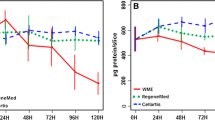
Aldehyde dehydrogenase was measured in primary cultures of hepatocytes obtained with a two-step collagenase perfusion either from human hepatic tissue or from livers of Fisher rats. Basal enzyme activity declines gradually as a function of time in culture, but remains at all times higher when measured with propionaldehyde and NAD (P/NAD) than with benzaldehyde and NADP (B/NADP). Treatment of the cultures with 2 μM of 3-methylcholanthrene for four days significantly increased the B-NADP activity of human and rat hepatocytes (tenfold and eightfold respectively). In human hepatocytes 3-methylcholanthrene increases also the P/NAD activity, but to a lesser extent (twofold), compared to the B/NADP activity. Due to the significant enhancement of B/NADP activity in cultures of human and rat hepatocytes after application of 3-methylcholanthrene, the initial difference in the basal activity levels between the P/NAD and B/NADP forms diminishes or, in the case of human hepatocytes, is even inverted. These results show for the first time that aldehyde dehydrogenase activity is increased in cultured human hepatocytes. This biochemical property is preserved in human and rat hepatocyte cultures, despite the rather quick loss of the basal aldehyde dehydrogenase activity.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ALDH:
-
aldehyde dehydrogenase
- B:
-
benzaldehyde
- p-p-DDT:
-
1,1,1,-trichlo-2,2,bis(p-chlorophenyl)ethane
- DMSO:
-
dimethylsulfoxide
- 3-MC:
-
3-methylcholanthrene
- MEM:
-
Minimal Essential Medium
- P:
-
proprionaldehyde
- TCDD:
-
2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin
References
BLAIR, A.H. and BODLEY, F.H. (1969). Human liver aldehyde dehydrogenase: partial purification and properties. Can. J. Biochem. 47:265–272.
BRADFORD, M.M. (1976). A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein, utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 72:248–254.
CRUISE, J.L. and MICHALOPOULOS, G. (1985). Norepinephrine and epidermal growth factor: dynamics of their interaction in the stimulation of hepatocyte DNA synthesis. J. Cell. Physiol. 125:45–50.
DEITRICH, R.A. (1971). Genetic aspects of increase in rat liver aldehyde dehydrogenase induced by phenobarbital. Science 173:334–336.
DEITRICH, R.A., BLUDEAU, P., STOCK, T. and ROPER, M. (1977). Induction of different rat liver supernatant aldehyde dehydrogenases by phenobarbital and tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin. J. Biol. Chem. 252:6169–6176.
DEITRICH, R.A., COLLINS, A.C. and ERWIN, V.G. (1972). Genetic influence upon phenobarbital-induced increase in rat liver supernatant aldehyde dehydrogenase activity. J. Biol. Chem. 247:7232–7236.
DULEY, J.A., HARRIS, O. and HOLMES, R.S. (1985). Analysis of human alcohol- and aldehyde-metabolizing isozymes by electrophoresis and isoelectric focusing. Alcoholism: Clin. Exp. Res. 9:263–271.
EDWARDS, A.M. (1984). Relationship between inductions of monoxygenase activity and α-glutamyl transpeptidase in rat hepatocyte primary cultures. Biochem. Pharmacol. 33:3839–3845.
FEINSTEIN, R.N. (1975). Aldehyde dehydrogenase isozymes in certain hepatomas. In: Isozymes III (ed. C.L. Markert) pp. 969–986. Academic Press, New York.
GOEDDE, H.W., MEIER-TACKMANN, D., AGARWAL, D.P. and HARADA, S. (1982). Physiological role of aldehyde dehydrogenase isozymes. In: Enzymology of carbonyl metabolism; Aldehyde dehydrogenase and Aldo/Keto Reductase, pp. 347–362. Alan R. Liss, Inc., New York.
GREENFIELD, N.J. and PIETRUSZKO, R. (1977). Two aldehyde dehydrogenases from human liver. Isolation via affinity chromatography and characterization of the isozymes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 483:35–45.
