Abstract
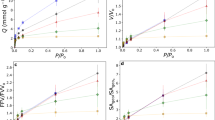
This work describes the adsorption behavior of associating and non-associating chains and their mixtures in pores with activated surfaces. The systems are studied using Gibbs ensemble Monte Carlo molecular simulations. Fluid molecules are modeled as freely jointed Lennard-Jones chains. Associating chains have, additionally, an associating square-well site placed in an end sphere. The pores are modeled as regular slit pores via an integrated Lennard-Jones potential (10-4-3); activation is achieved by placing specific association sites protruding from the surface. Two different solid-fluid interaction parameters are used, one of which corresponds roughly to alkanes on graphite, the other being a much weaker interaction. Adsorption isotherms are presented for several different cases: associating and non-associating chains confined within both neutral and activated walls. Mixtures of associating and non-associating chains are also considered. The effects of pore size, temperature and chain length are quantified. Selectivities obtained are in the range of those seen in adsorption experiments of alkane-alkanol mixtures.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen, M.P. and D.J. Tildesley, Computer Simulation of Liquids, Clarendon Press, Oxford, 1987.
Bandosz, T.J., J. Jagiello, and J.A. Schwarz, “Effect of Surface Chemical Groups on Energetic Heterogeneity of Activated Carbons,” Langmuir, 9, 2518 (1993).
de Pablo, J.J., M. Laso, and S.W. Suter, “Estimation of the chemical potential of chain molecules by simulation,” J. Chem. Phys., 96, 6157 (1992).
Israelachvili, J., Intermolecular & Surface Forces, 2nd ed., p. 125, Academic Press, 1992.
Mooij, G.C.A.M., D. Frenkel, and B. Smit, “Direct Simulation of Phase Equilibria of Chain Molecules,” J. Condens. Matter, 3, 3053 (1992).
Müller, E.A., L.F. Vega, and K.E. Gubbins, “Theory and Simulation of Associating Fluids: Lennard-Jones Chains with Association Sites,” Mol. Phys., 83, 1209 (1994).
Panagiotopoulos, A.Z., “Adsorption and Capillary Condensation of Fluids in Cylindrical Pores by Monte Carlo Simulation in the Gibbs Ensemble,” Mol. Phys., 62, 791 (1987).
Steele, W.A., The Interaction of Gases with Solid Surfaces, p. 56, Pergamon, Oxford, 1974.
Tee, L.S., S. Gotoh, and W.E. Stewart, “Molecular Parameters for Normal Fluids,” Ind. Eng. Chem. Fundam., 5, 356 (1966).
Valenzuela, D.P. and A.L. Myers, Adsorption Equilibrium Data Handbook, Prentice Hall, 1989.
Vega, L.F., E.A., Müller, L.F. Rull, and K.E. Gubbins, “Mixtures of Associating and Non-Associating Chains on Activated Surfaces: A Monte Carlo Approach,” Mol. Simulation, 15, 141 (1995).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vega, L.F., Müller, E.A., Rull, L.F. et al. Effect of surface active sites on adsorption of associating chain molecules in pores: A Monte Carlo study. Adsorption 2, 59–68 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00127099
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00127099