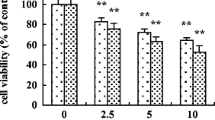
When isolated hepatocytes were exposed to tert-butyl hydroperoxide (tBOOH) they lost their cellular membrane integrity. Decreased levels of GSH, increased phosphorylase a activity (an indirect index of the amount of free cytosolic Ca2+), and increase in the formation of malondialdehyde (MDA)-like products (an index of lipid peroxidation) preceeded the release into the culture medium of the cytosolic enzyme lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), indicating that this later process was the consequence of the former intracellular events. While ATP levels were not modified during the incubation of cells with increasing concentrations of tBOOH, protein synthesis was decreased in a concentration-dependent manner. The glycogen content decreased at the same time as the increase in LDH leakage. The addition of promethazine (PMZ) an antioxidant molecule, prevented the lipid peroxidation, but did not protect cells against the oxidative effects of tBOOH, including loss of membrane integrity. Nevertheless, the addition of GSH to cell suspensions incubated with tBOOH, decreased the formation of MDA-like products, restored the protein synthesis rate, prevented partially the activation of phosphorylase a and preserved cell viability. On the basis of these results, we postulate that both GSH depletion and modification in phosphorylase a activity (Ca2+ levels) were the most relevant intracellular events to explain the cytotoxicity of tBOOH.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- tBOOH:
-
tert-butyl hydroperoxides
- GSH:
-
reduced glutathione
- LDH:
-
lactate dehydrogenase
- MDA:
-
malondialdehyde
- TBA:
-
thiobarbituric acid
- PMZ:
-
promethazin
- BSA:
-
bovine serum albumin
References
BELLOMO, G., JEWELL, S.A., THOR, H. and ORRENIUS, S. (1982). Regulation of intracellular calcium compartmentation: Studies with isolated hepatocytes and t-butyl hydroperoxide. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 79: 6842–6846.
BELLOMO, G., THOR, H. and ORRENIUS, S. (1984). Increase in cystosolic calcium concentration during t-butyl hydroperoxide metabolism by isolated hepatocytes involves NADPH oxidation and mobilization of intracellular calcium stores. FEBS, Lett. 168:38–42.
BERRY, M. and FRIEND, J. (1969). High-yield preparation of isolated rat liver parenchymal cells A biochemical and fine structural study. J. Cell Biol. 43:506–520.
DEBOYSER, D., GOETHALS, F., KRACK, G. and ROBERFROID, M. (1989). Investigation into the mechanism of tetracycline-induced steatosis: Study in isolated hepatocytes. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 97:473–479.
GOETHALS, F., KRACK, G., DEBOYSER, D. and ROBERFROID, M. (1983). Effects of diethylmaleate on protein synthesis in isolated hepatocytes. Toxicity. 26:47–52.
GOETHALS, F., KRACK, G., DEBOYSER, D., VOSSEN, P. and ROBERFROID, M. (1984). Critical biochemical functions of isolated hepatocytes as sensitive indicators of chemical toxicity. Fund. Appl. Toxicol. 4:441–450.
GORLA, N., DE FERREORA, E.C., VILLAROEL, M.c., dE FENOS, O.M. and CASTRO, J.A. (1983). Studies on the mechanism of glutathione prevention of carbon tetrachloride-induced liver injury. Br. J. Exp. Pathol. 64:388–395.
GRIFFITH, O.W. and MEISTER, A. (1979). Glutathione: Interorgan translocation, turnover and metabolism. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 76:5606–5610.
HILL, K.E. and BURK, R.F. (1984). Toxicity studies in isolated hepatocytes from selenium-deficient and vitamin E-deficient rats. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 72: 32–39.
HISSIN, P.J. and HILF, R. (1976). A fluorimetric method for determination of oxidized and reduced glutathione in tissues. Anal. Biochem. 74:214–219.
HOGBERG, J., ORRENIUS, S. and O'BRIEN, P. (1975). Further studies on lipid-peroxide formation in isolated hepatocytes. Eur. J. Biochem. 59:449–455.
HUE, L., BONTEMPS, F. and HERS, H.G. (1975). The effect of glucose and of potassium ions on the interconversion of the two forms of glycogen phosphorylase and of glycogen synthetase in isolated rat liver preparations. Biochem. J. 152:105–114.
