Abstract
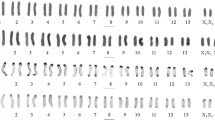
The diploid chromosome number is 2n=38. The fundamental number is 70. The autosomes consist of 11 pairs of metacentric, 5 pairs of submetacentric and 2 pairs of acrocentric chromosomes. The sex chromosomes are both acrocentric, the X-chromosome is the largest.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Khalili, A. D., 1984. New records of ectoparasites of small rodents from SW Saudi Arabia. Fauna of Saudi Arabia 6: 510–512.
Al-Saleh, A. A. & Khan, M. A., 1984a. Cytological studies of certain mammals of Saudi Arabia. 1. The karyotype of Jaculus jaculus. J. Coll. Sci., King Saud Univ. 15: 163–168.
Al-Saleh, A. A. & Khan, M. A., 1984a Cytological studies of certain mammals of Saudi Arabia. 2. The karyotype of Meriones libycus syrius Thomas 1919. Arab. Gulf J. Science Res. 2: 665–672.
Al-Saleh, A. A. & Khan, M. A., 1984c. Cytological studies of certain mammals of Saudi Arabia. 4. The karyotype of Allactaga euphratica. Proc. Saudi Biol. Soc. 7: 271–276.
Al-Saleh, A. A. & Khan, M. A., 1985. Cytological studies of certain mammals of Saudi Arabia. 3. The karyotype of Paraechinus aethiopicus. Cytologia 50: 507–512.
Al-Saleh, A. A. & Khan, M. A., 1987. Cytological studies of certain mammals of Saudi Arabia. 5. First report of chromosome number and karyotype of Meriones rex. Genetica 73: 185–187.
Badr, F. M. & Badr, R. S., 1970. The somatic chromosomes of a wild population of rats: Numerical polymorphism. Chromosoma 30: 465–475.
Bender, M. A. & Chu, E. H. Y., 1963. The chromosomes of primates. In: Evolutionary and genetic biology of primates, vol. 1, ed. by J.Buettner-Janusch. New York, Academic Press. pp. 261–310.
Buttiker, W. & Harrison, D. L., 1984. On a collection of Rodentia from Saudi Arabia. Fauna of Saudi Arabia 4: 488–502.
De-Hondt, H. A., Hussein, M. M., Younis, S. A. & Al-Eshmawy, S. H., 1977. Sex chromosome polymorphism in Egyptian rodents. Egypt. J. Genet. Cytol. 6: 199–206.
Diab, F. M., Hoogstraal, H., Wassef, H., Al-Khalifa, M. S. & Al-Asgah, N. A., 1985. Hyaloma (Hyalommina) arabica: Nymphal and larval identity and spiny mouse hosts in Saudi-Arabia (Acarina: Ixodoida: Ixodidae). J. Parasitol. 71: 630–634.
Harrison, D. L., 1972. The mammals of Arabia. 3. Lagomorpha, Rodentia. Benn, London pp. 384–670.
Jotterand-Bellomo, M., 1984. New developments in vertebrate cytotaxonony VII. Les chromosomes des Rongeurs (Order Rodentia Bowdich, 1821). Genetica 64: 3–63.
Levan, A., Fredga, K. & Sandberg, A., 1964. Nomenclature for centromeric position in chromosomes. Hereditas 52: 636–650.
Matthey, R., 1945. L'évolution de la formule chromosomiale chez les vertébrés. Experientia 1: 50–78.
Nasher, A. K., 1984. Helminth parasites of the spiny mouse Acomys dimidiatus (Cretzschmar) from Southwest Saudi Arabia. Fauna of Saudi Arabia 6: 127–129.
Pathak, S., 1976. Chromosomes of the Indian spiny mouse Mus saxicola Gurkha with a brief discussion on the mechanisms of karyological evolution in the genus Mus. Period. Biol. 78: 3–11.
Satya, P. K. L. & Aswathanarayana, N. V., 1973. Chromosomes and sex chromatin in the spiny mouse Mus platythrix platythrix, Rodentia, Muridae. Indian. Sci. Cong. Assoc. Proc. 60: 424.
Tobgy, A. H., Nasrat, G. E., De-Hondt, H. A. & El-Wardany, A. E., 1972. Karyological studies on some rodents of Egypt. Proc. Egypt. Acad. Sci. 25: 175–196.
Tranier, M., 1975. Etude préliminaire du caryotype de l'Acomys de l'Air (Rongeurs, Muridés). Mammalia 39: 704–705.
Vincett, B. A. L., 1982. Animal life in Saudi Arabia. Gazanti Editore-Cernusco, pp. 23 and 167.
Yosida, T. H., 1979. Possible evidence for the karyotype evolution of the Indian spiny mouse Mus platythrix due to tandem fusion of the house mouse Mus musculus chromosomes. Proc. Jpn. Acad. Ser. B. Phys. Bio. Sci. 55: 270–274.
Yosida, T. H., 1980. Karyotype of the Indian spiny mouse resulted from tandem fusion of some of the house mouse chromosomes. Cytologia 45: 753–762.
Yosida, T. H. & Inoue, 1981. Cytogenetic studies on the Indian spiny mouse Mus platythrix. 1. Frequency of sister chromatid exchanges in the lung primary cultures. Proc. Jpn. Acad. Ser. B. Phys. Biol. Sci. 57: 13–17.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This research (Zoo/1402/11) was supported by the Research Center, College of Science, Kind Saud University, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Al-Saleh, A.A. Cytological studies of certain desert mammals of Saudi Arabia 6.. First report on chromosome number and karyotype of Acomys dimidiatus . Genetica 76, 3–5 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00126004
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00126004