Abstract
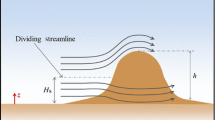
In a study using the plume from the Four Corners power plant, near Farmington, N.M., lee waves were observed during times when the plume flowed across the Hogback. Wavelengths were typically about 1.2 km; wave amplitudes were more variable, ranging from 20 to 100 m. The observed amplitudes imply an obstacle that is broader and shallower than is actually the case. This is in agreement with laboratory studies that show the existence of regions of complex flow both upstream and downstream from an obstacle, which have the effect of broadening the region over which laminar flow occurs. Visual observation, measurement of the plume cross-sectional area both upstream and downstream from the Hogback, and measurement of plume aerosol concentrations show that turbulent and eddy flow over and downwind from the Hogback increase the rate of mixing of the plume with the surrounding atmosphere. This in turn increases the rate at which plume components come into contact with the ground.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barrett, E. W., Parungo, F. P., and Pueschel, R. F.: 1979, ‘Cloud Modification by Urban Pollution: A Physical Demonstration’, Meteorol. Rdsch. 32, 136–149.
Corby, G. A.: 1954, ‘The Airflow Over Mountains’, Quart. J. Roy. Meteorol. Soc. 80, 491–521.
Deirmendjian, D.: 1969, Electromagnetic Scattering on Spherical Polydispersions, Elsevier, New York.
Gedayloo, T., Barr, S., Clements, W. E., and Wangen, L. E.: 1979, ‘Behavior of a Tall Stack Plume in Flow over a Ridge’, Report LA-7632-MS, Los Alamos Scientific Laboratory, Los Alamos, New Mexico.
Hirt, C. W., Nichols, B. S., and Romero, N. C.: 1975, ‘SOLA-A Numerical Solution Algorithm of Transient Fluid Flows’, Report LA-5852, Los Alamos Scientific Laboratory, Los Alamos, New Mexico.
Hunt, J. C. R. and Snyder, W. H.: 1980, ‘Experiments on Stably and Neutrally Stratified Flow Over a Model Three-Dimensional Hill’, J. Fluid Mech. 96, 671–704.
Hunt, J. C. R., Puttock, J. S., and Snyder, W. H.: 1979, ‘Turbulent Diffusion from a Point Source in Stratified and Neutral Flows Around a Three-Dimensional Hill — Part 1. Diffusion Equation Analysis’, Atmos. Environ. 13, 1227–1239.
Pearse, J. R., Lindley, D., and Stevenson, D. C.: 1981, ‘Wind Flow Over Ridges in Simulated Atmospheric Boundary Layers’, Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 21, 77–92.
Raymond, D. J.: 1972, ‘Calculation of Airflow Over an Arbitrary Ridge Including Diabatic Heating and Cooling’, J. Atmos. Sci. 29, 837–843.
Sawyer, J. S.: 1960, ‘Numerical Calculation of the Displacements of a Stratified Airstream Crossing a Ridge of Small Height’, Quart. J. Roy. Meteorol. Soc. 86, 326–345.
Sievering, H., Cooke, J., and Pueschel, R.: 1981, ‘Importance of Deposition Velocity for Sulfur Gas to Sulfate Particle Transformation Rates at the Four Corners Power Plant’, Atmos. Environ. 15, 2593–2596.
Stearns, L. P., Barrett, E. W., and Pueschel, R. F.: 1982, ‘Effects of a Power Plant Plume on Radiative Transfer’, Meteorol. Rdsch. 35, 76–84.
Yoshino, M. M.: 1975, Climate in a Small Area, University of Tokyo Press, Japan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Van Valin, C.C., Pueschel, R.F., Barrett, E.W. et al. Field observations of stratified atmospheric flow above an obstacle. Boundary-Layer Meteorol 24, 331–343 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00121598
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00121598