GUILLOUZO, A., BEGUE, J.-M., CAMPION, J.-P., GASCOIN, M.-N. and GUGUEN-GUILLOUZO, C. (1985). Human hepatocyte cultures: a model of pharmacotoxicological studies. Xenobiotica 15:635–641.
HARADA, S., AGARWAL, D.P. and GOEDDE, H.W. (1978). Isozyme variations in aldehyde dehydrogenase (E.C. 1.2.1.3) in human tissues. Hum. Genet. 44:181–185.
HARADA, S., MISAWA, S., AGARWAL, D.P. and GOEDDE, H.W. (1980). Liver alcohol dehydrogenase and aldehyde dehydrogenase in the Japanese: isozyme variation and its possible role in alcohol intoxication. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 32:8–15.
HENEHAN, G.T.M., WARD, K., KENNEDY, N.P., WEIR, D.G. and TIPTON, K.F. (1985). Subcellular distribution of aldehyde dehydrogenase activities in human liver. Alcohol 2:107–110.
ICHIHARA, A., NAKAMURA, T., TANAKA, K., TOMITA, Y., AOYAMA, K., KATO, S. and SHINNO, H. (1980). Biochemical functions of adult rat hepatocytes in primary culture. Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. 349:77–84.
JANSING, R.L. and SHAIN, W. (1985). Aryl hydrocarbon hydroxylase induction in adult rat hepatocytes in primary culture by several chlorinated aromatic hydrocarbons including 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin. Fundam. Appl. Toxicology 5:713–720.
JONES, D.E., JR., EEVCES, S. and LINDAHL, R. (1984). Expression of tumor-associated aldehyde dehydrogenase during rat hepatocarcinogenesis using the resistant hepatocyte model. Carcinogenesis 5:1679–1687.
KOIVULA, T. (1975). Subcellular distribution and characterization of human liver aldehyde dehydrogenase fractions. Life Sci. 16:1563–1570.
LAISHES, B.A. and WILLIAMS, G.M. (1976). Conditions affecting primary cell cultures of functional adult rat hepatocytes. II. Dexamethasone-enhanced longevity and maintenance of morphology. In Vitro 12:821–832.
LIN, K.H., WINTERS, A.L. and LINDAHL, R. (1984). Regulation of aldehyde dehydrogenase activity in five rat hepatoma cell lines. Cancer Res. 44:5219–5226.
LINDAHL, R. (1977). Aldehyde dehydrogenase in 2-acetamidofluorene-induced rat hepatomas. Ontogeny and evidence that the new isoenzymes are not due to normal gene depression. Biochem. J. 164:119–123.
LINDAHL, R. (1978). Aldehyde dehydrogenase in 2-acetylaminofluorene-induced rat hepatomas: Characterization of antigens recognized by anti-hepatoma aldehyde dehydrogenase sera. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 525:9–17.
MARSELOS, M. (1976). Genetic variation of drug-metabolizing enzymes in the Wistar rat. Acta Pharmacol. Toxicol. 39:186–197.
MARSELOS, M. and HäNNINEN, O. (1974). Enhancement of D-glucuronolactone and aldehyde dehydrogenase activities in the rat liver by inducers of drug metabolism. Biochem. Pharmacol. 23:1457–1466.
MARSELOS, M., TöRRöNEN, R., KOIVUSALO, T. and KOIVULA, M. (1979). Comparison of phenobarbital- and carcinogen-induced aldehyde dehydrogenases in the rat. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 583:110–118.
MICHALOPOULOS, G., CIANCIULLI, H.D., NOVOTNY, A.R., KLIGERMAN, A.D., STROM, S.C. and JIRTLE, R.L. (1982). Liver regeneration studies with rat hepatocytes in primary culture. Cancer Res. 42:4673–4682.
