Abstract
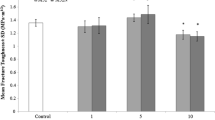
The fracture properties of bone cement are strongly influenced by the complex interactions between the residual monomer and components of the media surrounding the bone cement. The aim of this study was to eliminate the influence of the residual monomer by fully curing the cement prior to storage in air, water, lipid or Ringer's solution at room or body temperature for up to 18 months. Subsequent mechanical testing indicated that initially there was a significant increase in the work of fracture values for all the samples stored in the fluid media. With longer-term storage periods a decrease was observed; this was attributed to the process of physical ageing. The removal of the residual monomer eliminated the monomer: lipid interaction, consequently the effect of the storage in lipid was similar to that observed for the other fluid media.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. CHARNLEY, “Acrylic cement in orthopaedic surger” (E & S Livingstone, Edinburgh, 1970).
A. PIZZOFERRATO, G. CIAPETTI, S. STEA and A. TONI, Clin. Mater. 7 (1991) 51.
N. A. JOHANSON, P. G. BULLOUGH, P. D. WILSON, E. A. SALVATI and C. S. RANAWAT, Clin. Orthop. Rel. Res. 218 (1987) 123.
M. B. WATSON, A. W. MILES and S. E. CLIFT, Clin. Mater. 6 (1990) 299.
J. L. HAILEY, I. G. TURNER and A. W. MILES, In “Biomaterials-tissue interfaces”, Vol. 10 (Elsevier Science Publishers, Amsterdam, 1992) p. 325.
H. J. CAUL, W. T. SWEENEY and G. C. PAFFENBARGER, J. Amer. Dent. Assoc. 53 (1956) 60.
R. P. KUSY, J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 12 (1978) 271.
D. C. SMITH and M. E. D. BAINS, J. Dental Res. 35 (1956) 16.
H. G. TATTERSALL and G. TAPPIN, J. Mater. Sci. 1 (1966) 296.
P. W. R. BEAUMONT and R. J. YOUNG, J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 9 (1975) 423.
L. C. E. STRUIK, “Physical aging in amorphous polymers and other materials” (Elsevier Scientific Publishing, Amsterdam, 1978).
J. L. HAILEY, I. G. TURNER and A. W. MILES, Clin. Mater. 16 (1994) 211.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hailey, J.L., Turner, I.G. & Miles, A.W. Fracture properties of fully cured acrylic bone cement. J Mater Sci: Mater Med 6, 635–638 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00123443
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00123443