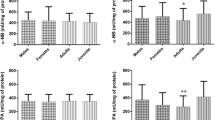
With the aim of developing a nondestructive biomarker (serum ‘B’ esterases) for monitoring bird populations exposed to azamethiphos S((6-chloro-2-oxooxazolo(4,5-b)pyridin-3(2H)-yl)methyl) 0,0-dimethyl phosphorothioate (9Cl), parallel laboratory and field studies were performed. In japanese quail (Coturnix coturnix japonica) treated with azamethiphos at 10 mg kg−1, serum butyrylcholinesterase (BChE) and carboxylesterase (CE) activities were inhibited by 88% and 35%, respectively, after 24 h. A gradual recovery was observed after 48 and 72 h. With a higher dose (50 mg kg−1), the birds died, or were killed 3 h after dosing. Serum BChE and brain acetylcholinesterase (AChE), in birds that were sampled at 3 h, were inhibited by 98% and 92%, respectively. Hepatic microsomal and serum CEs were also inhibited. There was a statistically significant correlation (r=0.9808, p<0.001) between the activities of serum BChE and brain AChE. Swallows (Hirundo rustica) nesting in a stable treated with azamethiphos showed a drastic reduction in BChE (56%) and CE (36%) 24 h after treatment of the stable.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aldridge, W.N. (1953) Serum esterases. 1. Two types of esterase (A and B) hydrolysing p-nitrophenyl acetate, propionate and butyrate, and a method for their determination. Biochem. J. 53, 110–7.
Aldridge, W.N., Hoskin, F.C.G., Reiner, E. and Walker, C.H. (1989) Suggestions for a nomenclature and classification of enzymes hydrolysing organophosphorus compounds. In Reiner, E., Aldridge, W.N. and Hoskin, G. eds. Enzymes Hydrolysing Organophosphorus Compounds. Chichester: Ellis Horwood Ltd.
Brealey, C.J., Walker, C.H. and Baldwin, B.C. (1980) A-esterase activities in relation to the differential toxicity of pirimiphos-methyl to birds and mammals. Pesticide Sci. 11, 546–54.
Bunyan, P.J. and Jennings, D.M. (1968) Organophosphorus poisoning; some properties of avian esterase. J. Agric. Food Chem. 16, 326–31.
Busby, D.G., Holmes, S.B., Pearce, P.A. and Fleming, R.A. (1987) The effect of aerial application of Zectran on brain cholinesterase activity in forest song birds. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 16, 623–8.
Busby, D.G., White, L.M. and Pearce, P.A. (1990) Effects of aerial spraying of Fenitrothion on breeding of the white-throated sparrow. J. Appl. Ecol. 27, 743–55.
Dieter, M.P. and Ludke, J.L. (1975) Studies on combined effects of organophosphates and heavy metals in birds. I. Plasma and brain cholinesterase in Coturnix quail fed methyl mercury and orally dosed with parathion. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 13, 257–62.
Ellman, G.L., Courtney, K.D., AndreasJr., V. and Featherstone, R.M. (1961) A new and rapid colorimetric determination of cholinesterase activity. Biochem. Pharmacol. 7, 88–95.
Fairbrother, A., Bennett, R.S. and Bennett, J.K. (1989) Sequential sampling of plasma cholinesterase in mallards (Anas platyrhynchos) as indicator of exposure to cholinesterase inhibitors. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 8, 117–22.
Fossi, M.C., Leonzio, C., Massi, A., Lari, L. and Casini, S. (1992) Serum esterase inhibition in birds: a nondestructive biomarker to assess organophosphorus and carbamate contamination. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 23, 99–104.
Fossi, M.C., Sanchez-Hernandez, J.C., Diaz-Diaz, R., Lari, L., Gaggi, C. and Garcia-Hernandez, J.E. (1993) The lizard Gallotia galloti as bioindicator of organophosphorus contamination in the Canary islands. Environ. Pollut., in press.
Gomori, G. (1953) Human esterases. J. Lab. Clin. Med. 42, 445–53.
Grue, C.E., Hart, A.D.M. and Mineau, P. (1991) Biological consequences of depressed brain cholinesterase activity in wildlife. In Mineau, P. ed. Cholinesterase Inhibiting Insecticides, pp. 152–209. Amsterdam: Elsevier.
Koeman, J.H., Kohler-Gunther, A., Kurelec, B., Rivière, J.L., Versteeg, D. and Walker, C.H. (1993) Applications and objectives of biomarker research. In Biomarkers. Research and Application in the Assessment of Environmental Health. Peakall, D.B. and Shugart, L. R. eds., pp. 1–14. NATO ASI Series 68. New York: Springer Verlag.
Lari, L., Massi, A., Fossi, M.C., Casini, S., Leonzio, C. and Focardi, S. (1993) Evaluation of toxic effects of the organophosphorus insecticide, azinphos-methyl, in experimentally and naturally exposed birds. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol., in press.
Ludke, J.L., Hill, E.F. and Dieter, M.P. (1975) Cholinesterase (ChE) response and related mortality among birds fed ChE inhibitors. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 1, 1–21.
Massi, A., Fossi, M.C., Lari, L., Leonzio, C., Casini, S. and Ferro, G. (1991). Effetto dell'uso di insetticidi organofsforici sul livello delle esterasi ematiche in esemplari di rondine, Hirundo rustica. Riv. Ital. Orn. 61, 101–6.
Mineau, P. and Peakall, D.B. (1987) An evaluation of avian impact assessment techniques following broad-scale forest insecticide spray. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 6, 781–91.
Peakall, D.B. (1985) Behavioral responses of birds to pesticides and other contaminants. Residue Rev. 96, 45–77.
Peakall, D.B. (1992) Animal biomarkers as Pollution Indicators. London: Chapman & Hall.
The Pesticide Manual (1983) 9th Edn. Worthing, C.H. ed. Farnham: British Crop Protection Council.
Russel, R.W. and Overstreet, D.H. (1987) Mechanisms underlying sensitivity to organophosphorus anticholinesterase compounds. Prog. Neurobiol. 28, 97–129.
Thompson, H.M., Walker, C.H. and Hardy, A.R. (1988a) Esterases as indicators of avian exposure to insecticides. In Field Methods for Study of Environmental Effects of Pesticides, British Crop Protection Council Monograph 40, pp. 39–45.
Thompson, H.M., Walker, C.H. and Hardy, A.R. (1988b) Avian esterases as indicator of exposure to insecticides: the factor of diurnal variation. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 41, 4–11.
Westlake, G.E., Bunyan, P.J. Martin, A.D., Stanley, P.I. and Steed, L.C. (1981) Organophosphorus poisoning: effects of selected organophosphorus pesticides on plasma enzymes and brain esterases of Japanese quail (Coturnix coturnix japonica). J. Agric. Food Chem. 29, 772–7.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fossi, M.C., Massi, A. & Leonzio, C. Blood esterase inhibition in birds as an index of organophosphorus contamination: field and laboratory studies. Ecotoxicology 3, 11–20 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00121385
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00121385