MICHALOPOULOS, G., SATTLER, G.L. and PITOT, H.C. (1976a). Maintenance of microsomal cytochromes b5 and P-450 in primary cultures of parenchymal liver cells on collagen membranes. Life Sci. 18:1139–1144.
MICHALOPOULOS, G., SATTLER, C.A., SATTLER, G.L. and PITOT, H.C. (1976b). Cytochrome P-450 induction by phenobarbital and 3-methylcholanthrene in primary cultures of hepatocytes. Science 93:907–909.
MIYAZAKI, M., HANDA, Y., ODA, M., YABE, T., MIYANO, K. and SATO, J. (1985). Long-term survival of functional hepatocytes from adult rats in the presence of phenobarbital in primary culture. Experim. Cell Res. 159:176–190.
NOVICKI, D.L., JIRTLE, R.L. and MICHALOPOULOS, G. (1983). Establishment of two rat hepatoma cell stains produced by a carcinogen initiation, phenobarbital promotion protocol. In Vitro 19:191–202.
PIETRUSZKO, R., HEMPEL, J.D. and VALLARI, R.C. (1982). Chemical modification and site of interaction of human aldehyde dehydrogenase E1 with disulfiram and iodoacetamide. In: Enzymology of Carbonyl Metabolism: Aldehyde Dehydrogenase and Aldo/Keto Reductase, pp. 61–75, Alan R. Liss, Inc., New York.
RITTER, E. and ERIKSSON, L.C. (1985). Aldehyde dehydrogenase activities in hepatocyte nodules and hepatocellular carcinomas from Wistar rats. Carcinogenesis 6:1683–1687.
SEGLEN, P.O. (1976). Preparation of isolated rat liver cells. Methods Cell. Biol. 18:29–83.
SIMPSON, V.J., BAKER, R. and DEITRICH, R.A. (1985). Inducible aldehyde dehydrogenases from rat liver cytosol. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 79:193–203.
STROM, S.C., JIRTLE, R.L., JONES, R.S., NOVICKI, D.L., ROSENBERG, M.R., NOVOTNY, A., IRONS, G., McLAIN, Y.R. and MICHALOPOULOS, G. (1982). Isolation, culture, and transplantation of human hepatocytes. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 68:771–778.
STROM, S.C. and MICHALOPOULOS, G. (1982). Collagen as a substrate for cell growth and differentiation. Methods Enzymol. 82:544–555.
TANAKA, K., SATO, M., TOMITA, Y. and ICHIHARA, A. (1978). Biochemical studies on liver functions in primary cultured hepatocytes of adult rats. I. Hormonal effects on cell viability and protein synthesis. J. Biochem. 84:937–946.
TÖRRÖNEN, R. (1981). Aldehyde and D-glucuronolactone dehydrogenases in rat liver and their induction by xenobiotics. Publications of the Univ. of Kuopio, Natural Sciences, Ser. Original Report 3.
TöRRöNEN, R. (1985). Isolation and characterization of rat liver cytosolic aldehyde dehydrogenases induced by phenanthrene or benzo[a]pyrene. Int. J. Biochem. 17:101–106.
TöRRöNEN, R., NOUSIAINEN, U. and HäNNINEN, O. (1981). Induction of aldehyde dehydrogenase by polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in rats. Chem.-Biol. Interactions 36:33–44.
TOTTMAR, S.O.C., PETTERSSON, H. and KIESSLING, K.-H. (1973). The subcellular distribution and properties of aldehyde dehydrogenases in rat liver. Biochem. J. 135:577–586.
WISCHUSEN, S.M., EVCES, S. and LINDAHL, R. (1983). Changes in aldehyde dehydrogenase activity during diethylnitrosamine- or 2-acetylaminofluorene-initiated rat hepatocarcinogenesis. Cancer Res. 43:1710–1715.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Marselos, M., Strom, S.C. & Michalopoulos, G. Enhancement of aldehyde dehydrogenase activity in human and rat hepatocyte cultures by 3-methylcholanthrene. Cell Biol Toxicol 2, 257–269 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00122694
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00122694