Abstract
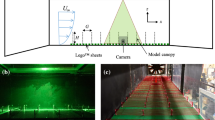
The deposition of 0.03 Μm particles to an assembly of 10 spruce shoots and a synthetic juniper shoot was studied by electrochemical transfer under conditions of Re and Sc similarity at flow velocities corresponding to wind speeds of 0.1 to 3 m s−1.
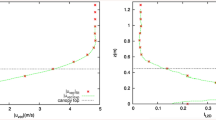
The concept of representing transfer to needle-type foliage by that to cylinders in crossflow, with adjustment factors for angle of incidence and for mutual interference of cylinders (needles), however imprecise, appears to be sufficient to interpret the results. The transfer data follow approximately a Re1/2 relationship with respect to flow velocity and the mass transfer coefficient calculated for cylinders in crossflow with a ‘shelter factor’ of the order of 2, to account for reduction in transfer due to mutual interference of needles, can be expected to be a reasonable first approximation of the deposition velocity.
Applications of the results to forest stands show very little absorption by stands of limited extension; distances of the order of kilometers would be required to reduce airborne concentrations to 1/e of their initial value for aerosol with negligible sedimentation and inertial impaction.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bach, W.: 1972, ‘Atmospheric Pollution’, McGraw Hill, New York, 144 pp.
Belot, Y.: 1976, ‘Etude de la captation des pollutants atmospheriques par les vegetaux’, Centre a l'énergie atomique (CEN), Fontenay aux Roses, France, 102 pp.
Brutsaert, W.: 1979, ‘Heat and Mass Transfer to and from Surfaces with Dense Vegetation or Similar Permeable Roughness’, Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 16, 365–388.
Campbell, G. S., McArthur, A. J., and Monteith, J. L.: 1980, ‘Windspeed Dependence of Heat and Mass Transfer through Coats and Clothing’, Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 18, 485–493.
Chamberlain, A. C.: 1967, ‘Transport of Lycopodium Spores and other small Particles to Rough Surfaces’, Proc. R. Soc. Lond., A, 296, 45–70.
Chamberlain, A. C.: 1974, ‘Mass Transfer to Bean Leaves’, Boundary-Layer Meteorol., 6, 477–486.
Chamberlain, A. C.: 1975, ‘The Movement of Particles in Plant Communities’ in J. L. Monteith (ed.), ‘Vegetation and the Atmosphere’, Vol. I., Academic Press, New York, 273 pp.
Fuchs, N. A.: 1964, ‘The Mechanics of Aerosols’, (transl. from Russian), Pergamon Press, Oxford, 408 pp.
Galloway, J. N. and Whelpdale, D. M.: 1980, ‘An Atmospheric Sulphur Budget for Eastern North America’, Atmos. Environ. 14, 409–417.
Gates, D. M., Tibbals, E. C., and Kreith, F.: 1965, ‘Radiation and Convection in Ponderosa Pine’, Am. J. Bot. 52, 66–71.
Grace, J. and Wilson, J.: 1976, ‘The Boundary Layer over a Populus Leaf’, J. Experim. Bot. 27, 231–241.
Heichel, G. H. and Hankin, L.: 1976, ‘Roadside Coniferous Windbreaks as Sinks for Vehicular Emission’, J. Air Poll. Control Assoc. 26, 767–770.
Incropera, F. P. and DeWitt, D. P.: 1981, ‘Fundamentals of Heat Transfer’, John Wiley, New York, 819 pp.
Jarvis, P. J., James, G. B., and Landsberg, J. J.: 1975, ‘Coniferous Forest’ (Case study), in J. L. Monteith (ed.), ‘Vegetation and the Atmosphere’, Vol. II, Academic Press, New York, 439 pp.
Landsberg, J. J. and Ludlow, M. M.: 1970, ‘A Technique for determining Resistance to Mass Transfer through the Boundary-Layer of Plants with Complex Structures’, J. appl. Ecol. 7, 187–192.
