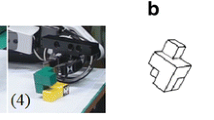
This paper elaborates an object-oriented and automated approach for generating assembly sequences and achieving robotic assembly. This system, built with database and artificial intelligence (AI) techniques, provides the robot with the assembly sequence layout for the automatic handling rule. The critical set of problems is derived from various schemes such as model-based object recognition, features information, geometric and physical constraints between components, knowledge interpretation and robot task sequencing. Pattern recognition regarding shapes and features, along with a knowledge-based assembly, are the key issues of the authors' work. The methodology is shown through two illustrative examples involving different designs of parts in an assembly environment.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Angermuller, G. and Hardeck, W. (1987) CAD integrated planning for flexible manufacturing systems with assembly tasks. IEEE CAD Journal, 1822–1826.
Conradson, S., Weinstein, M., Wilker, J.S. and Yencho, S.A. (1987) Automated material handling (automated assembly and product design as a system), in IEEE Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on Assembly Automation, pp. 67–68.
Ferland, M., O'Shea, J. and Rabemanantsoa, M. (1993) Robotic interface for CAD/CAM integration, in Proceedings of Department of National Defense on Workshop on Advanced Techniques in Knowledge-Based Systems and Robotics, Ottawa, Ontario, Canada.
Homen de Mello, L.S. and Sanderson, A.C. (1989) A correct and complete algorithm for the generation of mechanical assembly sequences. IEEE Journal of International Conference on Robotics and Automation, CH2750-8, 56–61.
Hurt, J. (1989) A taxonomy of CAD/CAE systems. Manufacturing Review, 2(3), 170–178.
Jarvis, R.A. (1988) Configuration space collision-free path planning for robotic manipulators, in Robots in Australia's Future Conference, ARA, pp. 193–204.
Lee, Y.C. and Fu, K.S. (1983) A CSG based DBMS for CAD/CAM and its supporting query language. CAD Journal, IEEE, 123–128.
Marque-Pacheu, G., Gallausiaux, J.M. and Jormier, G. (1984) Interfacing Prolog and relational DBMS, New Applications of Databases, Gelenbe, E. (ed.), Academic Press, New York.
Nnaji, B.O. (1988) A framework for CAD-based geometric reasoning for robot assembly language. International Journal of Process Research, 26(5), 735–764.
Pfeiffer, F. and Johanni, R. (1987) A concept for manipulator trajectory planning. IEEE Journal of Robotics and Automation, RA-3, 3, 115–123.
Rabemanantsoa, M. and Pierre, S. (1993a) A knowledge-based approach for achieving assembly tasks, in Proceedings of the 14th Canadian Congress of Applied Mechanics CAN-CAM 93, Kingston, Ontario, Canada, 1, pp. 51–52.
Rabemanantsoa, M. and Pierre, S. (1993b) An integrated knowledge-based system for flexible assembly process manufacturing, in 2nd International Conference on Computer Integrated Manufacturing, Singapore, pp. 789–798.
Rabemanantsoa, M. and Pierre, S. (1993c) A knowledge-based system for assembly process-planning, in IEEE SESS 93 International Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Brighton, England, pp. 267–272.
Rabemanantsoa, M. and Pierre, S. (1993d) A knowledge-based approach for robot assembly planner, in IEEE Proceedings of Canadian Conference on Electrical and Computer Engineering, Vancouver, Canada, pp. 829–832.
Sanderson, A.C., Peshkin, M.A. and Homen de Mello, L.S. (1988) Task planning for robotic manipulation in space applications. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 24(5), 619–628.
Shah, J. and Bhatnagar, S. (1989) Group technology classification from feature-based geometric models. Manufacturing Review, 2, 204–213.
Swift, K.G. (1987) Knowledge-Based Design for Manufacture, Prentice-Hall, London.
Woodbury, R.F. and Oppenheim, I.J. (1988) An approach to geometric reasoning in robotics. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 24(5), 630–645.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rabemanantsoa, M., Pierre, S. Toward an object-oriented and automated approach for achieving robotic assembly. J Intell Manuf 6, 355–364 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00124062
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00124062