.
Reid, J. D.: 1979, ‘Markov Chain Simulations of Vertical Dispersion in the Neutral Surface Layer for Surface and Elevated Releases’, Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 16, 3–22.
Shi, G.: 1987, ‘Turbulence Statistics within and above a Deciduous Forest’, M. Sc. Thesis, Univ. of Guelph, Guelph, Ont. Canada.
Tennekes, H. and Lumley, J. L.: 1972, A First Course in Turbulence, MIT Press, Cambridge, Mass, U.S.
Wilson, J. D., Legg, B. J., and Thomson, D. J.: 1983, ‘Calculation of Particle Trajectory is in the Presence of a Gradient in Turbulent-Velocity Variance’, Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 27, 163–169.
Wilson, J. D., Thurtell, G. W., and Kidd, G. E.: 1981a, ‘Numerical Simulation of Particle Trajectories in Inhomogeneous Turbulence, 1. Systems with Constant Turbulent Velocity Scale’, Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 1, 295–310.
Wilson, J. D., Thurtell, G. W., and Kidd, G. E.: 1981b, ‘Numerical Simulation of Particle Trajectories in Inhomogeneous Turbulence', 11. Systems with Variable Velocity Scale’, Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 21, 423–441.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Leclerc, M.Y., Thurtell, G.W. & Kidd, G.E. Measurements and Langevin simulations of mean tracer concentration fields downwind from a circular line source inside an alfalfa canopy. Boundary-Layer Meteorol 43, 287–308 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00128408
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00128408