JEWELL, S.A., BELLOMO, G., THOR, H., SMITH, M.T. and ORRENIUS, S. (1982). Bleb formation in hepatocytes during drug metabolism is caused by disturbances in thiol and calcium ion homeostasis. Science. 217:1257–1259.
KRACK, G., GRAVIER, O., ROBERFROID, M. and MERCIER, M. (1980). Subcellular fractionation of isolated rat hepatocytes. A comparison with liver homogenate. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 632:619–629.
LAMPRECHT, W. and TRAUSCHOLD, I. (1965). Adenosine-5′-triphosphate: Determination with hexokinase and glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase. In: Methods of enzymatic analysis (H.U. Bergmeyer, ed.), p. 543. Academic Press, New York; Verlag Chemie-GmbH, Weiheim.
LOWRY, O., ROSEBROUGH, N., FARR, L. and RANDALL, R. (1951). Protein measurement with the folin phenol reagent. J. Biol. Chem. 183:265–275.
MASAKI, N., KYLE, M.E., SERRONI, A. and FARBER, J.L. (1989a). Mitochondrial damage as a mechanism of cell injury in the killing of cultured hepatocytes by tert-butyl hydroperoxide. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 270: 672–680.
MASAKI, N., KYLE, M.E. and FARBER, J.L. (1989b). Tert-butyl hydroperoxide kills cultured hepatocytes by peroxidizing membrane lipids. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 269:390–399.
MOORE, G.A., JEWELL, S.A., BELLOMO, G. and ORRENIUS, S. (1983). On the relationship between calcium efflux and membrane damage during t-butyl hydroperoxide metabolism by liver mitochondria. FEBS Lett. 153: 289–292.
POLI, G., CHEESEMAN, K., SLATER, T.F. and DIANZANI, M.U. (1981). The role of lipid peroxidation in CCl4-induced damage to liver microsomal enzymes: Comparative studies in vitro using microsomes and isolated liver cells. Chem. Biol. Interact. 37:13–24.
RUBIN, R. and FARBER, J.L. (1984). Mechanisms of the killing of cultured hepatocytes by hydrogen peroxide. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 228:450–459.
RUSH, G.F. 1984. Species differences in the susceptibility of isolated hepatocytes to peroxidative injury. Toxicologist. 4:134.
RUSH, G.F., GORSKI, J.R., RIPPLE, M.G., SOWINSKI, J., BUGELSKI, P. and HEWITT, W.R.(1985). Organic hydroperoxide-induced lipid peroxidation and cell death in isolated hepatocytes. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 78:473–483.
RUSH, G.F., YODIS, L.A. and ALBERTS, D. (1986). Protection of rat hepatocytes from tert-butyl hydroperoxide-induced injury by cathecol. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 84:607–616.
SEGLEN, P.O. (1976). Incorporation of radioactive amino acids into protein in isolated rat hepatocytes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 442:391–404.
SMITH, M.T., THOR, H., HARTZELL, P. and ORRENIUS, S. (1982). The measurement of lipid peroxidation in isolated hepatocytes. Biochem. Pharmacol. 31:19–26.
STACEY, N.H., CANTILENA, L.R. and KLAASSEN, C.D. (1980). Cadmium toxicity and lipid peroxidation in isolated hepatocytes. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 53:470–480.
STARKE, P.E., HOEK, J.B. and FARBER, J.L. (1986). Calcium-dependent and calcium-independent mechanisms of irreversible cell injury in cultured hepatocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 261:3006–3012.
THOR, H., HARTZELL, P. and ORRENIUS, S. (1984). Potentiation of oxidative cell injury in hepatocytes which have accumulated calcium. J. Biol. Chem. 259:6612–6615.
THORNALLEY, P., TROTTA, R.J. and STERN, A. (1983). Free radical involvement in the oxidative phenomena induced by tert-butyl hydroperoxide in erythrocytes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 759:16–22.
WROBLESKI, F. and LADUE, J. (1955). Lactic deshydrogenase activity in blood. Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 90:210–213.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Buc-Calderon, P., Latour, I. & Roberfroid, M. Biochemical changes in isolated hepatocytes exposed to tert-butyl hydroperoxide. implications for its cytotoxicity.. Cell Biol Toxicol 7, 129–143 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00122827
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00122827