Summary
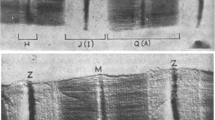
The characteristics of the titin filament in the vicinity of the Z-line were investigated using immunoelectron microscopy. We used monoclonal titin antibodies T-11 and T-12 on single fibres of frog skeletal muscle, and on Z-line-extracted fibres. It is well established that the I-band region of titin is elastic. We find, however, that the elastic properties are not uniform. The T-12 epitope, which binds near the Z-line at the N1-line level, hardly changes position relative to the Z-line as the sarcomere is stretched. This demonstrates the functional inextensibility of the N1-Z-line region. After extreme stretch (above 6-μm sarcomere length), this zone finally does elongate; thus, the titin molecule in this region is intrisically elastic. The functional inextensibility seen at shorter sarcomere lengths may, therefore, be a result of binding of titin to the actin filament in the zone near the Z-line. When the Z-line was extracted, the T-12 epitope remained in the same position as in the unextracted fibres; it did not retract from the Z-line. Failure to retract implies that functional anchoring of titin is not exclusive to the Z-line, but includes some site closer to the A-band. Combined with the results of the above-mentioned stretch experiment, this result implies a likely binding of titin to the thin filament either focally at the N1 line or all along the entire N1-Z region. Thus, this region of titin is functionally stiff, but intrinsically elastic.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akster, H. A., Granzier, H. L. M. & Focant, B. (1989) Differences in I-band structure, sarcomere extensibility, and electrophoresis of titin between two muscle fiber types of the Perch (Perca fluviatilis L.). J. Ultrastruct. Mol. Struct. Res. 102, 109–21.
Fürst, D. O., Nave, R., Osborn, M. & Weber, K. (1989) Repetitive titin epitopes with a 42 nm spacing coincide in relative position with known A-band striations also identified by major myosin-associated proteins: an immunoelectron-microscopial study on myofibrils. J. Cell Sci. 94, 119–25.
Fürst, D. O., Osborn, M., Nave, R. & Weber, K. (1988) The organization of titin filaments in the half sarcomere revealed by monoclonal antibodies in immunoelectron microscopy: a map of ten non-repetitive epitopes starting at the Z-line extends close to the M-line. J. Cell Biol. 106, 1563–72.
Itoh, Y., Suzuki, T., Kimura, S., Ohashi, K., Higuchi, H., Sawada, H., Shimizu, T., Shibata, M. & Maruyama, K. (1988) Extensible and less-extensible domains of connection filaments in stretched vertebrate skeletal muscle as detected by immunofluorescence and immunoelectron microscopy using monoclonal antibodies. J. Biochem. (Tokyo) 104, 504–8.
Luther, P. K. (1991) Three dimensional reconstruction of a simple Z-band in fish muscle. J. Cell Biol. 113, 1043–55.
Morimoto, K. & Harrington, W. F. (1973) Isolation and composition of thick filaments from rabbit skeletal muscle. J. Mol. Biol. 77, 165–75.
Morris, E. P., Nneji, G. & Squire, J. M. (1990) The three-dimensional structure of the nemaline rod Z-band. J. Cell Biol. 111, 2961–78.
Pierobon-Bormioli, S., Betto, R. & Salviati, G. (1990) The organization of titin (connectin) and nebulin in skinned muscle fibres of frog skeletal muscle. J. Muscle Res. Cell Motil. 10, 446–56.
Reedy, M. K. & Reedy, M. C. (1985) Rigor cross-bridge structure in tilted single filament layers and flared-X formations from insect flight muscle. J. Mol. Biol. 185, 145–76.
Reddy, M. K., Etlinger, J. D., Rabinowitz, M., Fischman, D. A. & Zak, R. (1975) Removal of Z-lines and alpha-actinin from isolated myofibrils by calcium-activated neutral protease. J. Biol. Chem. 250, 4278–84.
Rowe, R. W. D. (1973) The ultrastructure of Z disks from white, intermediate and red fibres of mammalian straited muscles. J. Cell Biol. 57, 261–77.
SZCESNA, D. & LEHRER, S. S. (1993) The visualisation of actin filaments in skeletal muscle fibrils with fluorescent phallotoxins. Biophys. J. 64, A147.
Trombitás, K. & Pollack, G. H. (1993) Elastic properties of connecting filaments along the sarcomere. In Mechanism of Myofilament Sliding in Muscle (edited by Sugi, H. & Pollack, G. H.). New York: Plenum Press (in press).
Trombitás, K. & Tigyi-Sebes, A. (1979) The continuity of the thick filaments between sarcomeres in the honey-bee flight muscle. Nature 281, 319–20.
Trombitás, K., Pollack, G. H., Wright, J. & Wang, K. (1990) Elastic behaviour and arrangement of titin filaments in the I-band. Proc. ICEM 3, 478–9.
Trombitás, K., Baatsen, P. H. W. W., Kellermayer, M. S. Z. & Pollack, G. H. (1991) Nature and origin of gap filaments in striated muscle. J. Cell Sci. 100, 809–14.
Trombitás, K., Pollack, G. H., Wright, J. & Wang, K. (1993) Elastic properties of titin filaments demonstrated using a ‘freeze-break’ technique. Cell Motil. Cytoskel. 24, 274–83.
Ullrick, W. C., Toselli, P. A., Chase, D. & Dasse, K. (1977) Are there extensions of thick filaments to the Z-line in vertebrate and invertebrate striated muscle. J. Ultrastruct. Res. 60, 263–71.
WANG, K. & WRIGHT, J. (1988) Sarcomere matrix of skeletal muscle: the role of thick filaments in the segmental extensibility of elastic thin filaments. Biophys. J. 53, 25a.
WANG, K., WRIGHT, J. & RAMIREZ-MITCHELL, R. (1984) Architecture of the titin/nebulin containing cytoskeletal lattice of the striated muscle sarcomere. Evidence of elastic and inelastic domains of the bipolar filaments. J. Cell Biol. 99, 435a (abstract).
Wang, K., McCarter, R., Wright, J., Beverly, J. & Ramirez-Mitchell, R. (1991) Regulation of skeletal muscle stiffness and elasticity by titin isoforms: a test of the segmental extension model of resting tension. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 88, 7101–5.
Whiting, A., Wardale, J. & Trinick, J. (1988) Does titin regulate the length of muscle thick filaments?. J. Mol. Biol. 205, 263–8.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Trombitás, K., Pollack, G.H. Elastic properties of the titin filament in the Z-line region of vertebrate striated muscle. J Muscle Res Cell Motil 14, 416–422 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00121293
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00121293