Abstract
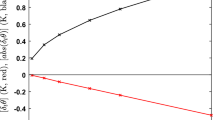
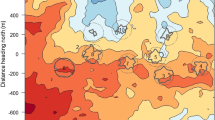
Observations from an instrumented aircraft are used to study the small-scale structure of turbulence and convection in well-mixed boundary layers and the erosion processes in the nocturnally-formed inversions above them. The ways in which turbulence statistics for temperature, humidity and vertical velocity scale with height in the mixed layer are compared with the results of a three-dimensional model by Deardorff (1974a, b), and agreement is found in many aspects. Conditional sampling enables the statistics of thermals and their environment to be considered separately and, in particular, shows that the mode of the vertical velocity in thermals markedly decreases with height in the upper half of the mixed layer. Thermals may be recognized equally readily by either their excess of temperature or humidity. Transfers of heat and moisture through the nocturnal inversions influence the structure of the upper region of the mixed layer and there is strong evidence that these transfer processes are turbulent and not organized on scales similar to convective thermals.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Coulman, C. E.: 1978, Boundary Layer Evolution and Nocturnal Inversion Dispersal — Part I, this issue, p. 471.
Coulman, C. E. and Warner, J.: 1977, ‘Observations of Temperature and Humidity Structure in the Sub-Cloud Layer over Land’, Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 11, 467–484.
Deardorff, J. W.: 1974a, ‘Three-Dimensional Numerical Study of Height and Mean Structure of a Heated Planetary Boundary Layer’, Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 7, 81–106.
Deardorff, J. W.: 1974b, ‘Three-Dimensional Numerical Study of Turbulence in an Entraining Mixed Layer’, Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 7, 199–226.
Frisch, A. S. and Businger, J. A.: 1973, ‘A Study of Convective Elements in the Atmospheric Surface Layer’, Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 3, 301–328.
Kaimal, J. C., Wyngaard, J. C., Haugen, D. A., Coté, O. R., Izumi, Y., Caughey, S. J., and Readings, C. J.: 1976, ‘Turbulence Structure in the Convective Boundary Layer’, J. Atmos. Sci. 33, 2152–2169.
Kendall, M. G. and Stuart, A.: 1963, Advanced Theory of Statistics, Vol. 1, C. Griffin, London.
Kovasznay, L. S. G., Kibens, V., and Blackwelder, R. F.: 1970, ‘Large-Scale Motion in the Intermittent Region of Turbulent Boundary layer’, J. Fluid Mech. 41, 283–325.
Kuo, H. L. and Sun, W. Y.: 1976, ‘Convection in the Lower Atmosphere and Its Effects’, J. Atmos. Sci. 33, 21–40.
Lenschow, D. H.: 1970, ‘Airplane Measurements of Planetary Boundary Layer Structure’, J. Appl. Meteorol. 9, 874–884.
Manton, M. J.: 1977, ‘On the Structure of Convection’, Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 12, 491–503.
Priestley, C. H. B.: 1959, Turbulent Transfer in the Lower Atmosphere, Univ. of Chicago Press.
Rayment, R. and Readings, C. J.: 1974, ‘A Case Study of the Structure and Energetics of an Inversion’, Quart. J. Roy. Meteorol. Soc. 100, 221–233.
Readings, C. J., Golton, E., and Browning, K. A.: 1973, ‘Fine-Scale Structure and Mixing within an Inversion’, Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 4, 275–287.
Smedman-Högström, A. S.: 1973, ‘Temperature and Humidity Spectra in the Atmospheric Surface Layer’, Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 3, 329–347.
Warner, J. and Telford, J. W.: 1967, ‘Convection below Cloud Base’, J. Atmos. Sci. 24, 374–382.
Wyngaard, J. C., Coté, O. R., and Izumi, Y.: 1971, ‘Local Free Convection, Similarity and the Budgets of Shear Stress and Heat Flux’, J. Atmos. Sci. 28, 1171–1182.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Coulman, C.E. Boundary-layer evolution and nocturnal inversion dispersal—Part II. Boundary-Layer Meteorol 14, 493–513 (1978). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00121890
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00121890