Landsberg, J. J. and Thom, A. S.: 1971, ‘Aerodynamic Properties of a Plant of Complex Structure’, Quart. J. Roy. Meteorol. Soc. 97, 565–570.
Little, P.: 1977, ‘Deposition of 2.75, 5.0 and 8.5 Μm Particles to Plant and Soil Surfaces’, Environ. Poll. 12, 293–305.
Little, P. and Wiffen, R. D.: 1977, ‘Emission and Deposition of Petrol Engine Exhaust Pb-I. Deposition of Exhaust Pb to Plant and Soil Surfaces’, Atmos. Environ. 11, 437–447.
Little, P. and Wiffen, R. D.: 1978, ‘Emission and Deposition of Lead from Motor Exhausts — II. Airborne Concentration: Particle Size and Deposition of Lead near Motorways’, Atmos. Environ. 12, 1331–1341.
Miller, D. F., Levy, A., Pui, D. Y. H., Whitby, K. T., and Wilson, W. E.: 1976, ‘Combustion and Photochemical Aerosols attributable to Automobiles’, J. Air Poll. Control Assoc. 26, 576–581.
Quraishi, M. S. and Fahidy, T. Z.: 1980, ‘A Study of Convective Flow Patterns via Electrochemical Means’, Americ. Soc. Mech. Eng. (ASME) report 80-HT-93, 7 pp.
Raynor, G. S., Hayes, J. V., and Ogden, E. C.: 1974, ‘Particulate Dispersion Into and Within a Forest’, Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 7, 429–456.
Roth, R.: 1975, ‘Der vertikale Transport von Luftbeimengungen in der Prandtl Schicht und die Deposition-Velocity’, Meteorol. Rundschau 28, 65–71.
Schuepp, P. H.: 1972, ‘Studies of Forced Convection Heat and Mass Transfer of Realistic Fluttering Leaf Models’, Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 2, 263–274.
Schuepp, P. H.: 1973, ‘Model Experiments of Free Convection Heat and Mass Transfer of Leaves and Plant Elements’, Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 3, 454–467.
Schuepp, P. H.: 1980, ‘Heat and Moisture Transfer from Flat Surfaces in Intermittent Flow: a Laboratory Study’, Agric. Meteorol. 22, 351–366.
Schuepp P. H.: 1981, ‘Electrochemical Simulation of Heat and Mass Transfer in Agrometeorology’, Can. J. Chem. Eng. 59, 164–172.
Schuepp, P. H. and White, K. D.: 1975, ‘Transfer Processes in Vegetation by Electrochemical Analog’, Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 8, 335–358.
Sehmel, G. A.: 1980, ‘Particle and Gas Deposition: a Review’, Atmos. Environm. 14, 983–1011.
Smith, W. H.: 1981, Air Pollution and Forests, Springer Verlag, New York, 379 pp.
Stewart, J. B. and Thom, A. S.: 1973, ‘Energy Budget in a Pine Forest’, Quart. J. Roy. Meteorol. Soc. 99, 154–170.
Thom, A. S.: 1971, ‘Momentum Absorption by Vegetation’, Quart. J. Roy. Meteorol. Soc. 97, 414–428.
Tibbals, E. C., Carr, E. K., Gates, D. M., and Kreith, F.: 1964, ‘Radiation and Convection in Conifers’, Am. J. Bot. 51, 529–538.
Whitby, K. T., Clarke, W. E., Marple, V. A., Sverdrup, G. M., Sem, G. J., Willeke, K., Lin, B. Y., and Pui, D. Y. H.: 1975, ‘Characterization of California Aerosols — I. Size distribution of Freeway Aerosol’, Atmos. Environ. 9, 463–482.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schuepp, P.H. Laboratory studies on dry deposition of submicron-size particles on coniferous foliage. Boundary-Layer Meteorol 24, 465–480 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00120734
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00120734